The process by which a cell divides into 2 genetically identical daughter cells.
What is cell division/mitosis?
This process/phase follows this one:
What is cytokinesis?
The name and purpose of this process:

What is crossing over / creates genetic recombination?
The creation of genetically identical offspring is the result of this type of reproduction.
What is asexual reproduction?
What are Rutgers and Princeton?
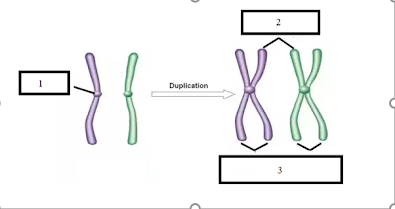
The term for these duplicated chromosomes:

What are sister chromatids?
Eukaryotic cells spend most of their time in this phase of the cell cycle.
What is interphase?
The term for four homologous chromatids:

What is a tetrad?
The fusion of two separate parent gametes resulting in offspring with a new genetic combination is this type of reproduction.
What is sexual reproduction?
Mardi gras is French for this term.
What is Fat Tuesday?
The production of a genetically identical offspring from a single parent is known as ______ ________.
Asexual Reproduction
During this phase of the cell cycle, chromosomes become pairs of sister chromatids.
What is the S phase of interphase?
You observe a cell from a diploid organism and see 7 chromosomes, each consisting of a pair of sister chromatids, it could be in this phase:
Prophase II of meiosis
Prophase of mitosis
Anaphase I of meiosis
Anaphase of mitosis
What is Prophase II of meiosis?
This is the true statement from those below:
1.Cell division only occurs after sexual reproduction.
2.Sexual reproduction is more likely to increase genetic variation than is asexual reproduction.
3. Sexual reproduction typically includes the development of unfertilized eggs.
What is 2?
These type of cells do not divide.
What are neurons/nervous system cells?
The fusion of two separate parent cells
Sexual Reproduction
Identify this phase of mitosis:
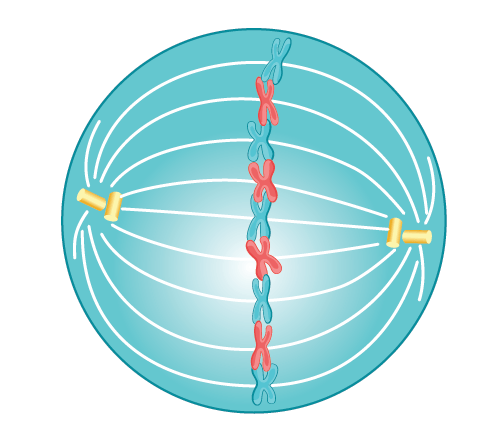
What is metaphase?
The term for the process causing the genetic error seen below: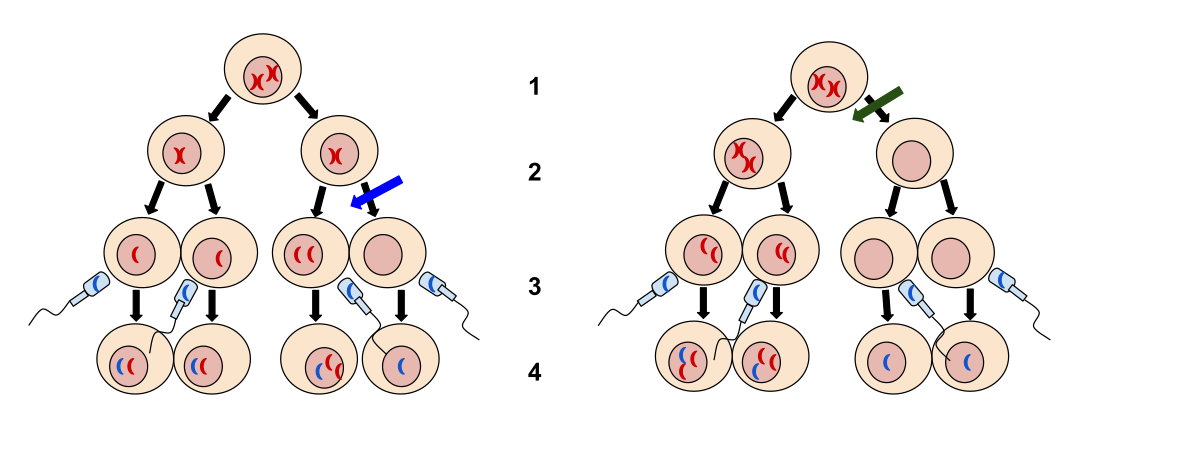
What is nondisjunction?
Offspring produced by sexual reproduction inherit some of this from each parent
What is genetic information?
This is the term for this and what it shows:
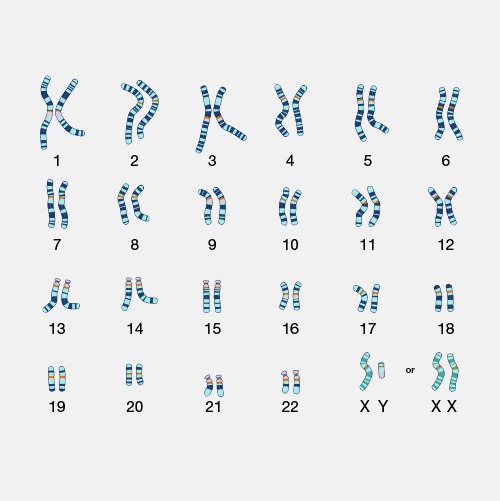
What is a karyotype / a person's chromosomes? (homologous chromosomes)
Uncontrolled cell growth is a cause of this.
What is cancer?
You're observing an organism in G2 and see 120 chromatids. This is how many chromosomes a female of this organism would have in her egg cells.
What is 30?
This is the phase seen here:
What is Anaphase I?
The asexual reproduction of bacteria is called this process.
What is binary fission?
1. centromere
2. homologous chromosomes
3. sister chromatids