What is the independent variable in an experiment measuring plant height with different amounts of sunlight?
The amount of sunlight
Which characteristic of life is demonstrated when your pupils contract in bright light?
Response to stimuli
Organisms interacting with each other and the non-living environment form what level of organization?
Ecosystem
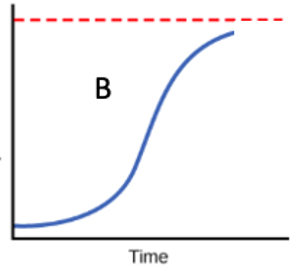
Type of growth that occurs with a species where there is competition and limiting factors that occur
Logistic Growth
This organelle is responsible for producing ATP
Mitochondria
This organelle has a lot going on! With grana inside, and a whole dark cycle process in the stroma, it is essential for photosynthesis
Chloroplast
This is not how you will learn for the final, but it is the passive movement of water across a membrane
Osmosis
What kind of variable must remain unchanged in all groups
Controlled variable
What cellular structure is shared by all living organisms?
Cell membrane
This term describes the full range of physical and biological conditions in which an organism lives and the way it obtains the resources it needs to survive and reproduce, including its role in the food web, behaviors, and interactions with biotic and abiotic factors.
niche
Aquatic biome in which light doesn't penetrate and no photosynthesis takes place
Aphotic zone
This organelle packages and ships proteins.
Golgi apparatus
This structure is responsible for breaking down waste in the cell
Lysosome
This kind of transport uses proteins to move molecules without energy..almost like it has help or something.
Facilitated diffusion
Qualitative data
Characteristic of living things that is the process to pass traits from one generation to the next
reproduction
A relationship where one organism benefits and the other is harmed is called this.
Parasitism
An illustration that portrays all the different populations of an ecosystem and what each feeds and what each feeds on.
Food Web
This structure supports and protects plant cells and is made of carbohydrates.
What is the cell wall?
This part of the cell's fundamental structure is made up of hydrocarbons and determines what is allowed to enter and exit.
Phospholipid bilayer of the plasma membrane
This is the movement of materials against a concentration gradient using energy
Active transport
What is the term for a testable, educated guess in a scientific investigation?
Hypothesis
Steady..steady..this process by which organisms maintain a stable internal environment
Homeostasis
Which ecological process begins on bare rock after a volcanic eruption?
Primary succession
The red dashed line in the figure is called ...

Carrying Capacity
Which organelle is studded with ribosomes and helps synthesize proteins?
Rough ER
Go webs go! Spindle fibers, that is..this organelle organizes chromosomes during cell division in animal cells, but is never truly center stage.
Centrioles
Sip sip, this type of bulk transport brings liquids into the cell
Pinocytosis
In an experiment with five identical plants, which group would receive no treatment for comparison
Control Group
Which characteristic of life allows populations to adapt over generations?
Evolution
What kind of growth is shown when resources are unlimited?
Exponential Growth
Which color depicts the "Zone of Physiological Stress"
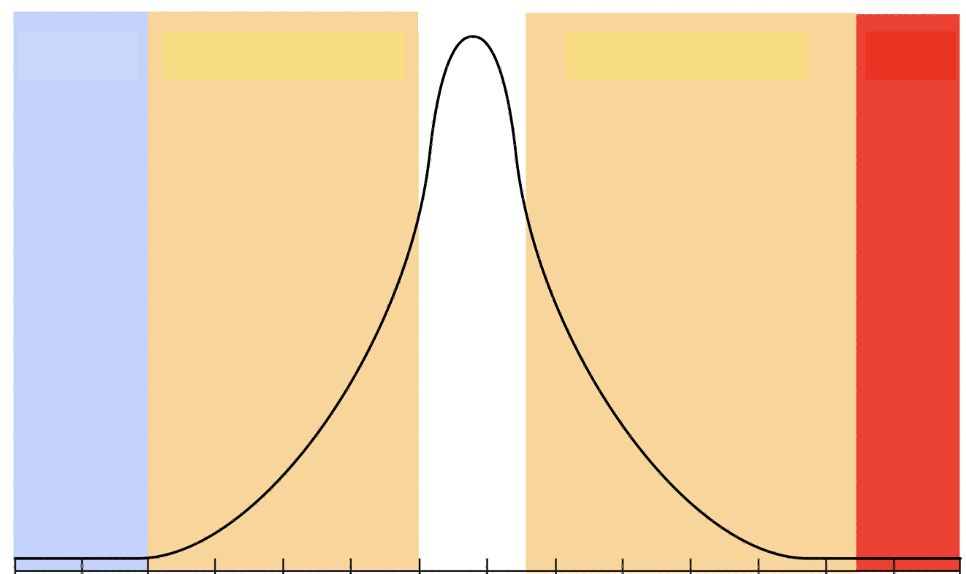
Gold/Yellow
This is the major difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Membrane bound organelles
Choo chooo! The folded membranes inside the mitochondria, are specifically called this, and they house the ETC and make MOST of the ATP.
Cristae
This is as natural as it gets..its the property of the membrane that allows it to regulate what enters and exits
Selective permeability