What is the purpose of meiosis?
What is creating sperm and egg cells?
In this example tree, this species is equally related to the minke and humpback whales, but is more closely related to sheep and goats.
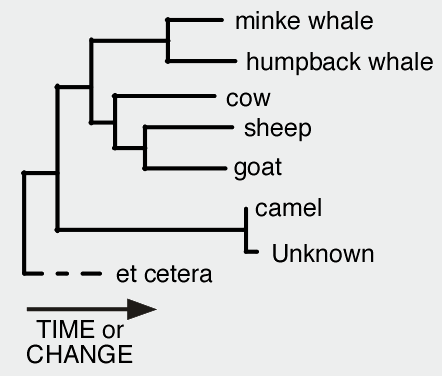
What is the cow?
An organism that must get its energy by eating other organisms is called this
What is a consumer?
What is incomplete dominance?
What are the three parts of a nucleotide?
What is sugar, phosphate, and nitrogen base?
What is Mr. Mietka's favorite color?
What is Dark red / maroon?
Where does meiosis take place?
In comparative anatomy, the presence of these types of structures may indicate convergent evolution.
What are analogous structures?
Most of the energy at any trophic level is used for movement, reproduction, and metabolism, but this amount is passed on to the next trophic level
What is 10%?
In a cross between two parents who are heterozygous, this is the percent likelihood that they will have a child with the dominant phenotype.
What is 75%?
What is U?
This is where Mr. Alperin went to college.
What is University of Illinois?
Urbana-Champaign
What is the outcome of meiosis?
What is 4 sperm or 1 egg with 3 polar bodies
Homologous structures and similar gene sequences can be evidence for this pattern of evolution
What is divergent evolution?
Create a food chain and food web in 2 minutes or less.
Answers will vary
What is the possible blood type of a child if the parents have A type Blood and B type Blood?
What is Type A, Type B, Type O, Type AB?
Why do we need DNA Transciption?
What is DNA is too wide to fit through the nuclear pore?
How old is Mr. Mietka?
What is age 27?
How come are all of the cells created in meiosis unique and what is the purpose of this?
Who is the father of evolution/natural selection? Where did he study?
What is Darwin, galapagos islands?
These are living or nonliving components of ecosystems which can raise or lower the carrying capacity.
What are limiting factors?
This type of inheritance is shown in the image. For half credit, what do we call these?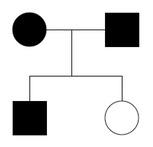
What is autosomal dominant?
Half credit : Pedigree
These types of mutations cause a frameshift mutation, which really dramatically changes the resulting protein
What is an insertion or deletion mutation?
Name two activities Ms. Fee enjoys doing in her free time.
What is hosting trivia and doing art?
Draw an image representing all phases of meiosis.
Answers will vary
What are the 3 out of the 5 fingers of evolution?
What is small population, non-random mating, mutations, gene flow, adaptations
This type of organism is particularly important in primary succession, but may be less important in secondary succession (one example is a lichen).
What is a pioneer species?
These are Mendel's three laws of inheritance.
1. Dominance
2. Segregation
3. Independent Assortment
This process occurs at the ribosome, and converts mRNA to an amino acid sequence.
What is translation?
What is Mr. Mietka's favorite plant called?
Hint* It is in the room
What is pothos?