There are 2 different types of stems. Woody containing bark and this one....
What is herbaceous?
There are 2 ways to identify plants. Classifications and .....
What is nomenclature?
The largest/widest part of the leaf is referred to as the....
What is the leaf blade?
This person is significant to horticulture because he was a botanist that created a classification system for minerals, plants and animals.
Who is Carl von Linne?
Other than absorb water/minerals and anchor the plant to the ground, a roots function is this.
What is store food from photosynthesis?
These 3 parts of the flower make up the carpal.
What is the stigma, style, and ovary?
This modified stem grows underground with a short, flattened stem and has a fleshy scale like leaf attached.
What is a bulb?
This is the general mode of growth of a plant.
What is growth habit?
This leaf shape is heart-shaped.
What is cordate?
This is the study of naming organisms.
What is taxonomy?
This long narrow epidermal root grows perpendicular to the surface root. It greatly increases the surface area of the root and thereby increases the absorption of water.
What is the root hairs?
This is a microspore made in the anther that is essentially the same thing as sperm.
What is pollen?
We measured the movement of materials through stem vascular tissue with food coloring and flowers. This movement is called....
What is translocation?
The most accurate method of plant identification.
What is Expert Identification?
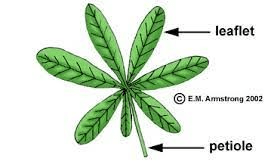
This type of broadleaf is a compound leaf that has all it's leaflets attached to a common point.
What is a Palmately Compound Leaf?
This kind of plant has a life cycle of more than 2 growing seasons.
What is a perennial?
The roots that are readily produced along the stem at nodes of the stem or from leaves.
What is adventitious roots?
This image shows a flower that lacks one or more of the 4 main flower parts. It it known as....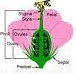
What is an incomplete flower?
This vascular tissue is responsible for materials flowing up and down, made of living cells with cytoplasm and has thin cell walls.
What is phloem?
Acts as a flow chart to identify different plants types leading users though a series of choices.
What is a dichotomous key?
This term refers to the shedding of plant parts including leaves, flowers and fruit.
What is abscission?
The 7 classification systems in order.
What is kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species?
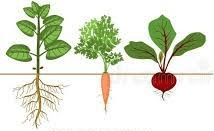 Carrots are an example of this type of root system.
Carrots are an example of this type of root system.
What is tap root system?
This type of flower has a spike with a thickened fleshy axis, usually enveloped by a showy bract. 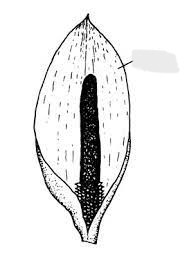
What is a Spadix?
This modified stem is thick, fleshy and juicy.
What is a succulent?
Leave B is referring to what kind of leaf structure? 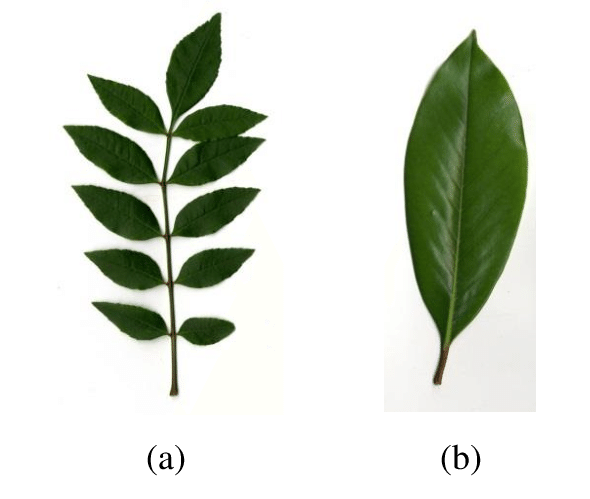
What is a simple leaf?
This modified leaf twines around objects to provide support, like climbing vines.
What is a tendril?
This taxonomic class of plant produces seeds that are NOT enclosed in an ovary.
What is a gymnosperm?
This is a form of symbolism where both species of plants benefit each other.
What is mutualism?
The initiation of flowering by satisfying a cold requirement in the plant is known as....
What is vernalization?