The charge of an electron
What is negative?
An arrow is used to describe the positive and negative charge of an atom and/or molecule
What is a dipole?
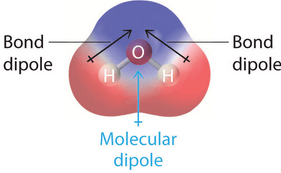
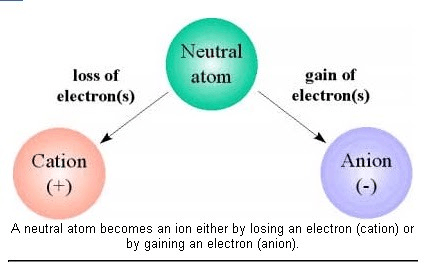
An atom or molecule with an electric charge due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons
What is an ion?
the tendency of an atom to attract a shared pair of electrons towards itself
What is electronegativity?
Is there a “desirable” or optimal number of valence electrons that atoms want to have?
Claim: There is a desirable or optimal number of valence electrons
Evidence: Atoms want to have their outermost shell filled with electrons; the desirable number is 2 (Hydrogen and Helium) or 8 (all other elements) electrons in their shell
Reasoning: This is desirable/optimal because atoms are most stable when their outermost shell is filled
The outermost electrons
What are valence electrons?
Non-integer (not a number) value to describe positive and negative charges
What are partial charges?
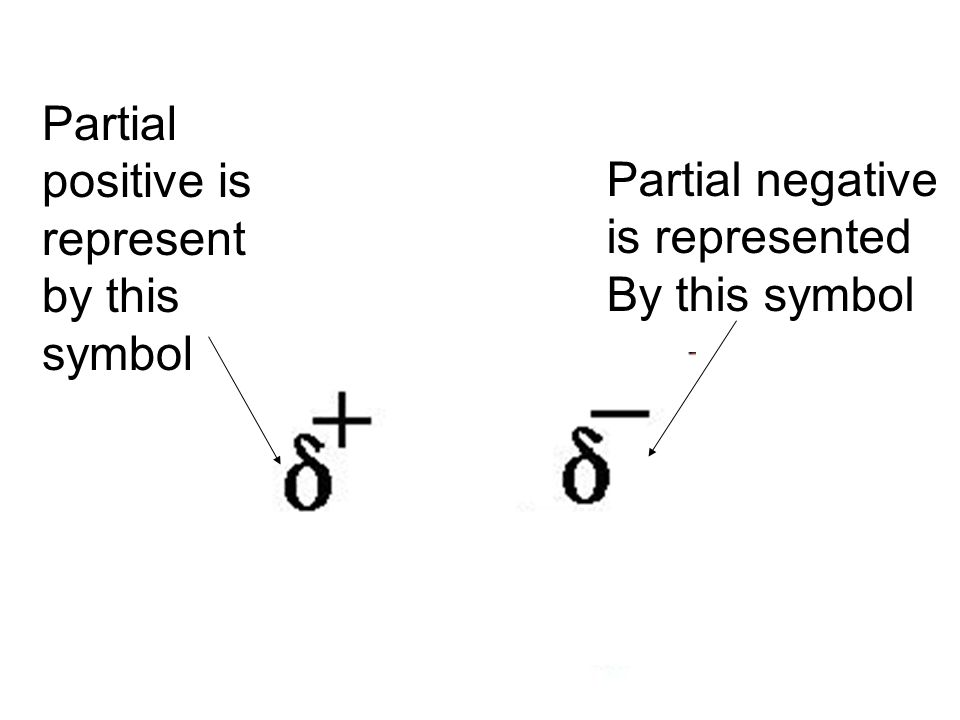
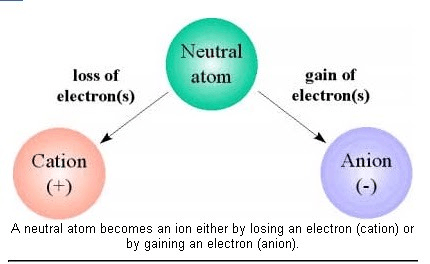
The two types of ions
What is a cation (positive ion) and an anion (negative ion)?
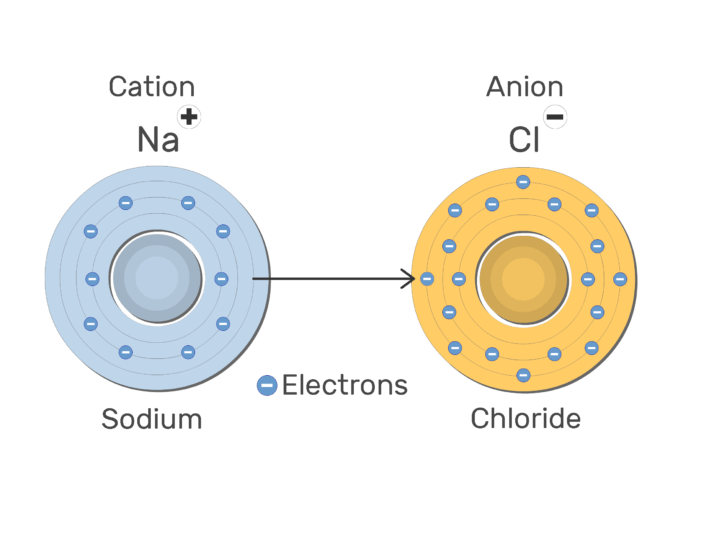
When an atom is easily able to attract electrons, it is more or less electronegative?
When is difficult for an atom to attract electrons, it is more or less electronegative?
When an atom is easily able to attract electrons, it is more electronegative?
When is difficult for an atom to attract electrons, it is less electronegative?
Can an atom become charged? If so, how?
Claim: An atom can be charged (positive or negative); we call charged atoms ions.
Evidence: An atom becomes charged when it loses or gains electrons. Atoms become positive when they lose electrons; atoms become negative when they gain electrons.
Reasoning: These charged atoms (ions) are charged in order to fulfill the octet rule.
Listed on the periodic table, it helps you determine the number of valence electrons
What are groups? 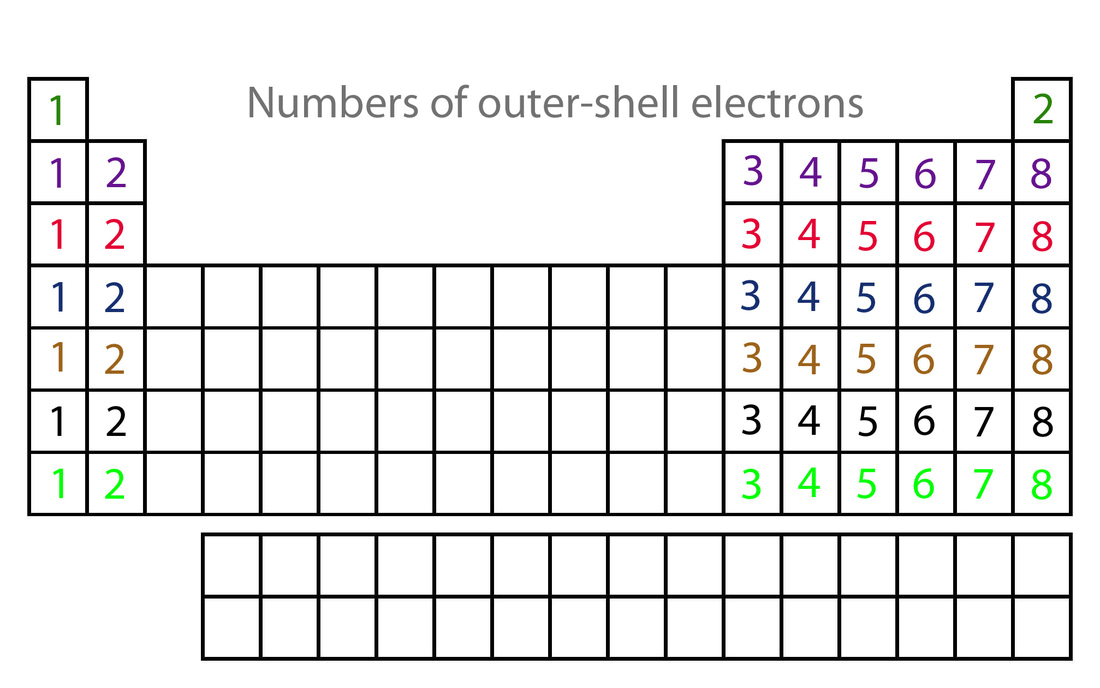
a field that surrounds electric charges
What is an electric field?
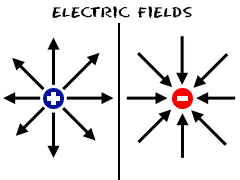
Describe how anions and cations are formed.
Anions are formed when there is a gain of electrons; Cations are formed when there is a loss of electrons.
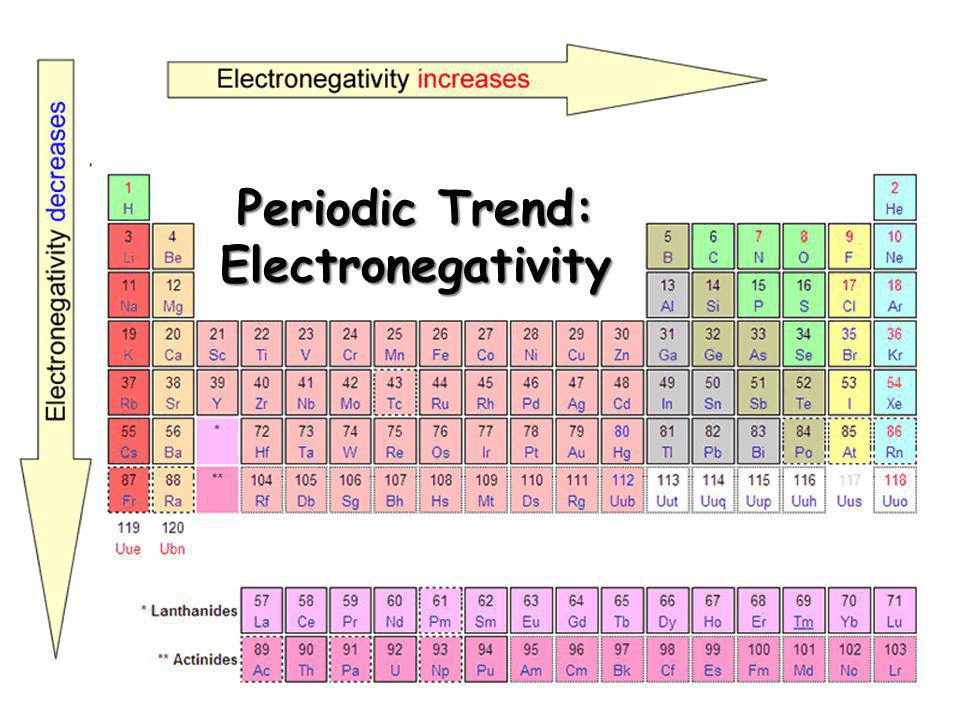
Describe the trends of electronegativity on the periodic table.
What is electricity? What does it have to do with electrons?
Claim: Electricity is a form of energy caused by the concentration (a lot) of charged particles.
Evidence: Electrons are charged particles that flow together causing electricity.
Reasoning: Electricity and electrons are related because the flow of charged particles (specifically electrons) allows for electricity to occur.
Number of valence electrons in sodium (Na)
 What is one (1) valence electron?
What is one (1) valence electron?
Determine the charges of the following ions:
Na + Cl -> NaCl

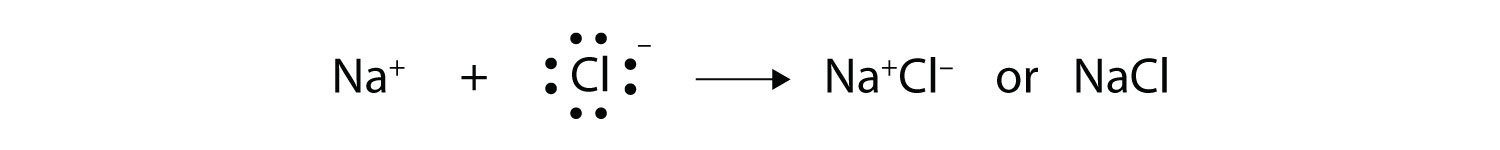
The overall charge is positive when there is a (loss or gain of electrons).
The overall charge is negative when there is a (loss or gain of electrons).
The overall charge is positive when there is a loss of electrons.
The overall charge is negative when there is a gain of electrons.
Which list of elements is arranged in order of increasing electronegativity?
F, Cl, Br or K, Ca, Sc
- incorrect F, Cl, Br (decreases down the group/column)
Do atoms ever “steal” electrons from other atoms? If so, why?
Claim: Atoms do 'steal' electrons from other atoms.
Evidence: For example in the formation of salt, chlorine has 7 valence electrons and sodium has 1 valence electron. In order to fulfill the octet rule, chlorine will 'steal' sodium's one valence electron to have a full outermost shell.
Reasoning: Atoms 'steal' and electrons to fulfill the octet rule and become more stable.
Number of valence electrons in chlorine (Cl)
 What are seven (7) valence electrons?
What are seven (7) valence electrons?
Listed on the periodic table, it helps you determine the ionic charge of atoms
Periods

Using CER and the picture listed, describe the role of ions in ionic bonding.
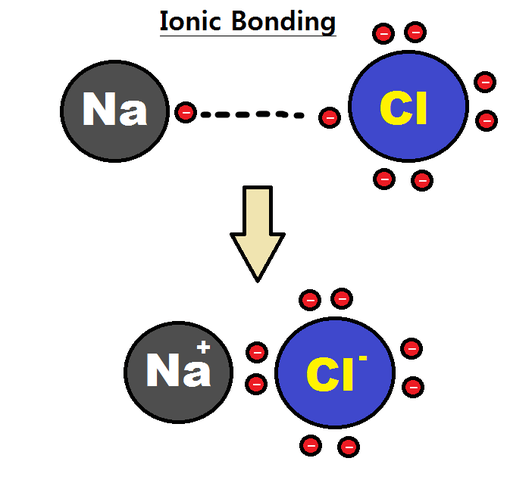
Claim: Ionic bonding is the transfer of valence electrons between atoms.
Evidence: Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond that creates two oppositely charged ions. In ionic bonds, the cation loses electrons to become positively charged and the anion accepts those electrons to become negatively charged.
Reasoning: When atoms lose electrons, ionic bonding happens so that elements that have few electrons in their outer-most orbitals can achieve the noble gas configuration and satisfy the octet rule.
Using CER, describe how electronegativity can help us understand ionic bonding?
Claim & Reasoning: Electronegativity helps us to understand ionic bonding because we are able to predict which atoms are able to attract electrons to themselves.
Evidence: Ionic bonding happens when more electronegative atoms (anions) steal the electrons of less electronegative atoms (cations). An example would the formation of salt; chlorine is less electronegative than sodium and attracts the valence electron of sodium to itself, creating salt.
Using CER, describe how the salt breaks apart into ions when mixed with water.
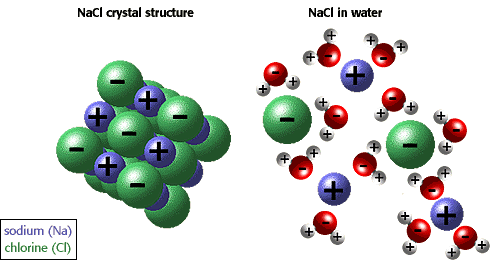
Claim: The picture listed shows a salt crystal structure and how this salt crystal breaks apart in water.
Evidence: The NaCl crystal structure (on the left) shows sodium as a blue cation (positive ion) and chlorine as a green anion (negative ion). This salt crystal breaks a part into two separate ions when in water; water molecule are attracted to these separate ions (specifically, the hydrogen part of water is attracted to the negative chlorine ion and the oxygen part of water is attracted to the positive sodium ion).
Reasoning: Salt breaks apart into ions when mixed with water due to the polarity (distinct opposite charges) of these molecules (i.e. water, + sodium ion, - chlorine ion).
