Definition: Meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
Sustainability
Difference between monitoring and evaluating
Monitoring: to watch and check a situation carefully for a period of time
Evaluating: to judge or calculate the quality, importance, amount, or value of something using specific targets, criteria, etc
Monitoring leads to evaluating...
Identify the latitude, type of climate, annual rainfall and temperature range
30-50 degrees, Mediterranean, 700mm, 10-20 degrees Celcius
Identify the 5 reasons to value ecosystems
Maintenance of genetic diversity: Antarctica
Utility Values: Rainforests for medicines
Intrinsic values: Blue Mountains World Heritage area
Heritage values: Ningaloo reef
Need to allow natural change to proceed: Mt St Helens National Volcano Monument.
What is a choropleth map?
A choropleth map is a thematic map that is used to represent statistical data using the color mapping symbology technique
What are the Pillars of Sustainability?
Social, Economic, Environmental and Cultural
What is an economic activity? Define
A process that leads to the manufacture of a good or the provision of a service.
Identify 5 Old and New world producers
Italy, France, Spain, Portugal, Germany
USA, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, Chile, China
Define dynamic equilibrium and feedback loops
“refers to a state where, despite ongoing changes and fluctuations, the system remains stable”
Feedback loops: affecting the stability of the system. Feedback loops permit systems to adjust their response to change (forcing factors) to return to stable conditions.
How do you calculate percentage change?
(Difference/Original Value) x 100
What are the principles of ecologically sustainable development?
precautionary principle, intergenerational equity, conservation of biological diversity and ecological integrity
What criteria can be used for evaluating the sustainability of economic activities
The four pillars of sustainability and principles of ecologically sustainable development underpin all criteria (ex: UNSDG's) for evaluating economic activities.
Identify the 5 influences on the economic activity
biophysical
economic
technological
political/organisational
Otherwise known as …
B.E.T.O.P
Provide an example of a positive and negative feedback loop
Increased water vapour in the atmosphere, acting as a greenhouse gas (P)
Melting of Ice caps, reducing albedo (P)
Rising sea levels causing glacier calving (P)
Water vapour forms clouds which reflect radiation (N)
The ocean’s ability to transport carbon from the atmosphere and dissolve it (N)
How do you calculate local relief AND gradient?
Local relief = difference in elevation between highest and lowest points in a given area
Gradient = rise/run (in the same units)
Name THREE SDG's

What are some of the influences of sustainable development?
political, economic, technological, social, cultural and environmental
a term in wine tasting used to describe the degree to which a wine reflects its varietal origins and thus demonstrates the signature characteristics of the grape from which it was produced, e.g., how much a Merlot wine “tastes like a Merlot”.
Typicity
Define THREE reasons for valuing ecosystems
The full range of genetic diversity is known as biodiversity. Biodiversity provides the maximum amount of material for continued natural selection and evolution
Utility value is the usefulness of ecosystems.
The intrinsic value refers to the inherent ecological values that a place possesses.
Heritage protection of areas seen as having outstanding universal value
Ecosystems are continually changing and evolving. If we don’t allow this to occur naturally then ecosystems can be damaged and the quality of human life can be affected
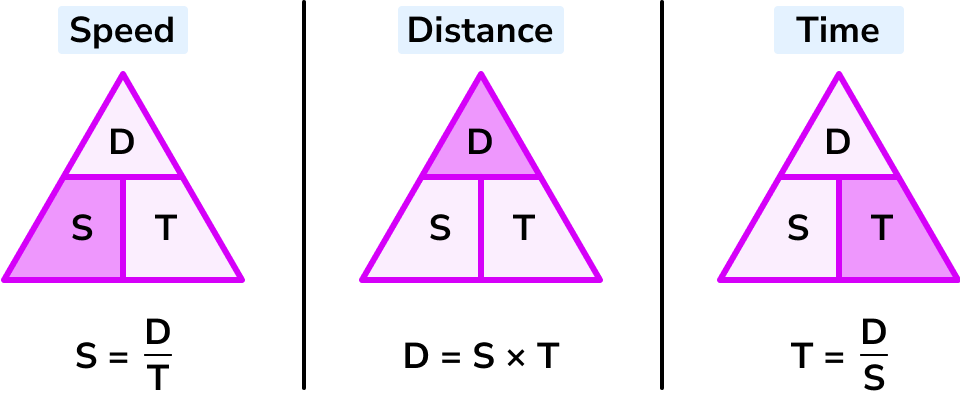
Draw a speed time distance triangle
Give an example of each of the following: global forums, international agreements and cooperation
Global forums: Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development (OECD) or United Nations (UN)
International agreements: Rio 1992, Montreal Protocol, Paris 2016, Kyoto Proocol etc.
International cooperation: UN and its agencies
Name 2 of the SDG we used to evaluate the sustainability of Lithium mining in Western Australia.
SDG 1 - No Poverty
SDG 3 - Good Health and Well-being
SDG 8 - Decent Work and Economic Growth
SDG 9 - Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
SDG 10 - Reduced Inequality
SDG 11 - Sustainable Cities and Communities
SDG 12 - Responsible Consumption and Production
SDG 13 - Climate Action
SDG 14 - Life Below Water
SDG 15 - Life on Land
SDG 16 - Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions
SDG 17 - Partnerships for the Goals
What is ONE OIV General Principle of Sustainable Vitiviniculture Standard?
Principle 1: Sustainable approach integrates environmental, social and economic aspects
Principle 2: Sustainable vitiviniculture respects the environment
Principle 3: Sustainable vitiviniculture is sensitive to social and cultural aspects
Principle 4: Sustainable vitiviniculture seeks to maintain economic viability
Principle 5: Sustainable initiatives require planning and assessment
Differentiate between linear comprehensive management and cyclical incremental management
Linear comprehensive management is an approach that assumes all elements of aproject, development or conservation effort will occur within sequential phases andrelies on the ability to manipulate, predict and control all outcomes.
Cyclical incremental management – focuses on monitoring and working with natural cycles, in increments (many small adjustments made) instead of 'comprehensive'
Name ALL of the case studies we have covered in the THREE topics studied during the HSC
Global sustainability - Vitiviniculture (bonus points for Lithium mining)
Rural and urban places - Tamworth, Darling Harbour Prescient and Mumbai
Ecosystems and global biodiversity -
Coastal Dunes (Bengello /South Broulee beach AND Point Reyes National Seashore, CA, USA)
Fiordlands - (Fiordland National Park, New Zealand AND West Norwegian Fjords)