What does HTML stand for?
This element creates a table.
<table>
This element is a great tool for collecting information
<form>
This is the concept of checking user provided data against the required data.
Validation
What word means "relating to meaning"
Semantic
These 3 languages have been referred to as "los tres amigos" of web development.
HTML, CSS, JavaScript
Fill in the the 2 yellow blanks
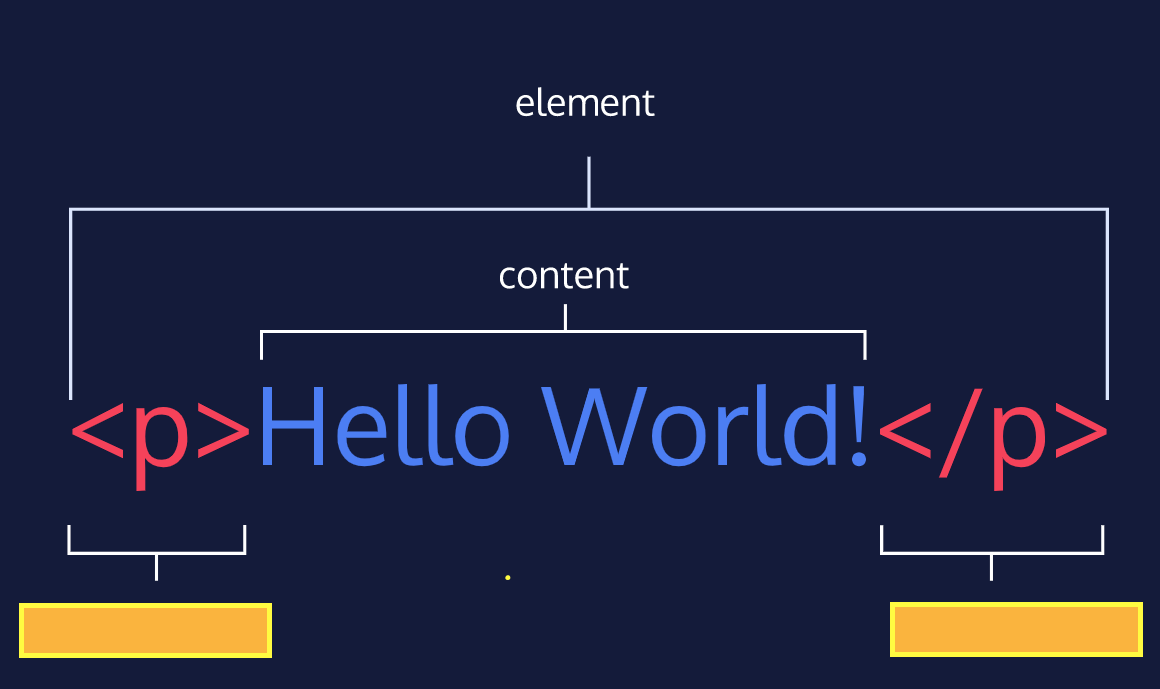
Opening Tag and Closing Tag
This element adds rows to a table.
<tr>
This input type attribute will replace input text with another character like an asterisk( * ) or a dot ( . ).
<input type="password">
Adding this attribute to an input related element will validate that the input field has information in it.
required
This element is used to encapsulate the dominant content within a webpage.
<main>
By using <main> as opposed to a <div> element, screen readers and web browsers are better able to identify that whatever is inside of the tag is the bulk of the content.
What is the current HTML Standard?
HTML5
Fill in the blank. Only content inside the opening an closing ______ tags can be displayed to the screen
<body></body> tags
These clarify the meaning of data, and are added using the <th> element.
Table Headings
True or False. To associate a <datalist> element with the <input> element, the <input>‘s list attribute value must match the id of the <datalist> element.
True
Fill in the blank. To set a minimum number of characters for a text field, we add the ________ attribute and a value to set a minimum value. Similarly, to set the maximum number of characters for a text field, we use the _________ attribute and set a maximum value
minlength, maxlength
This element holds content that makes sense on its own. It can hold content such as blogs, comments, and magazines.
<article>
An <article> tag would help someone using a screen reader understand where the article content (that might contain a combination of text, images, audio, etc.) begins and ends.
This is the discouragement of use of some terminology, feature, design, or practice, typically because it has been superseded or is no longer considered efficient or safe, without completely removing it or prohibiting its use.
Deprecation (Deprecated)
<head>
table data can span rows using this attribute
What is rendered on the web page as a result of the code provided?

A form containing a slider that has a maximum value of 100, a minimum value of 0 and moves in steps of 10.
This type of validation happens when when data is sent to another machine (typically a server) for validation.
server-side
With regard to Semantic HTML, How could this code snippet be improved?
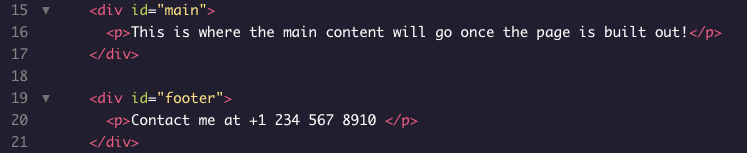
Change Line 15 to <main>, change Line 17 to </main>, change Line 19 to <footer>, change Line 21 to </footer>.
You Choose: This person wrote the first version of HTML.
The first version of HTML was written in this year.
Tim Berners-Lee, 1993
What is metadata?
Metadata is data about data. In this context, metadata is information about the page that isn’t displayed directly on the web page. Ex. <title>My Webpage's Title</title>
According to w3schools.com, this HTML attribute specifies whether a header cell is for a column, row, or group of columns or rows. This attribute has not visual effect on web browsers, but can be used by screen readers.
scope
Fill in the blank. The _______ attribute is assigned a HTTP verb that is included in the HTTP request. The HTTP Verb we used in our Codecademy example was _____.
method, POST.
These types of validations happen in the browser before information is sent to a server.
Client-side
3 reasons why Semantic HTML is important to use
Accessibility, SEO, Easy to understand
Accessibility: Semantic HTML makes webpages accessible for mobile devices and for people with disabilities as well. This is because screen readers and browsers are able to interpret the code better.
SEO: It improves the website SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, which is the process of increasing the number of people that visit your webpage. With better SEO, search engines are better able to identify the content of your website and weight the most important content appropriately.
Easy to Understand: Semantic HTML also makes the website’s source code easier to read for other web developers.
This is the main international standards organization for the World Wide Web.
W3C (World Wide Web Consortium). More info can be found on https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/World_Wide_Web_Consortium