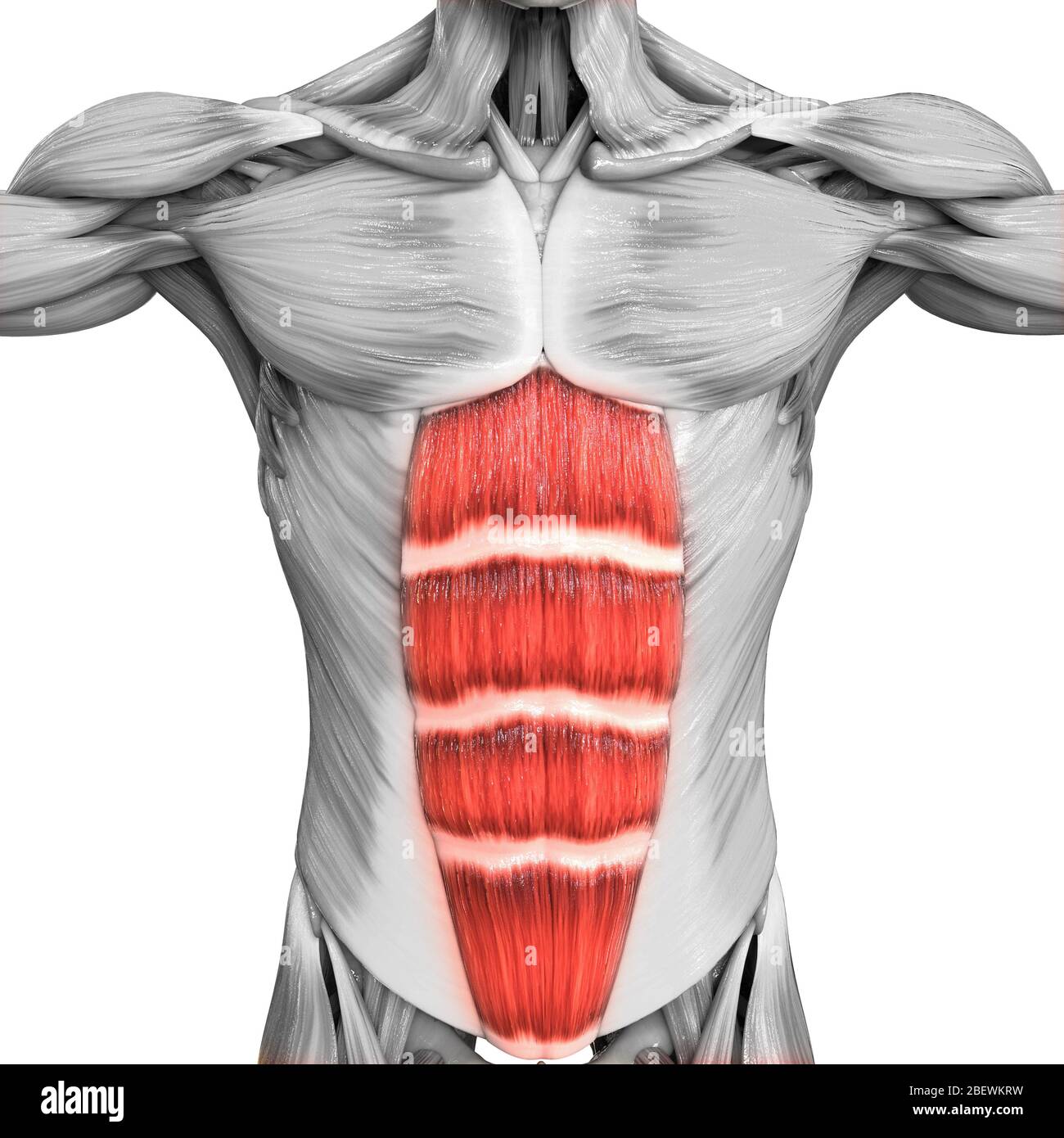
 What is the full correct term for this muscle?
What is the full correct term for this muscle?
Rectus Abdominis
What stimuli does a photoreceptor respond to? Give an example.
Responds to light energy. Example: Retina.
What is a motor areas function?
Controls Voluntary movement.
Is it made up of gray or white mattered structures?
Gray Matter.
Where is the pons located? (What is it between)
Located between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata.
What is the term for the muscle in green?:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13058/vcrefJ8Pj16AgRaoFe8Hg_Orbicularis_oculi_muscle_01.png)
Orbicularis Oculi
What does a mechanoreceptor respond to?
Touch, Pressure, Vibration, and Stretch.
What is the function of the sensory areas in the cerebral cortex?
It controls voluntary movement.
What is the overall function of the Diencephalon?
It acts as a relay station. It takes information from various parts of the body and helps process it.
What is the function of the pons?
It helps relay information between different parts of the brain. Helps with coordinating functions like breathing ,sleep-wake cycles, and facial movements.
What is the muscle in green and what does it do?:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13018/THwhYo2jzJRpQrouoLw3hA_pp5Pfy4TfU_M._pronator_teres_1.png)
Pronator Teres. It allows your arm to pronate (or rotate your palm downwards).
What stimuli is a nociceptor sensitive to? Give an example of a stimuli that it might respond to.
Pain-causing stimuli such as extreme heat or cold, excessive pressure and inflammatory chemicals.
What is the function of association areas?
Integrates diverse information.
What is the Thalamus and what is its function?
The Thalamus mediates impulses. processes them and acts as the "relay station".
Which cranial nerves is the pons the origin of ?
V,VI,VII
What is this muscle and what does it allow you to do?/images/library/5504/Uv9Kbp7NXenQd3a3D9SgcA_dRZFoaTaHX_M._rectus_femoris_NN_1.png.jpeg)
Rectus Femoris, it allows you to extend your leg at the knee.
What does a nonencapsulated nerve ending respond to? Is it nonmyelinated or myelinated?
It mostly responds to pain, temperature, light and touch. It is nonmyelinated.
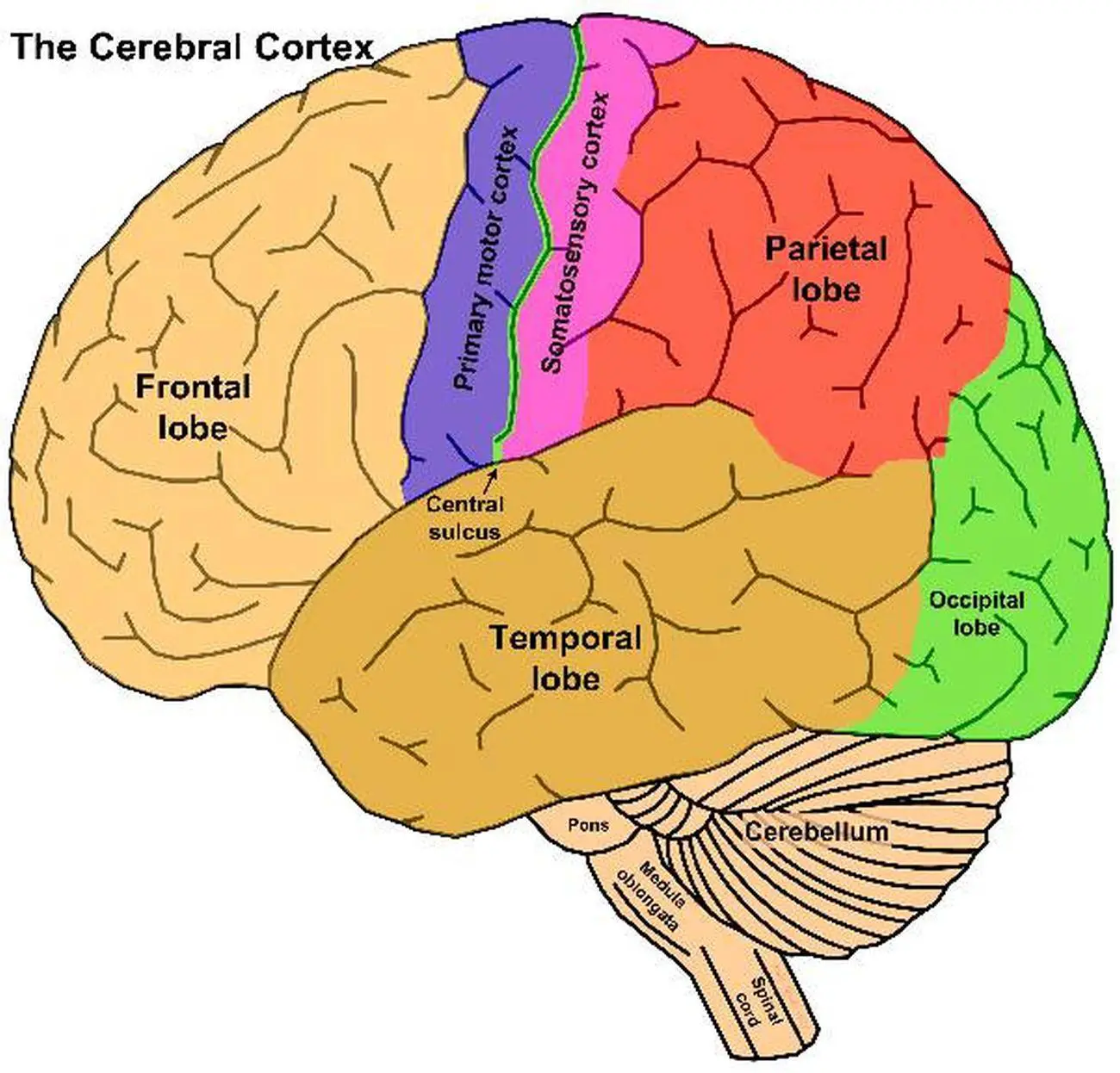 What part of the cerebral cortex has to do with vision?
What part of the cerebral cortex has to do with vision?
Green, the occipital lobe.
What is the hypothalamus and what is its function?
The hypothalamus is a regulator for homeostasis and modulates the autonomic system.
What is the function of the medulla oblongata?
It picks up nerve signals from the rest of your body and helps control vital processes like your heartbeat, breathing and blood pressure.
What is the muscle in the green?:watermark(/images/watermark_only_sm.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/external-intercostal-muscles/KgvHVds4KmLjMc2yGFCnw_Musculi_intercostales_externi_2.png)
External Intercostal muscles
Mechanoreceptors.
 Where is hearing located in the cerebral cortex?
Where is hearing located in the cerebral cortex?
Orange, Temporal lobe.
What is the function of the epithalamus and what gland does it contain?
The epithalamus secretes melatonin to regulate the sleep-wake cycle as well as contains the pineal gland.
What Cranial nerves is the Medulla oblongata the origin to ?
VIII, IX,X,XII