The largest white matter tract between the two cerebral hemispheres.
Corpus Callosum.
A life-threatening condition caused by dopaminergic blockade that results in neuromuscular anomalies, altered mental status, fever, and autonomic nervous system dysfunction.
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) causing FARM (fever, autonomic, rigidity, mental)
A 27 year old man presents to urgent care with 3 weeks of progressive shortness of breath. History is significant for travel to Ohio for a camping trip with friends in which the patient went spelunking. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Histoplasmosis.
Degeneration of these neurons leads to a loss of dopamine in the brain.
Substantia Nigra and/or Ventral Tegmental Area (VTA).
Excessive levels of this neurotransmitter may cause mental status changes, neuromuscular abnormalities, and autonomic nervous system abnormalities.
Serotonin
A 70 year old man with past medical history of BPH and diabetes presents to the ER after a syncopal episode. His blood sugar and temperature are within normal limits. CBC reveals a left shift of white blood cells. What is the diagnosis?
Urosepsis likely.
Antibodies against this neuromuscular junction channel may cause difficulty rising from a chair and increasing muscle recruitment with repetitive nerve stimulation testing.
Voltage Gated Calcium Channel, as seen in LEMS.
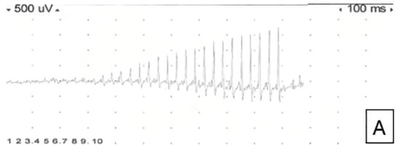
A 30 year old man is being treated for Major Depressive Disorder (MDD). His wife made him a charcuterie board for his birthday. One hour later, he presents to the ER with a severe headache, neck stiffness, and a blood pressure of 205/170. Bloodwork would reveal high levels of which amino acid?
Tyramine caused by MAOi usage.
A 27 year old man presents to his PCP with shortness of breath on exertion. His past medical history is not significant. His family history reveals several relatives that died of sudden deaths in their late 20s. The patient has occasional palpitations and his shortness of breath is relieved by crouching. What is the inheritance pattern of this patient's condition?
Autosomal Dominant (HOCM).
A 30 year old primagravida woman presents to her gynecologist for a mid-pregnancy well check. Bloodwork reveals an elevated level of Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP). The patient's PMH is significant for Bipolar 1. Which medication likely caused this finding?
Valproic Acid may increase the risk of open neural tube defects (myelomeningocele or anencephaly) and therefore increase levels of AFP.
An 18 year old woman is brought to the ER by her college roommate. Her roommate says she found her unconscious next to a bottle of pills. The patient's blood pressure is 80/55 and ECG reveals electrical abnormalities. Her PMH is significant for depression. Antagonism against which G-protein coupled receptor is most likely responsible for the patient's low blood pressure?
alpha-1 adrenergic receptor antagonism by TCAs.
A 50 year old man presents to his PCP with diarrhea and nausea. He is diagnosed with salmonellosis. Three weeks later he develops blurry vision, urogenital issues, and inflammation of his PIP joints. Serum testing would likely reveal antibodies against which cellular structure?
Reactive arthritis (can't see, can't pee, can't climb a tree) is associated with HLA B27 and antibodies against histones.
A 23 year old man presents to the ER with shortness of breath that began 2 hours ago. His vitals show BP 110/78, temperature 99F, height 6'3" and a weight of 130 pounds. He is a marathon runner. Physical exam reveals decreased breath sounds over the apex of the right lung. Which intervention should the physician consider?
Chest tube placement (after CXR)