This large chest muscle helps with arm movement and is activated during bench presses.
What is the pectoralis major?
Water moves across a semi-permeable membrane from low to high concentration.
What is osmosis?
This muscle contraction occurs as the muscle lengthens under force
What is an eccentric contraction?
This heart chamber receives deoxygenated blood from the body via the superior and inferior vena cavae.
What is the right atrium? 
This type of exercise involves short bursts of intense activity.
What is high-intensity interval training (HIIT)?
Located on the front of the upper arm, this muscle is responsible for flexing the elbow joint.
What is the biceps brachii?
This transport requires no energy and moves substances down their concentration gradient.
what is Passive transport?
This type of exercise, such as sprinting or weightlifting, primarily relies on energy systems that do not require oxygen.
What is anaerobic exercise? (Muscles break down glycogen to produce ATP)
This term refers to an irregular heartbeat that can affect blood pumping.
What is arrhythmia?
This medical term describes the study of the causes and effects of diseases
What is Pathology?
This posterior leg muscle is responsible for plantar flexion, allowing you to stand on your toes. (lateral side of the leg)
What is the gastrocnemius?
What term describes a cell's ability to keep a stable internal environment despite external changes?
What is homeostasis?
These muscle fibers generate high force quickly but fatigue quickly.
What is Fast-twitch muscle fibers (type II)?
This term refers to the amount of blood the heart pumps in one contraction.
What is stroke volume?
This condition results from excessive fluid accumulation in the body's tissues, often linked to heart or kidney problems.
What is Edema?
This flat, pear-shaped muscle lies beneath the gluteus maximus and aids in thigh lateral rotation and hip stabilization during walking or running.
What is the piriformis?

Which ion, essential for muscle contraction, is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
What is calcium (Ca 2+)?

This term refers to the maximum oxygen the body can use during intense exercise, a key indicator of cardiovascular fitness.
What is VO2 max?
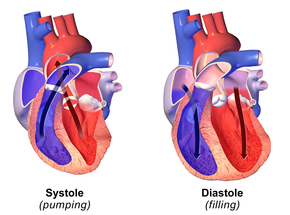
This phase involves the heart muscle relaxing and the chambers filling with blood.
What is diastole?
This blood protein produced by the liver, is essential for maintaining osmotic pressure and transporting substances like hormones and drugs through the bloodstream.
What is Albumin?
This muscle group along the spine extends the back, maintains posture, and stabilizes the spine during lifting and bending.
What is the Erector spinae?
The sodium-potassium pump is an example of this type of transport mechanism.
What is active transport? (Uses ATP to move against gradients)
This polysaccharide is the main form of carbohydrate storage in the body, primarily found in the liver and muscles
What is glycogen?
This condition involves plaque buildup in the arteries, reducing blood flow.
What is atherosclerosis?
This degenerative joint disease is marked by cartilage and bone breakdown.
What is osteoarthritis?