What are Routine Practices?
Routine practices are a set of infection control strategies and standards designed to protect workers from exposure to potential sources of infections diseases
Define Donning
Putting on
How long do you wash your hands?
15-20 seconds
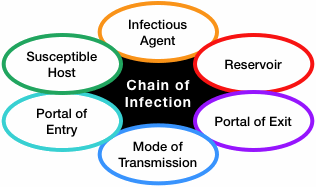
what is the chain of infection?
Mr. Star has high fever, cough and a sore throat
contact and droplet
Additional Precautions are?
Define Doffing
Taking off
What are the four moments of hand hygiene?
- Before initial patient/ patient environment contact. (before entering room)
- Before aseptic procedure
- After body fluid exposure or risk of exposure
- After patient/ patient environment contact. (Leaving Room)
Who is at risk for infection?
- immune-compromised
- diabetics
- ederly
- infants/babies
-unimmunized
- people with breaks in their skin
- low-income households
- frequently exposed people
- people on steroids
- uneducated
- physically disabled
- chemo patients
Your Patient has the Measles
airborne precautions
These are additional precautions for contact spread infections
Gown, mask, goggles/face shield, signage on door
Gloves
Don't move equipment in and out of room
What is the proper way to don PPE?
1) Clean hands
2)Put on gown
3)Put on mask/N95
4)Put on eye protection
5) put on gloves
When do you wash your hands with soap and water?
When your hands are visibly soiled or exposed to spore-forming organisms such as Clostridium difficle or Bacillus anthracis
How do you break the chain of infection at the mode of transmission?
- hand hygiene
- PPE
- Coughing into the elbow
- don't share urinals/basins with different patients
- Don't use the same equipment on different patients without cleaning first
Your patient is a 8 year old with the chicken pox. He is coughing and sneezing and his spots are oozing a clear fluid
airborne
These are additional precautions for droplet spread infections
Mask, face shield, social distance, gowns, signage on door
How do you properly Doff PPE?
1) Remove gloves
2)Remove gown
3)Clean hands
4) remove eye protection
5) remove mask or N95
6) clean hands
When using an antiseptic hand rub, how long do you rub your hands for?
15-20 seconds or until product is dry
- Vaccination
- isolation
- education
- medicine
- nutriotion
- exercise
- intact skin
Mrs. Summer has a cold
contact and droplet
These are additional precautions for airborne spread infections
N95 mask
have the air sucked out of the room
nobody immune-compromised enters the room
door signage
Where do you remove PPE?
- must be removed carefully to avoid self-contamination
- doff PPE at the doorway before leaving the patient room or in the anteroom
-take off N95 outside of the room after the door has been closed
What areas of the hands are usually missed when performing hand hygiene?
wrists, between fingers, back of the hand, thumb, and under the fingernails
What is Asepsis and what are the two types?
Asepsis - practices designed to keep areas/objects as free from microorganisms as possible.
2 types: medical asepsis and surgical asepsis.
Medical asepsis:
Medical asepsis is clean technique- aims to reduce and prevent the spread of microorganisms.
The equipment used can be sterile but the environment is considered clean not sterile.
Surgical Asepsis:
AKA sterile technique
Absence of all microorganisms
OR setting
Mr. Rock is the 5th person on your floor to have vomitting and diarrhea. He's confused and the vomitting is projectile.
contact