According to the ACC 2025 concise clinical guideline, what is the preferred treatment option for patients with pericarditis that fail to respond to NSAIDs + colchicine with inflammatory pericarditis?
Anti-IL-1 - rilonacept, anakira or goflikicept
In addition to continuing NSAID + colchicine

Name one FDA approved treatment for ALS
Riluzole - 3 month increased survival (1997)
Edaravone - decreased functional decline (2017)
Tofersen - for rare SOD1 mutation ALS (2023) - increases survival, functional decline (may even stabilize functional decline)
Classic lab finding in DIC (high/low):
___ plt
___ aPTT
___ PT
___ INR
___ fibrinogen
Low plt
High aPTT
High PT
High INR
Low fibrinogen
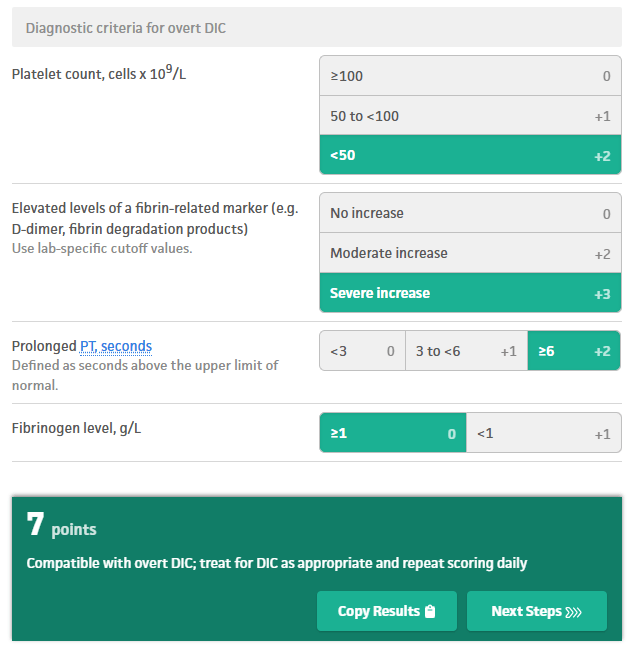
ISTH Criteria DIC score:
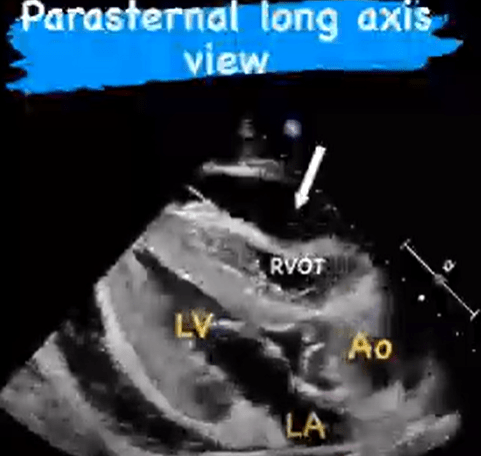
What is the most specific and concerning finding on POCUS for cardiac tamponade?
Diastolic right ventricular free wall collapse.
Assuming good patient technique, A NIF value worse than ___ is concerning for impending respiratory failure
-30
Oftentimes limited by poor technique, so always ask RT if they think seal/effort was good.
How does the American Society of Hematology recommend that patients with stable CVD on aspirin started on therapeutic anticoagulation for a new DVT/PE be managed?
Hold asp for duration of anticoagulation.
For patients with DVT/PE with stable cardiovascular disease, the ASH guidelines suggest suspending aspirin therapy when initiating anticoagulation. The combination of anticoagulation plus aspirin increases the risk of bleeding without clear evidence of benefit for patients with stable cardiovascular disease.
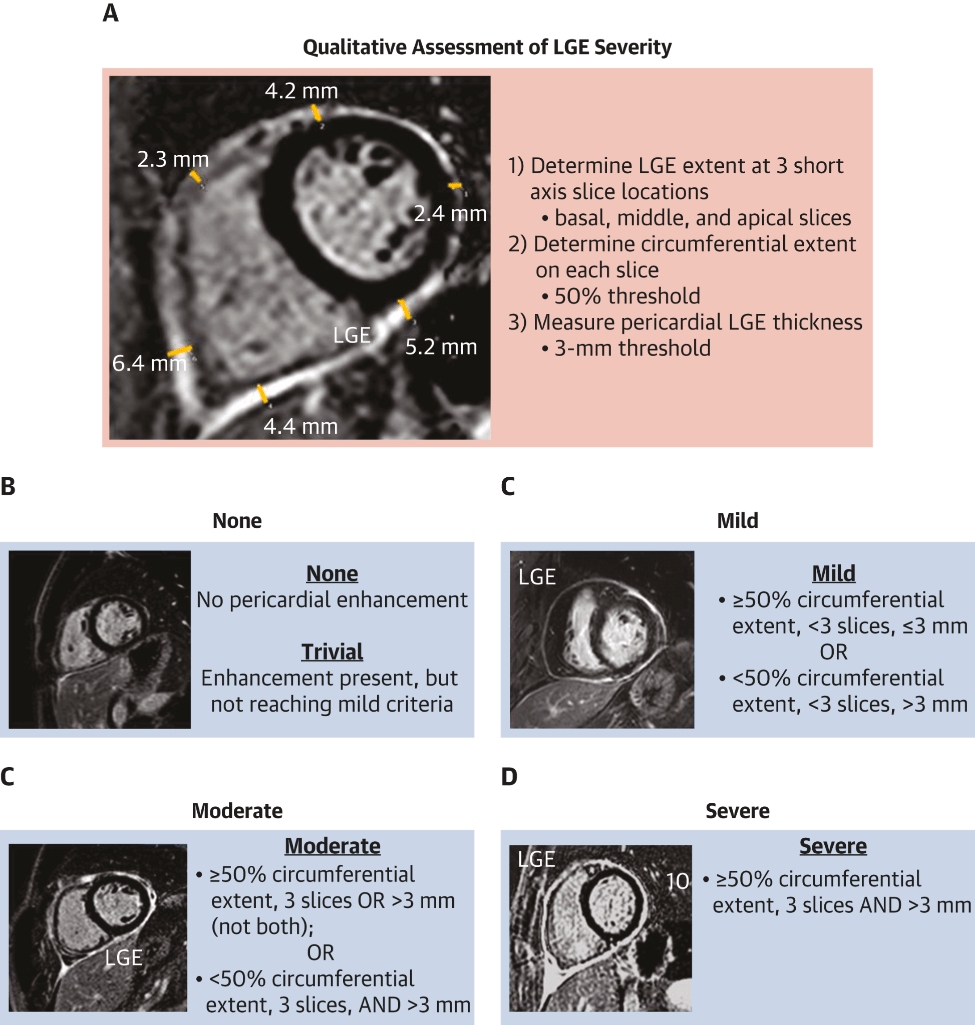
What finding on cardiac MR is primarily used to establish a diagnosis of pericarditis and grade it's severity?
Late gadolinium enhancement/edema - on phase-sensitivity inversion recovery sequence (ideally fat-suppressed), indicating neovascularization or inflammation
A 44F patient reports diplopia, ptosis, and dysphagia that occurs towards the end of the day/before bed. Denies waking up with symptoms. She undergoes evaluation and found to have positive ACh-R antibodies. In addition to electrodiagnostic confirmation, what additional evaluation should they undergo (2)?
Myasthenia Gravis
Chest CT → Thymoma
TFTs → Autoimmune thyroid disease
What laboratory testing can help differentiate DIC from liver-induced coagulopathy, and what result might be expected?
Factor VIII levels, which are produced by endothelial cells and independent of liver function.
DIC: consumption of all factors - usually low
Liver-induced coagulopathy: endothelial cells increase production to offset coagulopathy - usually high
Which patients should be hospitalized for acute pericarditis (5)?
High fevers (>38°C)
Subacute course
Presence of large pericardial effusion with echocardiography features of tamponade physiology
Failure to respond to outpt nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Concomitant myocarditis
Can consider immunosuppression, oral anticoagulation, and trauma
Name 3 meds known to worsen myasthenia
antibiotics including fluroquinolones + macrolides + aminoglycosides
AEDs; antipsychotics, BBs, CCBs, Mg, iodinated contrast rarely
How is catastrophic APLS (3 or more organ thrombosis in less than 1 week) treated?
For refractory cases, rituximab or eculizumab can be considered
50% mortality
How can you establish a definite diagnosis of myocarditis? How about a probable diagnosis?
Definite - Cardiac MRI or endomyocardial biopsy
Possible -
elevated trop
LV +/- RV dysfunction (abnmormal strain, wall motion or reduced EF)
ST-T changes - nonspecific, but still count
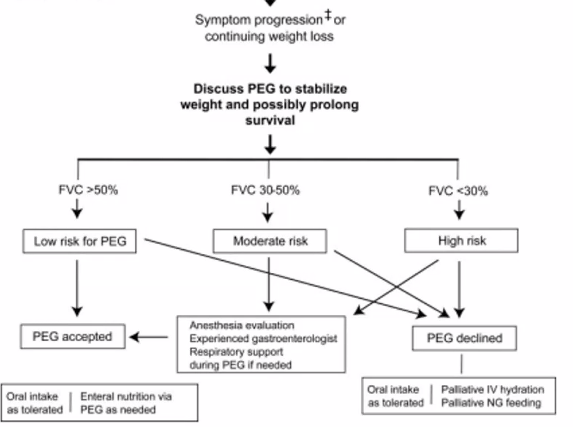
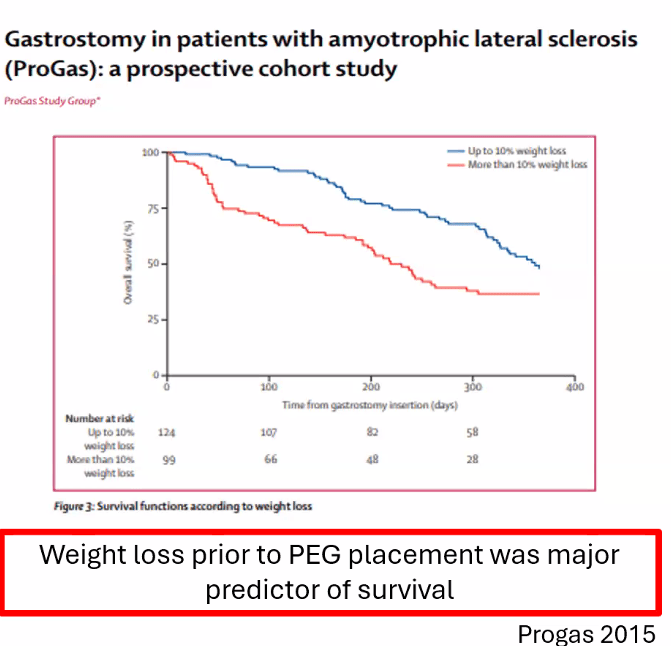
Which patients with ALS are likely to have a survival benefit of gastrostomy tube placement?
FVC> 50%, ideally before significant weight loss (>10% of BW)
FVC 30-50% less likely to see survival benefit, but may have symptom improvement + weight gain
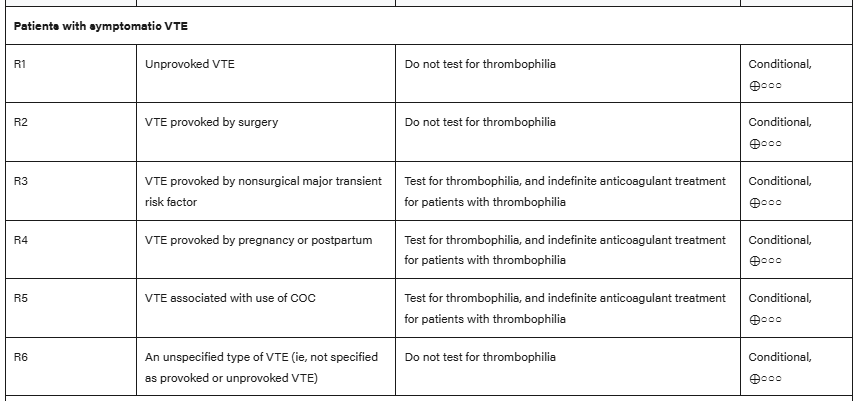
Per the American Hematologic Society Guidelines, which patient populations should not undergo testing for thrombophilia conditions after a new diagnosis of venous thromboembolism at a usual site (2)?
Unprovoked DVT - warrants indefinite anticoagulation, regardless of etiology. Exception is high suspicion of APLS, because it can change management
VTE provoked by surgery or other clear predisposing medical syndrome.
Testing indicated for: VTE provoked by nonsurgical major transient risk factor, cerebral/splanchnic VTE, age < 45, recurrent/multiple thrombosis, arterial thrombosis (needs APLS testing).