Outline 3 components of Cell Theory
-all cells come from other pre-existing cells
-all living organisms are made of one or more cells
-cells are smallest unit of life
The monomer of nucleic acids are called...
nucleotides
FALSE
Name any three organs involved in the digestive system.
-alimentary canal
-stomach
-small/large intestine
-pancreas
-liver
What types of species might do both photosynthesis and cell respiration within the same cell?
plant, algae
Draw a simple diagram of a single phospholipid.

Briefly explain when and why DNA replication must occur.
Must occur before mitosis/division so that both daughter cells contain 2 complete, identical sets of DNA.
Define a gene.
a heritable factor that consists of a sequence of DNA and influences a specific characteristic.
atrio-ventricular valves
Name 2 pigments in leaves that are responsible for absorbing photons during photosynthesis.
-chlorophyll a
-chlorophyll b
-b carotenoid
Compare and contrast active and passive transport.
Active: uses energy (or ATP) to move molecules against concentration gradient
Passive: does not use energy to move molecules with/along concentration gradient
Label the arrows below with the names of the processes they represent.
DNA --> RNA --> Protein
Transcription
Translation
Short tails are recessive to long tails in a species of tropical lizard. A heterozygous individual and a homozygous long tail lizard are crossed. Complete a Punnet grid to determine the phenotypic ratios of the offspring.
100% long tail lizards
What structure surrounds the axon of neurons and increases the speed of signal transduction?
myelin sheath
pyruvate
List 3 structures you're likely to find in a micrograph of an animal cell that you won't find in a bacteria cell.
-nucleus
-mitochondria
-GA
-RER
-lysosomes
-vacuoles
The 2 strands of nucleotides are held together by _______________ bonds to create a double helix.
hydrogen
State 2 aspects of meiosis that increase genetic variability among individuals of a species.
-crossing over
-random orientation of homologous chromosomes and spindle fiber connections
Diaphragm relaxes.
External Intercostals relax and Internal Intercostals contract.
State 2 possible products of anaerobic respiration.
lactic acid and ethanol
Draw a digram that represents all the stages of mitosis in order.

A sequence of anti-sense strand DNA reads: CCGTAGATA
What polypeptide would be produced from this DNA sequence?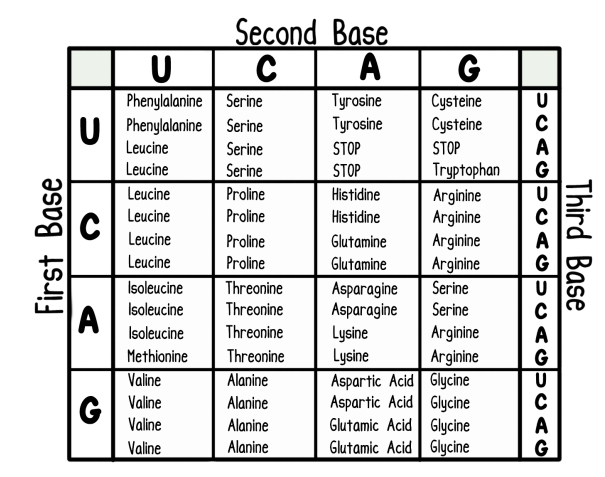
Glycine - Isoleucine - Tyrosine
Insulin is a protein typically produced by the liver but some diabetics aren't able to produce enough insulin to control the glucose in their blood. Outline the biotechnology process of making recombinant insulin.
-Isolate insulin gene
-Remove a plasmid from E. coli
-Clone/insert the insulin gene into the plasmid
-Place the plasmid back into the E. coli and grow a bunch of the bacteria
-Harvest E. coli, then extract and purify insulin protein
-damaged blood vessel sends signal to platelets
-platelets get stickier and send clotting factors that change prothrombin --> thrombin
-Thrombin converts fibrinogen --> fibrin, a fibrous protein that makes a mesh net on the vessel and catches platelets/cells to form clot
Briefly compare and contrast light-dependent and light independent reactions.
-both components of photosynthesis
-light-dependent utilize and absorb light energy and convert it to chemical energy (ATP)
-light-independent reactions utilize the ATP to convert CO2 and water into glucose