Glucose (dextrose), fructose (levulose), galactose are what
What are the monomers of carbohydrates (monosaccharides)?
Name two type of ecological relationships between organisms
-Mutualism
-Parasitism
-Commensalism
-interspecific competition
-intraspecific competition
- Predator Prey
-Carnivore, herbivore
Identify the type of cell, justify your reasoning
A plant cell, it has chloroplast a central vacuole, and a cell wall. 
What is one biological benefit of the cohesive properties of water
surface tension allows water to act as a habitat for small insects, allows water to be transported up the xylem, gives water its thermal properties.
What monomer is cellulose made of
(Beta) Glucose
How and why do flowers attract bee
colour/patterns on flower parts; b. scent; c. providing nutrients/nectar; so that it can polinate for the flower
Identify the function and structure of the nucleus Which type of cell contain a nucleus.
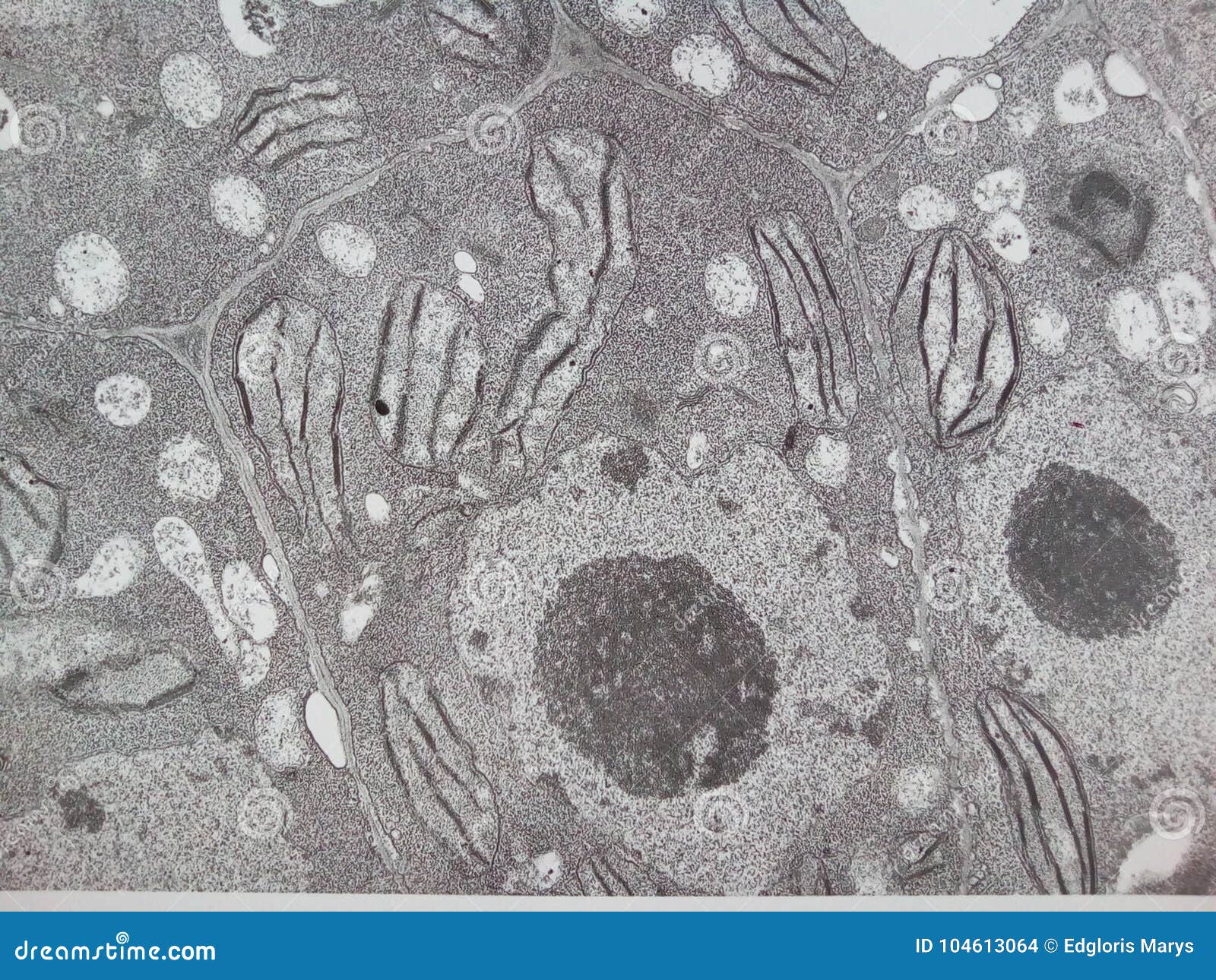
Nucleus contains DNA; which has the instructions to code for protein. It is found in eukaryotes 
How does the structure of cellulose relate to its function
a. stable (covalent) bonds between monomers ensure that the molecule is strong/rigid/inelastic; b. absence of branching allows fibers to pack closely/form hydrogen bonds; c. cross linkages/hydrogen bonds provide strength/stability/resists digestion; d. chain molecules allow for structure / strength; e. (beta-) glucose molecules provide energy (to organisms that can digest cellulose)
How do mutations lead to cancer
mutations are random changes in the sequences of genes/DNA; b. (mutation) may involve addition/deletion/substitution/inversion of DNA bases; c. (mutations) in tumour suppressor genes/oncogenes; d. uncontrolled cell division/mitosis occurs; e. abnormal cells cannot perform their function; f. they divide repeatedly to form tumours;
Describe the difference between Prokaryote and Eukaryote DNA
in prokaryotes circular whereas in eukaryotes linear; b. in eukaryotes associates with histones whereas in (most) prokaryotes not/naked DNA in prokaryotes
How does water interact with lipids and carbohydrates
Most lipids—fats, oils, phospholipids—are made mostly of long nonpolar hydrocarbon chains.
Water is polar, so it cannot form hydrogen bonds with these nonpolar regions making them unable to dissolve.
Carbohydrates—like glucose, starch, and cellulose—contain many polar hydroxyl (–OH) groups.
These groups form hydrogen bonds with water very easily. Most simple carbohydrates dissolve well in water, while larger molecules like starch or cellulose do not dissolve easily due to their large size.
Describe the structure of amylopectin and glycogen. How does it contribute to its function
branched, which makes it easier to remove the glucose monomers for respiration
Which group of organisms contain linear DNA that contain histones
Eukaryotes
Branched polymer of alpha-D-glucose linked by 1,4 glycosidic linkages with branches linked by 1,6 glycosidic linkages
Glycogen
Describe one thermal property of water and the consequences for organisms using water as a habitat
1. Water has a high specific heat, it takes a lot of energy to change the temperature of water due to its hydrogen bonds. Making it a stable habitat, animals do not need to adapt to quickly changing temperatures.
3. Water has high thermal conductivity, it conducts thermal energy easily, making it a poor insulator and causing rapid heat loss in aquatic animals. This requires insulation like blubber.
4. Water is more viscus than air, so more energy to move through water due to drag requiring more streamlined bodies.
5. Water has high buoyant force, so animals can float and stay suspended easier. Fish have air bladders to change their position in the water column.
Describe 2 properties of starch that make it a good energy storage molecule
1. Low solubility so it doesn´t impact osmosis
2. Compact structure makes it so that it can hold a lot of glucose
3.Branched structure makes it easier to remove glucose monomers
4. Composed of glucose molecule that can be used in cellular respiration
What is the function of structure one
The cell wall provide structure for plant cells
Describe the structure of starch. (4 marks)
a. starch is a carbohydrate
b. starch is formed by carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
c. it is a polymer/chain/polysaccharide
d. formed from monosaccharides/simple sugars/glucose
e. linked together by condensation/dehydration
f. consists of amylose and amylopectin
g. amylose is a long chain/unbranched
h. amylopectin is branched