2.3
What does it mean for water to be polar?
Water has a partial negative charge at one end (O) and a partial positive at the other (H).
Which biomolecule has the following molecular ratios
1Carbon:2Hydrogens:1Oxygen
carbohydrates
What type of biomolecule are enzymes?
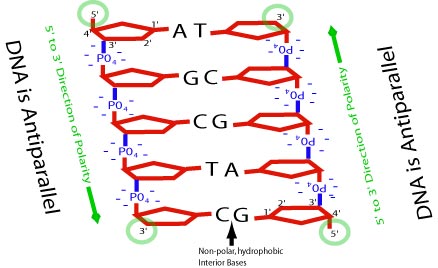
What does it mean for DNA to be antiparallel?
The two strands go in opposite directions.
What is the equation for aerobic cellular respiration?

The weak bonds between polar molecules
Give an example of one monosaccharaide and one polysaccharide.

Describe the function of enzymes using the term reaction, substrate, active site and product.
Enzymes are proteins that increase the rate of a chemical reaction. Substrates bind into the active site, creating an ideal environment for the formation of the product.
Compare DNA and RNA structure [3 marks]


ATP is a short-term energy storage molecule
Energy is released when a phosphate is broken off
Describe how water is used as a coolant.
The evaporation of water requires energy from the surface of the skin. Because water has a high specific heat capacity, it absorbs a lot of thermal energy before it evaporates, cooling the skin
Identify two examples of lipids and their functions.
phospholipid - cell membrane
triglyceride - store energy
wax - waterproofing
cholesterol - membrane fluidity
What happens to proteins when they are in environments with very different pH or temperature?
Denaturation - losing of protein shape (and function) due to changes in hydrogen bonds and charges
Put these steps of protein synthesis in the correct order:
1. mRNA travels to the ribosome (rRNA)
2. DNA is read to create mRNA by following the base-pairing rules
3. Amino acids are attached to the growing polypeptide chain.
4. Anticodons of tRNA bind to codons mRNA
1. DNA is read to create mRNA by following the base-pairing rules
2. mRNA travels to the ribosome (rRNA)
3. Anticodons of tRNA bind to codons mRNA
4. Amino acids are attached to the growing polypeptide chain.
What are the products and uses of anerobic respiration by yeast?
ethanol - alcohol
CO2 - rising bread
Water is considered the universal solvent. Name 2 things that can dissolve well in water.
Anything hydrophilic.
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) is freely transported within the blood
- Oxygen is soluble in water but in low amounts – most oxygen is transported by haemoglobin within red blood cells
- Glucose contains many hydroxyl groups (–OH) which may associate with water and thus can freely travel within the blood
- Amino acids will be transported in the blood in an ionized state

Draw a generalized dipeptide.

List the components of polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Taq polymerase - a heat-stable DNA ploymerase
RNA primers - bind to the correct sequence of DNA to initiate replication
DNA nucleotides - to form the new strands
Thermocycler - machine that uses variation in temperature to :1. denature DNA (90C) 2. Anneal primers (55C) 3. Elongate strands (75C)
What is the role of chlorophyll?
Absorbs red and blue light and reflects green light in the chloroplast. The energy absorbed is used for photosynthesis.
Why does water have a much higher boiling point than methane?
- Water is polar and can form intermolecular hydrogen bonds (due to high electronegativity of oxygen atom)
- Methane is non-polar and can only form weak dispersion forces between its molecules (carbon has a lower electronegativity)
Describe the health effects of cis, trans and saturated fatty acids.

Describe the process of the production of lactose free milk.
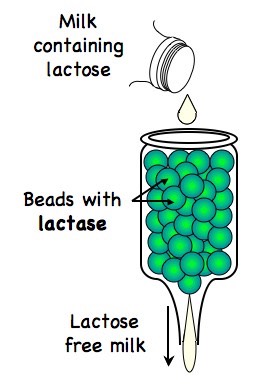 Lactase breaks lactose into glucose and galactose, which people with lactose intolerance can digest.
Lactase breaks lactose into glucose and galactose, which people with lactose intolerance can digest.
Translate the RNA sequence: AUG ACG AAU GGG UAA

Met Thr Asn Gly STOP
Describe the effect of changing CO2 concentration on photosynthesis.
