These plant structures minimize water loss due to transpiration.
What are guard cells?
This tissue is responsible for transporting water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the leaves where it will be used for photosynthesis.
What is the xylem?
The diffusion of H+ ions from high to low concentration across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
What is chemiosmosis?
A sample of DNA is analyzed and found to contain 24% A. One would expect to find _____ % C.
What is 26%
The enzyme represented by the gray oval in the image below:
RNA Polymerase
Involves a response that reinforces the change detected (it functions to amplify the change).
The birth process is an example of this process.
- In the case of childbirth, fetal growth eventually causes stretching of the uterine walls, which is detected by stretch receptors
- This triggers the release of hormones (oxytocin) that induce uterine muscles to contract, further reducing space in the womb
- This causes more stretching and hence more contraction until the origin stimulus (the fetus) is removed (i.e. birth)
What is a positive feedback process?
The site(s) of amylase production.
What are the salivary glands and pancreas?
National holiday celebrated on July 14th.
What is Bastille Day?
Located near the tip of the root. This is where the root generates cells for the growing root.
What is apical meristem?
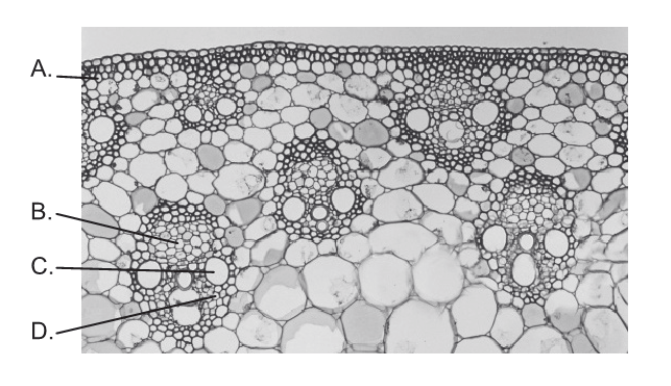
Structure "B" in the image above
What is phloem?
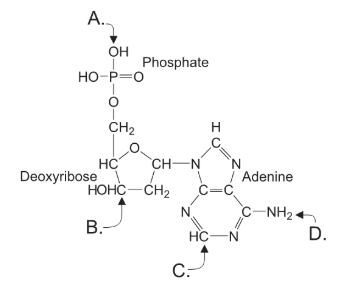
What molecules do A and D represent?
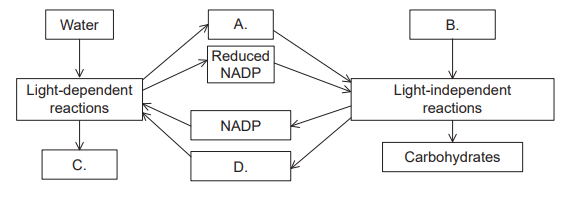
What are A: ATP and D: ADP?
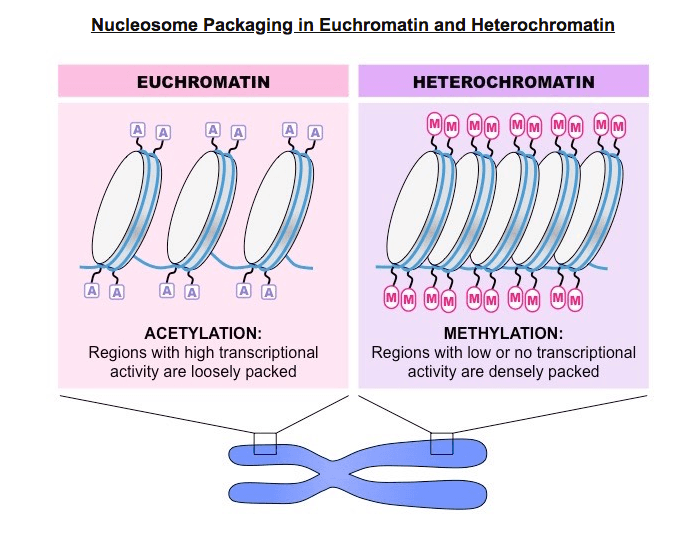
When DNA is supercoiled and not accessible for transcription
Heterochromatin
What is represented by "W" and "X" in the image below:
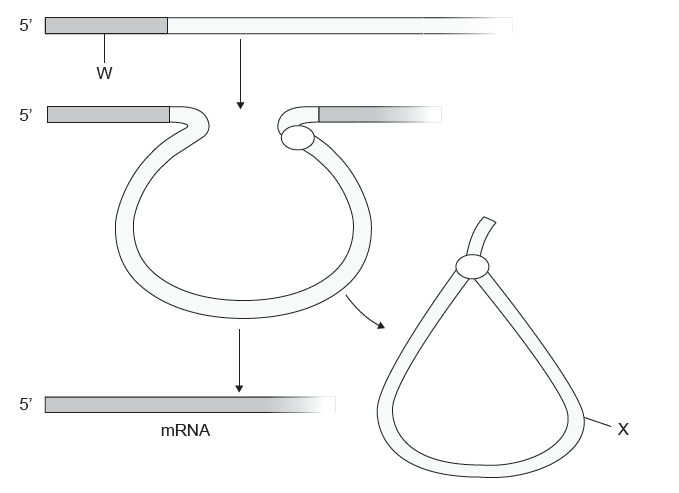
"W" = exon
"X" = intron
A sudden change in neuron membrane potential – usually from a (relatively) negative to positive internal charge. Occurs in response to a signal initiated at a dendrite.
What is depolarization?
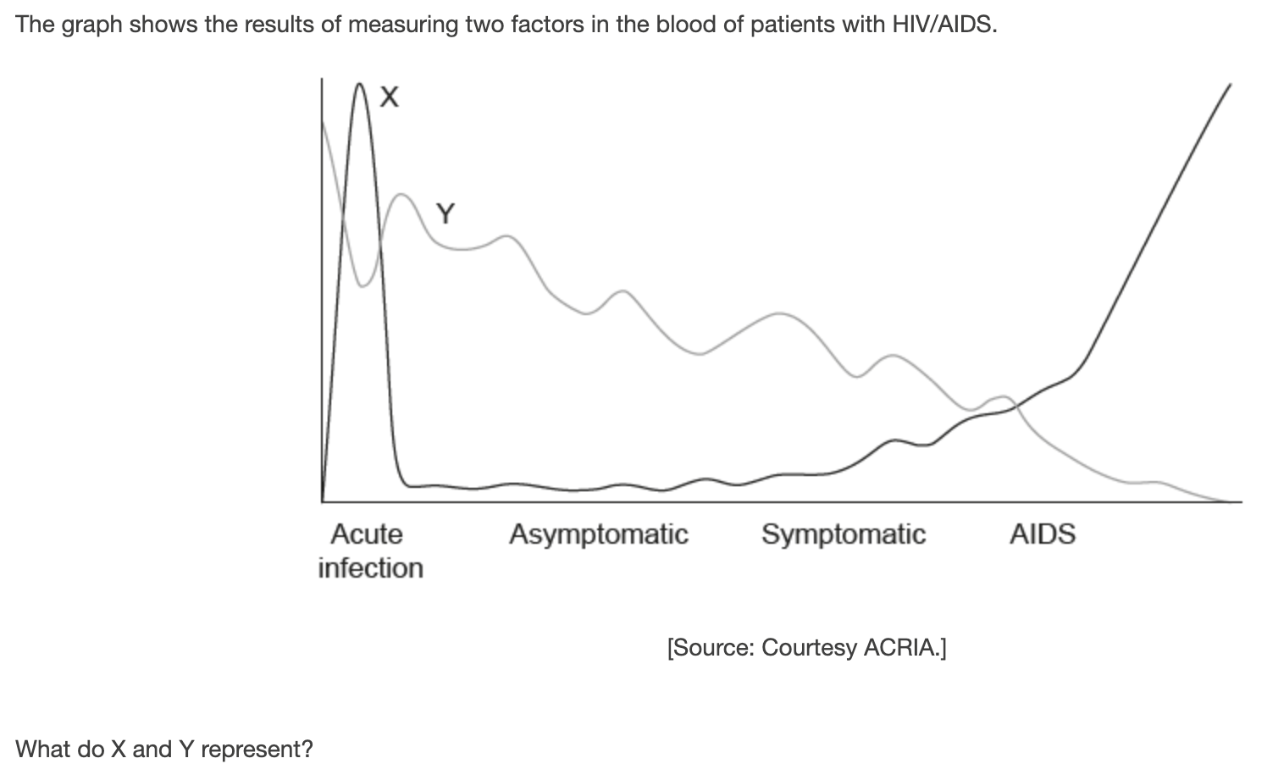
What are..
X: HIV virus
Y: Lymphocytes (T Cells)?
Planet with the most gravity.
What is Jupiter?
This device can be used to measure the rate or transpiration from a leaf clipping.
What is a potometer?
The respective roles of bees and squirrels in the reproductive mechanisms of angiosperms.
What are pollination (bees) and seed dispersal (squirrels).
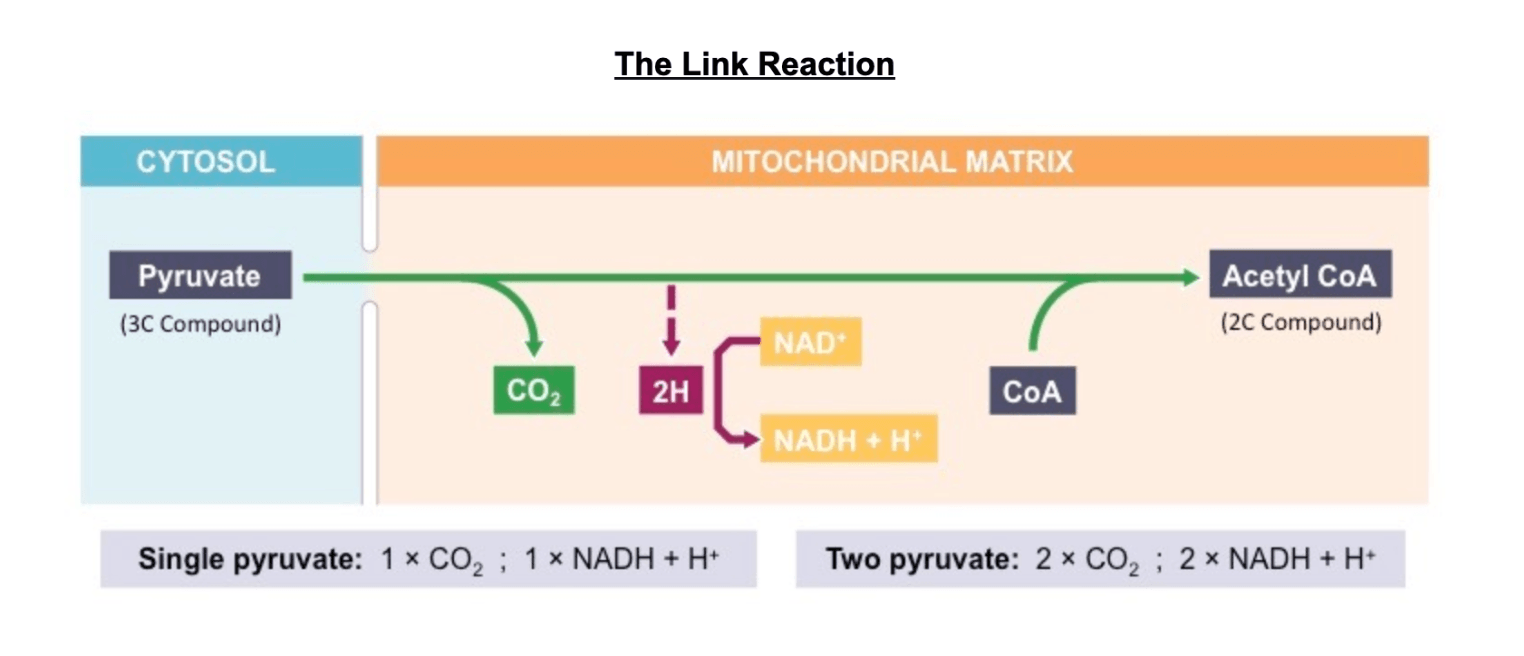
Stage when the reaction below occurs
Pyruvate →→ Acetyl CoA + CO2
What is the LINK REACTION or pyruvate decarboxylation?
The link reaction is named thus because it links the products of glycolysis with the aerobic processes of the mitochondria
- Pyruvate is transported from the cytosol into the mitochondrial matrix by carrier proteins on the mitochondrial membrane
- The pyruvate loses a carbon atom (decarboxylation), which forms a carbon dioxide molecule
- The 2C compound then forms an acetyl group when it loses hydrogen atoms via oxidation (NAD+ is reduced to NADH + H+)
- The acetyl compound then combines with coenzyme A to form acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA)
Consists of a molecule of DNA wrapped around a core of eight histone proteins
What is a Nucleosome?
The DNA is complexed with eight histone proteins (an octamer) to form a complex called a nucleosome
Nucleosomes are linked by an additional histone protein (H1 histone) to form a string of chromatosomes
These then coil to form a solenoid structure (~6 chromatosomes per turn) which is condensed to form a 30 nm fibre
These fibres then form loops, which are compressed and folded around a protein scaffold to form chromatin
Chromatin will then supercoil during cell division to form chromosomes that are visible (when stained) under microscope
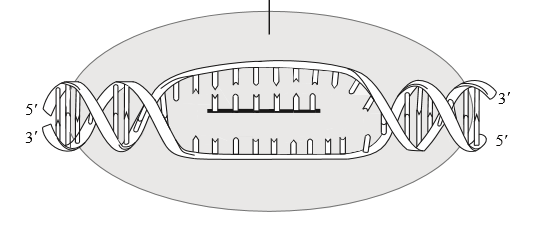
Indicate where in the image below a new DNA nucleotide would be attached.
What is "B"?
This hormone functions to maintain the endometrium (which is nourishing the embryo) and thicken the cervix during pregnancy.
What is progesterone?
Animal with a purple tongue
What is a giraffe?

Spiral thickening of the walls of the vessel elements which give extra strength allowing the vessels to remain rigid.
What is Lignin?
Plant hormone involved in germination that is activated by the influx of water through the micropyle.
What is gibberellin?
The flow of electrons (the path they the electrons take) from H2O to NADPH in the light reactions of photosynthesis.
What is H2O --> Photosystem II --> Electron transport chain --> Photosystem I --> NADP+ (making NADPH)
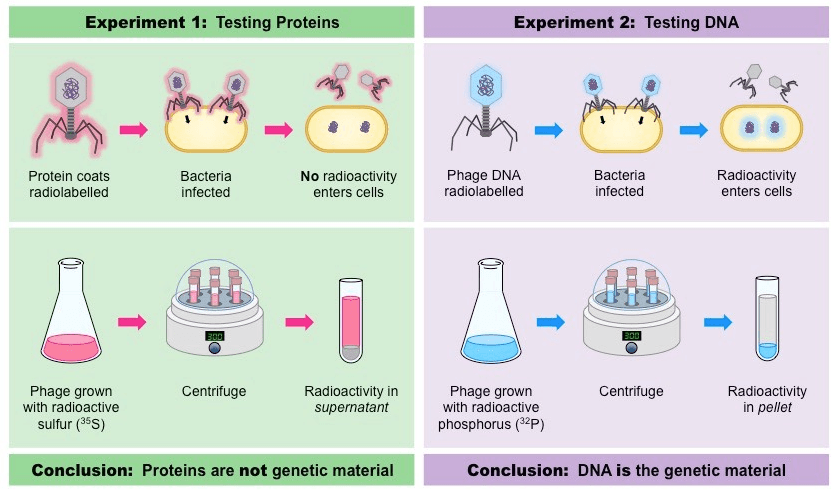
Scientist(s) who proved that DNA, not protein, was the primary genetic material.
Who were Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase.
Two groups of proteins that mediate binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter and regulate transcriptional activity.
Transcription factors form a complex with RNA polymerase at the promoter
-physically can't transcribe without these
Location of the SA node.
What is the right atrium?
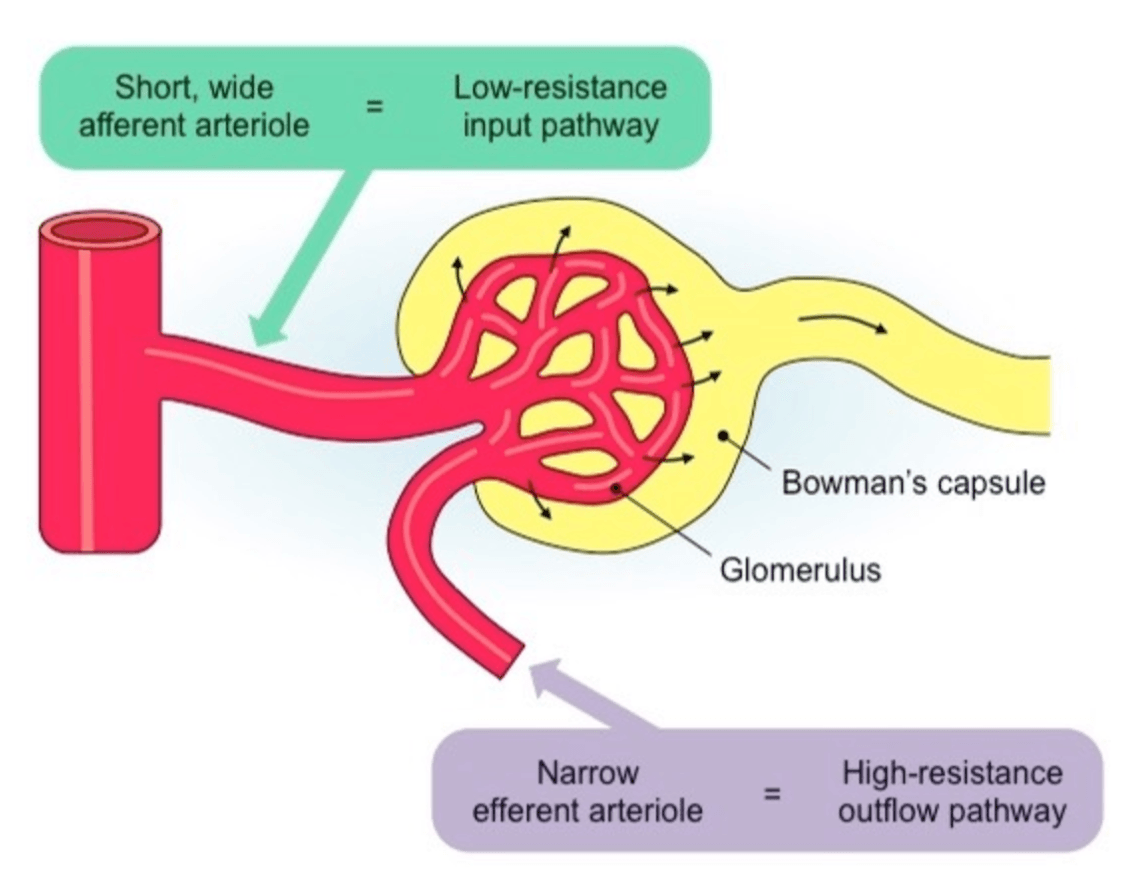
Ultrafiltration involves blood being forced at high pressure against the basement membrane, optimising filtration in the kidney. This is the cause of the high hydrostatic pressure in the kidney's glomerulus.
What is having a wide afferent (incoming) arteriole and a narrow efferent (outgoing) arteriole?
This 1988 work by Roald Dahl has won many awards including the Children's Book Award in 1999.
What is Matilda?
The effect of high concentration of IAA in a root cell.
What is inhibit growth?

Explain 3 structures and/or processes that allow plants growing in hot, dry conditions to replace the water lost from transpiration.
Evaporation of water «in leaf/mesophyll» creates tension/low pressure/negative pressure «potential»/pulling force/transpiration pull
Water drawn through cell walls/out of xylem «in leaf» by capillary action/adhesion «to cellulose»
Low pressure/tension/suction/pulling force in xylem
Hydrogen bonds make water cohesive/allow water to be pulled up under tension/allow the transpiration pull «to move water»
Xylem resists tension/low pressure/collapse with thickened/lignified walls
Water travels from the roots to the leaves in xylem
Water absorbed in roots by osmosis
Active transport of ions/solutes into roots «enabling osmosis»
Deep/wide ranging/extensive root systems/taproots/many root hairs
Thick/waxy cuticle reduces transpiration/water loss/evaporation
Small/no leaves/reduced surface area of leaves/thorns instead of leaves
Few stomata/stomata in pits/rolled leaves
Hairs on leaf surface «to reduce air flow near the leaf/reflect sunlight»
Stomata open at night/CAM physiology to reduce water loss
Phase of Photosynthesis identified by letter "C" in the diagram below.
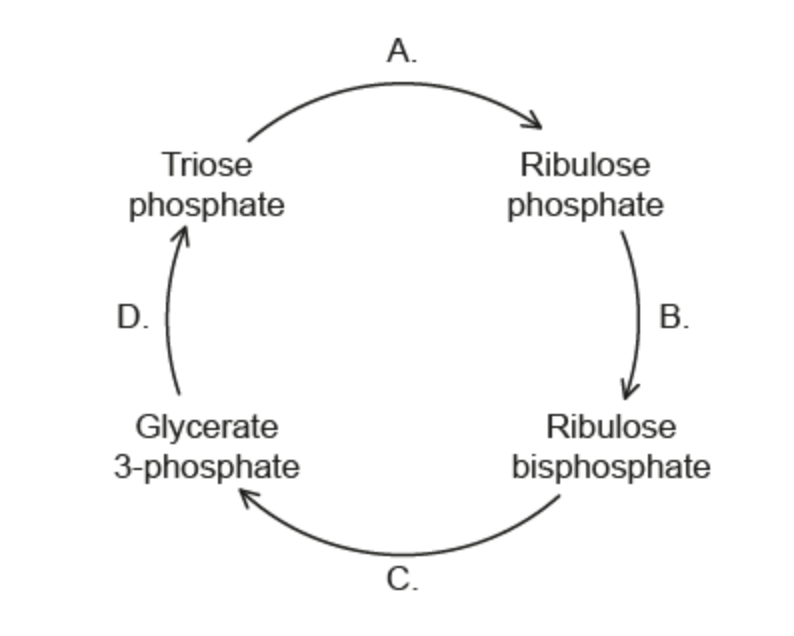
What is Carbon fixation or carboxylation?
Regions of repetitive DNA located at each end of a chromatid and function to prevent chromosomal deterioration
What are Telomeres?
Lack the 3’-hydroxyl group necessary for forming a phosphodiester bond and can therefore be used in DNA sequencing
What are Dideoxynucleotides?
This hormone, released by the posterior pituitary in response to dehydration, increased the permeability of the collecting duct to water.
What is Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) a.k.a. vasopressin?
Improves the speed of electrical transmission via saltatory conduction
What is myelination or the presence of the myelin sheath on axons?
'F' is for friends who do stuff together 'U' if for you and me 'N' is for anywhere and anytime at all Down here in the deep blue sea!
What is Spongebob Squarepants?
Group of glycoproteins responsible for the transportation of the plant hormone Auxin.
What are PIN3 proteins?
The role of Phytochrome far red (Pfr) in short day plants.
What is inhibit flowering?

Name the molecule being (1) reduced, (2) oxidized and (3) decarboxylated in the image below:
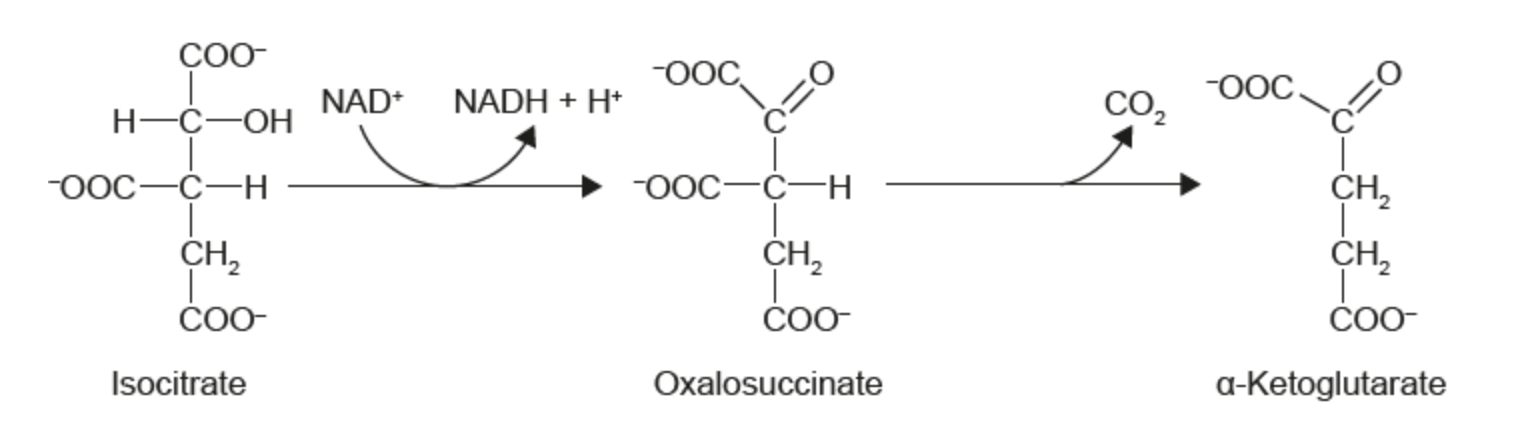
1 - NAD+ is reduced
2 - Isocitrate is being oxidized
3 - Oxalosuccinate is being decarboxylated
Example of non-coding DNA
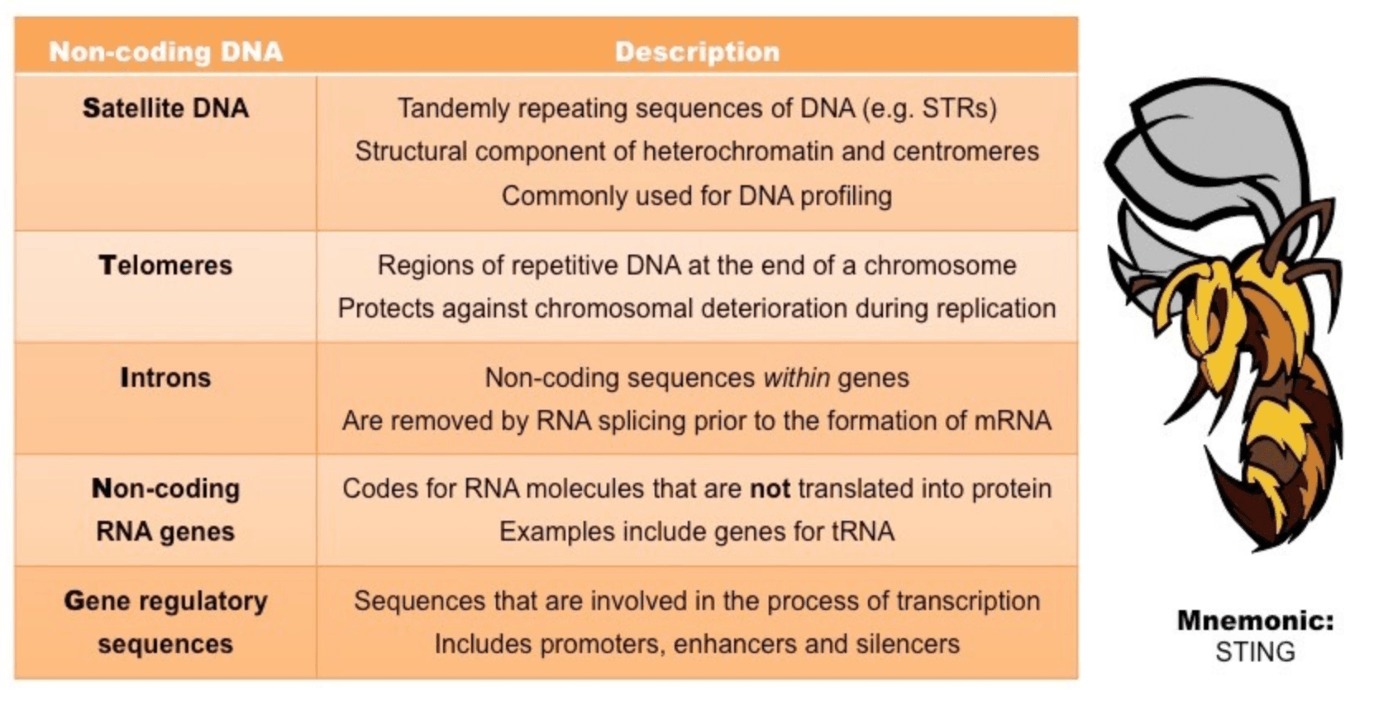
Decreases gene expression (by preventing the binding of transcription factors)
What is DNA Methylation?
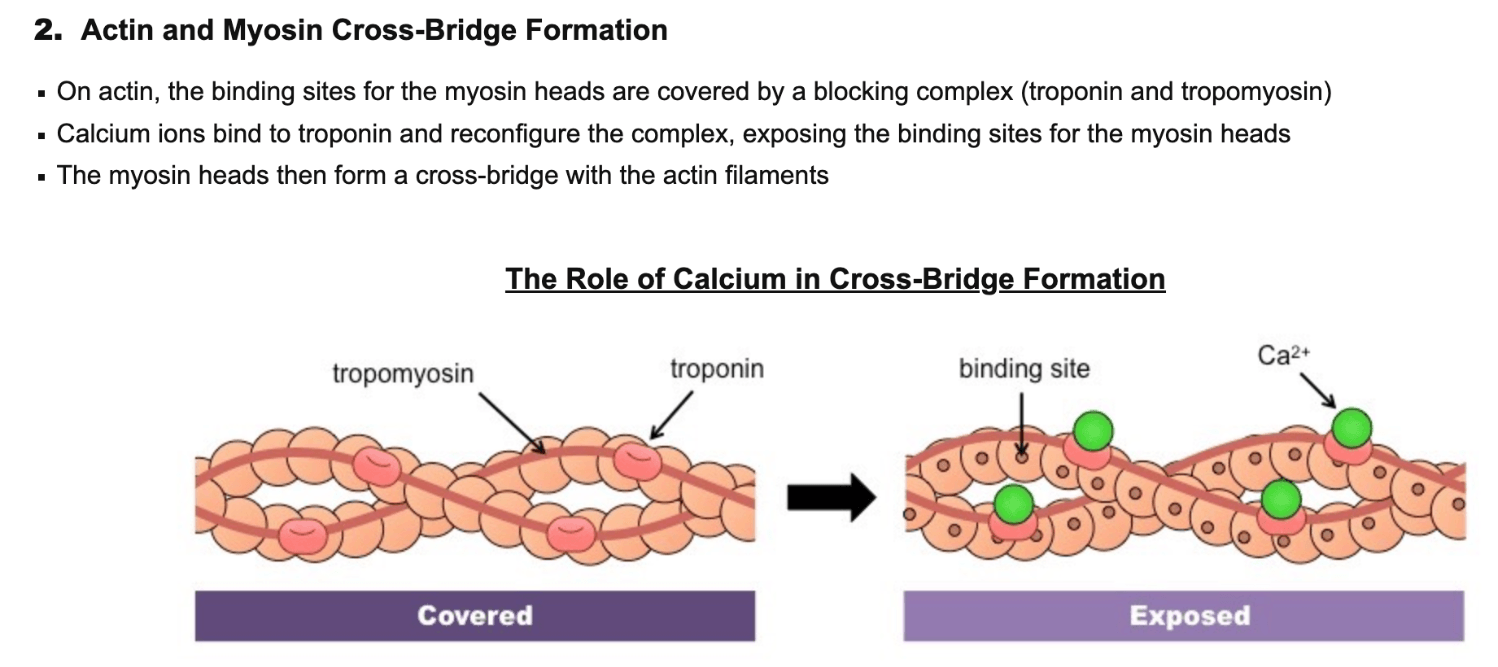
In muscle contraction, calcium ions bind to this structure and reconfigure the complex, exposing the binding sites for the myosin heads
What is troponin?
The flower Daisy compares Nick to
What is a rose?