2 most common cause of (CKD) chronic kidney disease?
1- diabetes
2- hypertension
Name the condition that caused by Overgrowth of yeast on the skin and results in red , itchy , scaly patches often in the groin , armpit, or between the fingers and toes ?
Tinea Versicolor
How to assess Ascites by physical examination?
1- shifting dullness
2- fluid thrill
Which type of microscopy is best suited for visualizing live, unstained bacteria?
a) Bright-field microscopy
b) Dark-field microscopy
c) Phase-contrast microscopy
d) Electron microscopy
Phase-contrast microscopy - This technique provides good contrast for observing unstained bacteria by highlighting differences in light refraction.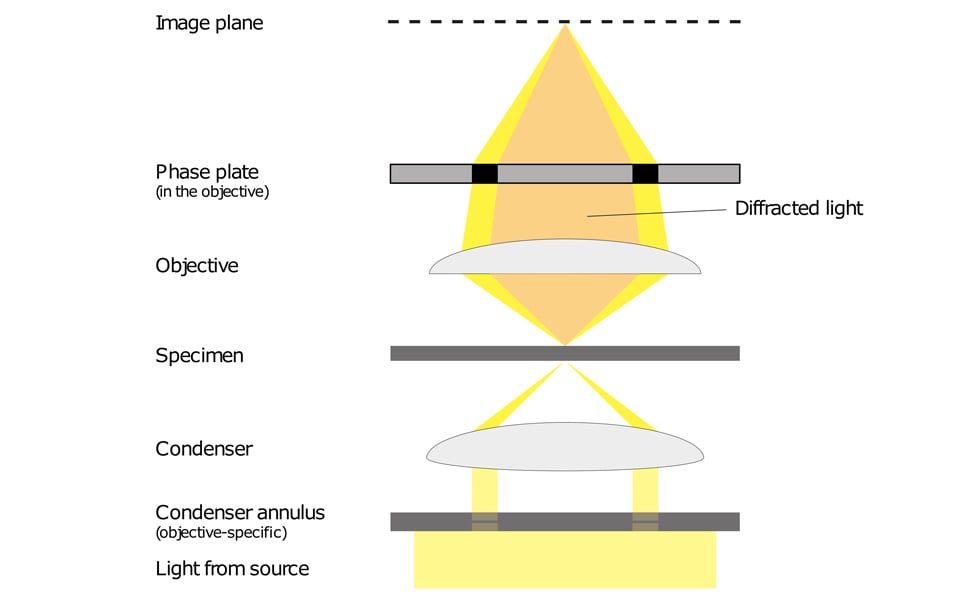
What are three layers of the skin?
The skin's main layers include the epidermis, dermis and in some sources hypodermis
Give 2 causes of collapsing pulse?
1- Aortic regurgitation.
2- hyper-dynamic circulation.
Most common type of skin cancer?
Basal cell carcinoma .
where can you see a positive Murphy’s sign ?
Cholecysitits
Explain the concept of emerging infectious diseases and discuss some factors that contribute to their emergence.
Emerging infectious diseases are new, or previously controlled, infections that appear in a population. Factors contributing to their emergence include:
- Antimicrobial resistance: Microbes develop resistance to existing drugs.
- Changes in human behavior: Globalization, travel, and agricultural practices can increase exposure to new pathogens.
- Animal-human transmission: Zoonotic diseases can jump from animals to humans.
- Climate change: Environmental alterations can influence the spread of pathogens.
What is the name of the largest bone in the human body?
Femur
What is the classic triad of symptoms seen in Behcet’s disease?
1- recurrent oral ulcer
2- genital ulcers
3- uveitis
rare autoimmune disease that causes severe blistering and skin erosions ?
Bullous pemphigoid
What is recommended valve replacement for a pregnant woman ?
Biological valve
What is the mechanism of action of penicillin
It disrupts the bacterial cell wall. - Penicillin prevents the formation of a strong bacterial cell wall, making the bacteria susceptible to bursting.
Name the carpal bones
The proximal row of carpal bones (moving from radial to ulnar) are the scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, and pisiform, while the distal row of carpal bones (also from radial to ulnar) comprises the trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate.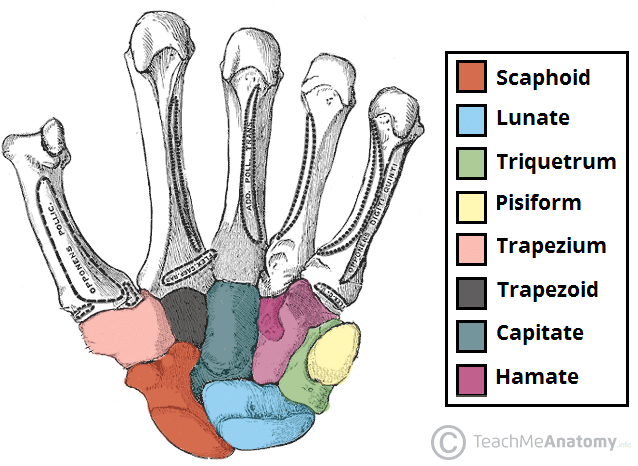
Cause of unilateral pitting lower limb edema?
DVT
what is the dermatological manifestation of insulin resistance?
Acanthosis nigricans
location of Mcburney’s point?
1/3 along line extending from ASIS to the umbilicals
How does the immune system differentiate between "self" and "non-self" molecules?
a) By recognizing specific antigens on the surface of pathogens.
b) Through the action of antibodies produced by B lymphocytes.
c) By the presence of Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) molecules.
d) All of the above are involved.
All of the above are involved. - The immune system uses a combination of self-recognition mechanisms, including antigen recognition, antibodies, and MHC molecules to distinguish between self and non-self.
What are the 12 cranial nerve?
There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves: olfactory (CN I), optic (CN II), oculomotor (CN III), trochlear (CN IV), trigeminal (CN V), abducent (or abducens; CN VI), facial (CN VII), vestibulocochlear (CN VIII), glossopharyngeal (CN IX), vagus (CN X), accessory (CN XI), and hypoglossal (CN XII). 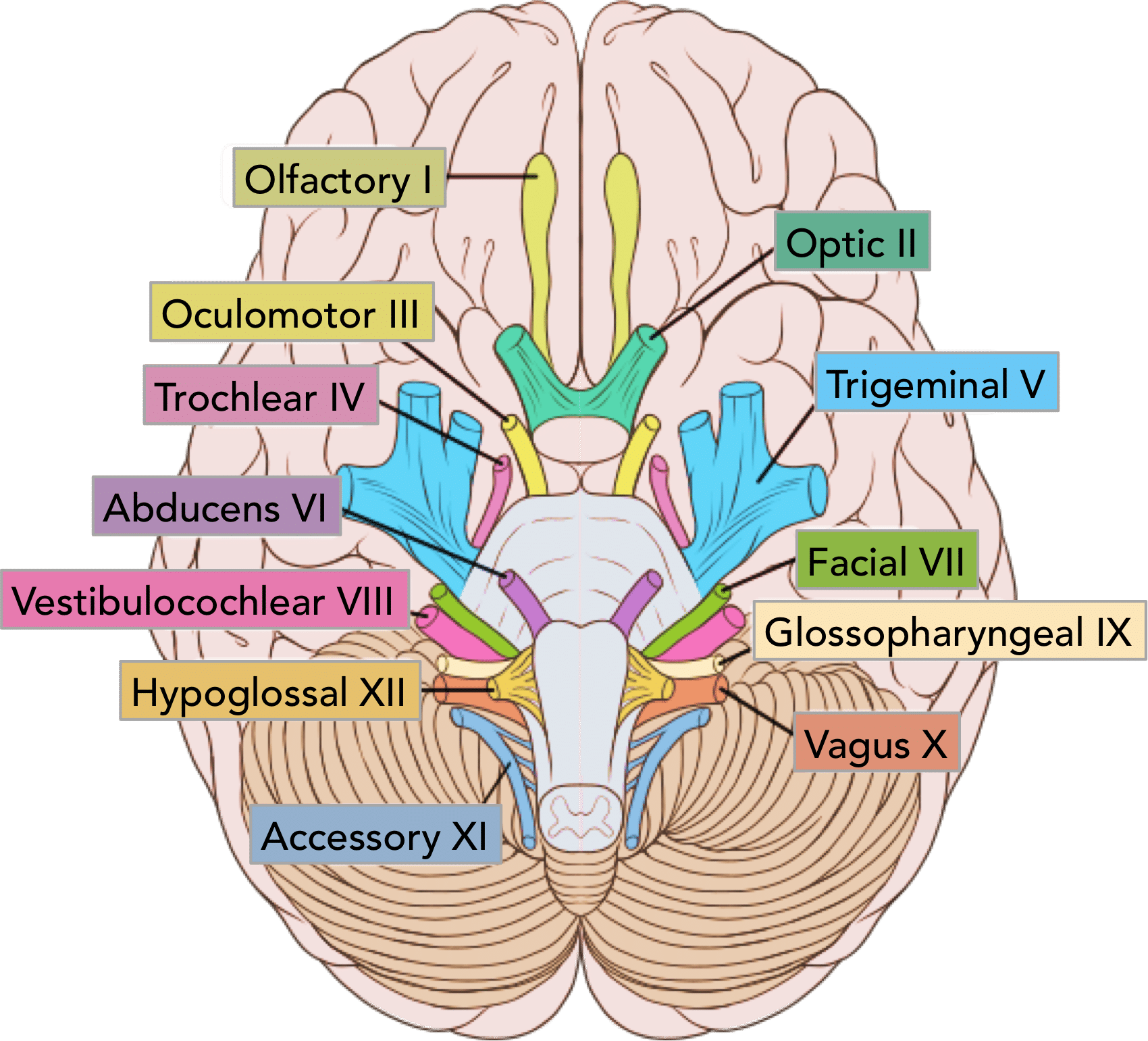
What are the borders of traube’s area during spleen examination?
superior: left sixth rib
Inferior: left costal margin
lateral : left anterior axillary line
name the condition that characterized by red itchy inflamed patches with silvery scales ?
Psoriasis
What is the initial imaging in abdominal pain?
Abdominal X-ray
Compare and contrast the mechanisms of pathogenesis (how they cause disease) employed by bacteria and viruses.
Bacterial pathogenesis mechanisms:
- Attachment and colonization: Bacteria adhere to host cells and tissues.
- Toxins: Bacteria may produce toxins that damage host cells or tissues.
- Invasion: Some bacteria can invade host cells and replicate intracellularly.
- Immune system evasion: Bacteria may have mechanisms to avoid immune detection or destruction.
Viral pathogenesis mechanisms:
* Attachment and entry: Viruses bind to specific receptors on host cells and enter the cell.
* Viral replication: The virus hijacks the host cell machinery to replicate its own genetic material and produce new virus particles.
* Cell lysis: The host cell bursts open, releasing new virus particles that can infect other cells.
* Immunomodulation: Some viruses can suppress or alter the host immune response.
Name the 5 major nerves of the brachial plexus