This mean arterial pressure (MAP) goal is targeted in the ICU to maintain organ perfusion
> 65
This mode of ventilation allows the patient to breathe on their own but will deliver a set tidal volume
Assist Control
This is the dose of IV epinephrine during cardiac arrest
1mg
Fentanyl
ICU patients should receive prophylaxis with SQ Heparin or LMWH/Lovenox for this reason
Prevention of DVT/PE
This is the placement of a 5 lead ECG
White on Right Arm
Black on Left Arm
Green on Right Leg
Red on Left Leg
Brown in the Middle of chest equal to nipple line
(Salt & Pepper, Lettuce & Tomato, Hamburger/Meat in the middle) :)
This vasopressor is first line for hypotension refractory to adequate fluid resuscitation in septic patients
Norepinephrine/ Levophed
The volume of oxygen delivered by the ventilator is known as
tidal volume
CAB is an acronym for
Circulation, Airway, Breathing
This medication is used to treat unstable SVT
Adenosine
This prophylactic therapy should be initiated in ICU
patients who are mechanically ventilated >48 hours
Stress Ulcer Prophylaxis (PPI)
A patient is noted to be in sinus tachycardia. What are possible causes of this disorder?
caffeine
fever
pain
anxiety
hypovolemia
The Surviving Sepsis Campaign recommends at least this amount of IV fluid (mL/kg) be given as a bolus for fluid resuscitation in septic patients
30 mL/kg
This is the amount of oxygen that should be delivered to prevent barotrauma
tidal volume 5-7ml/kg
This is the rate of chest compressions
30:2 or 100-120bpm
Magnesium Sulfate
Insulin should be re-initiated in ICU patients after two BG readings over this value are obtained (mg/dL)
150 mg/dL
What is the treatment for this rhythm if the patient is unstable?
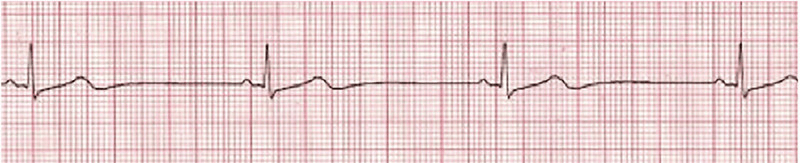
Pace the patient
Antimicrobial agents should ideally be administered within this time frame (hours) after recognition of sepsis
1 hour
This type of noninvasive ventilation (NIV) may be utilized to provide extra support to a patient but requires the patient to breathe on their own
BiPap
This is the depth of chest compression
At least 2 inches
This medication should only be administered AFTER sedation in the ICU and is used for vent synchrony
Paralytics- i.e. Vecuronium, Atracurium, Cisatracurium, Rocuronium, Mivacurium
This sedative is the only agent approved for use in non-intubated ICU patients
Dexmedetomidine/ Precedex
A patient with this rhythm would likely experience what kind of signs/symptoms?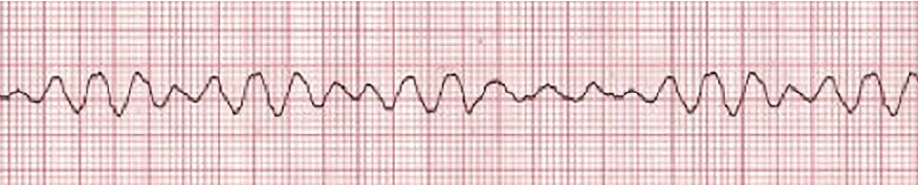
This patient would have no pulse and would be unresponsive.
Sepsis is associated with an increase or decrease in preload and afterload?
decrease in both preload (CVP) and afterload (SVR)
Name two nursing interventions to prevent ventilator associated pneumonia
HOB > 30
oral care at least q4h
suction prn
turn q2h
GI prophylaxis
Name 1 of 2 alternative routes of medication administration if IV access is unavailable
Intraossesous
Endotracheal
This medication may be used to treat heart failure and is a positive inotrope
Digoxin-oral agent
Dobutamine- IV agent
Parenteral nutrition should only be considered in ICU patients who cannot be fed by the enteral route after this many days
7 days
The nurse understands increased risks associated with a client being in the following rhythm. What signs and symptoms would alert the nurse to potential complications of this rhythm?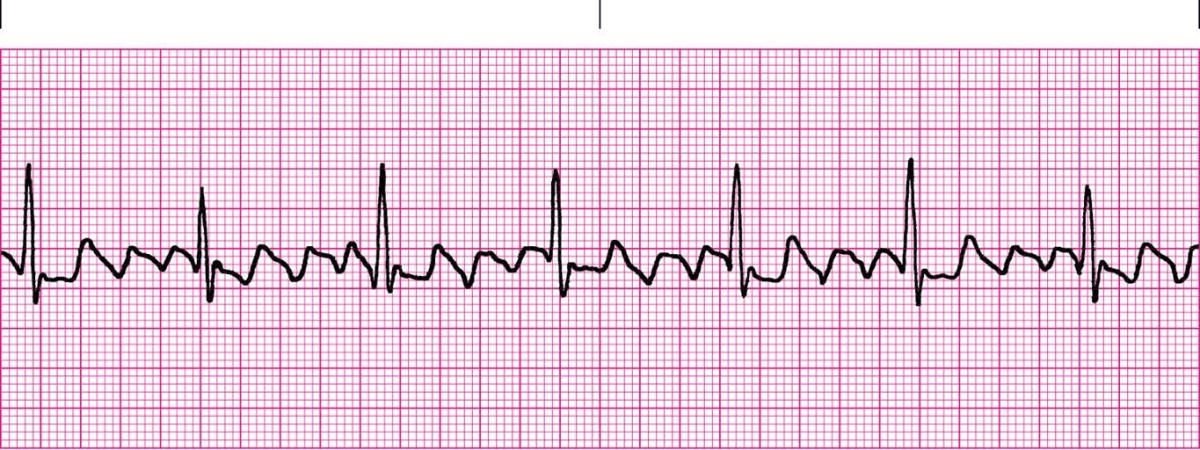
increased risk for stroke--> unilateral weakness, slurred speech, decreased responsiveness, etc
increased risk for PE--> tachycardia, CP, SOB
A nurse is caring for a client with sepsis and notes a CVP of 20. What signs and symptoms would the nurse expect to see?
CVP is too high--> we want CVP higher than normal, but this high could indicate we have overloaded the patient. volume overload s/s? SOB, crackles, edema
A patient is agitated and breathing over the ventilator. this would cause what type of alarm?
high pressure alarm
A patient is in unstable ventricular tachycardia. What treatment is associated with improved outcomes and should be initiated as soon as possible?
Synchronized Cardioversion
The nurse should be aware that this vasopressor can worsen tachycardia
Epinephrine
This is used for hypothermia in the ICU
Bair Huggar/ warmer
A patient is noted to be in asystole and CPR is initiated. What is the initial drug of choice for a patient in this rhythm?
Epinephrine
Most common antibiotics given for septic patients
Vancomycin and Zosyn
A nurse is caring for a patient on mechanical ventilation and notes a low pressure alarm. What should the nurse do first?
Check the connections from the vent to the patient
This is often given during code situations to reverse acidosis but is not part of the ACLS algorithm
sodium bicarbonate
This vasopressor is a known vesicant and should be administered through a central line
Norepinephrine/ Levophed
A patient in the ICU is confused and pulling at lines. This may be caused by:
ICU Delirium
Identify the following rhythm: 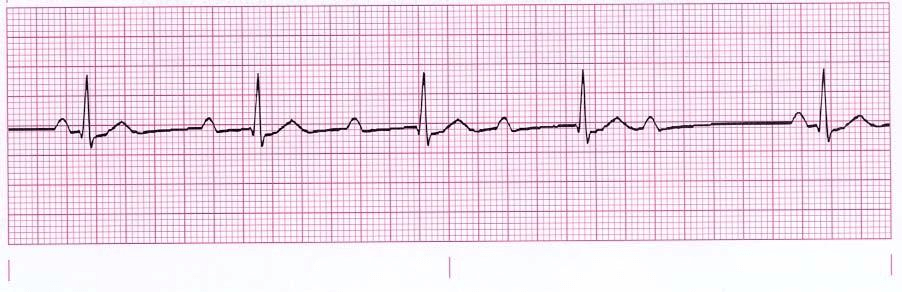
Second degree heart block type I/Wenckebach/Mobitz I