The area of lymph nodes where B cells are activated.
Lymph node follicle
The pathogen associated molecular pattern (PAMP) associated with gram-negative bacteria.
LPS
The cytokines/interleukins that cause fever.
IL-1,IL-6 and TNF-alpha
The name of the process by which neutrophils release DNA to trap and kill extracellular pathogens.
Neutrophil Extracellular trap (NET).
A chronic, multi-organ autoimmune disease in which the body creates antibodies against its own healthy tissues.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.
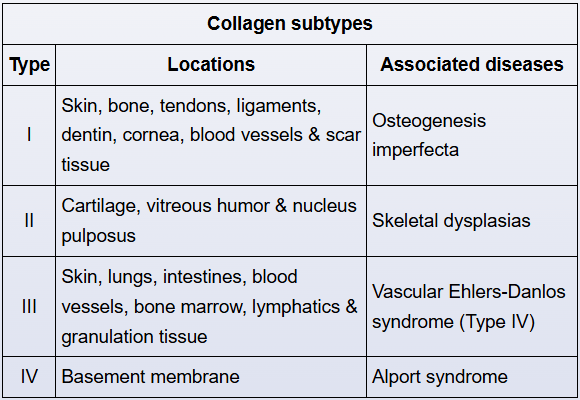
The type of collagen found in bones, ligaments, and tendons.
Collagen Type 1
The type of bacteria that cannot be destroyed by the membrane attack complex (MAC).
Gram-positive bacteria
The cytokine secreted by Th1 cells that activates macrophages.
IFN-gamma
The activated form of B cells that produces antibodies.
Plasma cells or plasmacytes or CD138+ cells.
A chronic inflammatory disorder resulting from stimulation of sebaceous glands by circulating androgens, dysbiosis of the pilosebaceous follicle microbiome, and cellular immune responses.
Acne Vulgaris (common acne).
The malignancy associated with "punched out, lytic lesions" in bone on x-ray imaging.
Multiple myeloma.
The bacteria, that if left untreated by antibiotics, may lead to inflammation of heart, joints, skin, and nervous system.
Group A Strep or S. pyogenes.
The primary interleukin(s) responsible for T cell maturation in the thymus.
IL-2 and IL-7 (and notch)
The primary immune cells responsible for destruction of alveolar space in centriacinar emphysema.
Neutrophils and macrophages (in response to inflammation and damage caused by components in cigarette smoke).
A group of malignant mesenchymal neoplasias that typically affect people ages 10-20 that arise from fusion of the EWSR1 and FLI1 gene leading to aberrant cell proliferation.
Ewing Sarcoma.
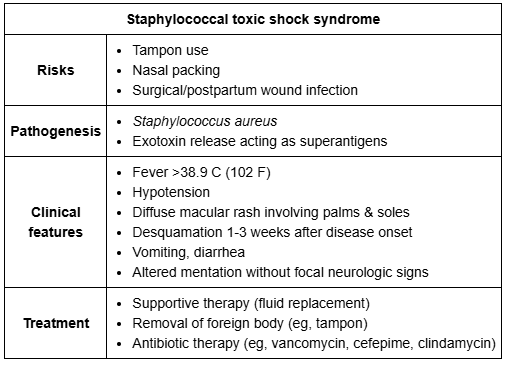
The syndrome caused by toxin-producing streptococci or S. aureus resulting in overactivation of Th cells and a cytokine storm.
Toxic Shock Synde (TSS).
The primary interleukin(s) responsible for B cell activation and immunoglobulin class switching to IgE.
IL-4 and IL-13.
The cells that express CD68.
Monocytes, macrophages, or tissue macrophages (ex. microglia and Kupffer cells).
The condition characterized by short stature, webbed neck, nail dysplasia, premature ovarian failure, and lymphatic network dysgenesis resulting in congenital lymphedema.
Turner's Syndrome. (45X)
The syndrome associated with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), deep fibromatosis (desmoid tumor), and osteoma.
Gardner's Syndrome.
The condition caused by allergic hypersensitivity to Aspergillus fumigatus that most commonly manifests as bronchiectasis on imaging, history of asthma, and IgE/IgA antibodies against Aspergillus.
ABPA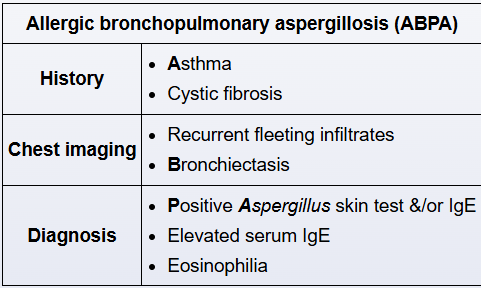
The cytokine released from Th cells that stimulates proliferation and differentiation of dendritic cells (DCs) and monocytes.
Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor (GM-CSF)
The primary leukocyte responsible for death of cancer cells in response to small monoclonal antibody therapy.
Natural Killer Cells (NK cell).
Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) occurs when an antibody binds to the surface of a cell, then NK cells bind the Fc region using CD16, then NK cells release perforin and granzymes to kill the target cell.
A severe form of immunodeficiency caused by mutations in the IL2RG gene leading to improper leukocyte function.
X-linked SCID.