(Hypothermia)
What is a diabetic emergency?
A chronic condition characterized by the body's inability to process sugar creating blood sugar levels that are too high (hyperglycaemic) or too low (hypoglycaemic).
What is a seizure?
A seizure is an episode of abnormal brain function caused by irregular electrical activity. A seizure may cause uncontrollable muscle movement.
What are the three types of heat emergencies?
1. Heat Cramps (may or may not be present)
2. Heat Exhaustion
3. Heat Stroke
How do you treat frostbite?
- Remove anything that may restrict blood flow to the affected area
- Thaw the area only if you are sure it will not freeze again. Use warm (not hot) water or use body heat.
- Protect skin with loose, dry dressings. Place gauze between the fingers or toes if they are affected. Leave any blisters intact.
-If possible, elevate any thawed extremeities above the level of the heart.
- Rehydrate the person by providing plenty of fluids (no alcohol!)
- Encourage the person to seek follow up medical attention
What are some of the signs and/or symptoms of a diabetic emergency?
- changes in the level of responsiveness
- changes in behaviour, such as confusion or aggression
- rapid breathing
- cool, pale, sweaty skin, looking ill
- appearance of intoxication (slurred speech, difficuly walking, etc . . .)
- seizures
What should you do when performing first aid for someone having a seizure?
Protect them from harm by moving objects that could cause injury and place something soft under their head.
True or False - If the person is experiencing a heat emergency, you can provide a cool drink.
True. As long as the person is alert, providing a cool drink can help cool their body down. They should take small sips.
**Bonus Points** - What is the best cool drink for them to have?
How do you prevent, recognize and treat trench foot?
1. Get the person’s foot warm, clean, and dry. Handle the area gently and warm it slowly.
2. Elevate the injured foot or feet.
3. Continue to monitor the person and the affected area. If a person’s feet have redness, red streaks, blisters, or cracks that do not go away after basic foot care, advise them to contact their care provider.
Under what circumstances should you give insulin to someone in a diabetic emergency?
Never! This includes glucagon. Only a medical professional can diagnose the cause of the emergency and be certain that insulin is the proper treatment.
True or False - You should put something in a person’s mouth when they are having a seizure.
False! If the person suffers an injury, assess once the seizure is over and call EMS/911 if necessary.
What are the signs and/or symptoms of (life threatening) heat stroke?
- Dry, hot skin (temperature over 40 degrees Celsius)
- Seizures
- Unresponsiveness
- Severe headache
- Changes in behaviour, such as irritableness, aggressiveness, or bizarre behaviour
- Rapid, shallow breathing
How can you tell if someone is cold stressed versus hypothermic?
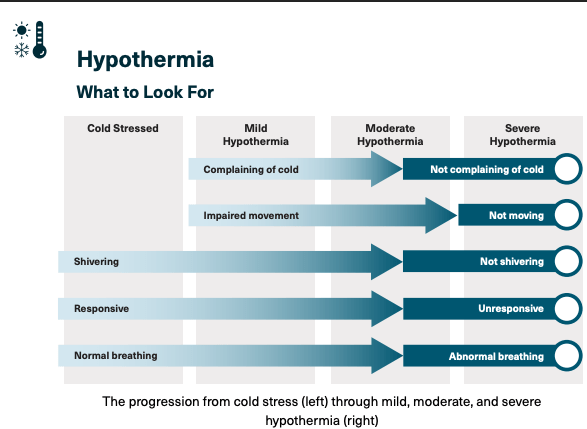
What can you do for someone who is experiencing a diabetic emergency?
If the person is able to do so safely, have them swallow sugar (such as oral glucose tablets, chewable candy, fruit juice, fruit strips, and milk).
What are the signs and/or symptoms of a seizure?
- may experience an aura (a unusual sensation or feeling) before the onset of the seizure
- hallucinations
- uncontrollable muscle movement
- eyes rolling upward into the head
- drool or foaming at the mouth
- uncontrolled repetitive motions (partial seizures)
**Note - Not all seizures involve convulsions. **
If the person is experiencing heat exhaustion, how can we actively cool them down?
Remove the person from the heat and loosen tight clothing.
DO NOT DRY THE SKIN!!!
Pour water on the person’s clothing and/or on towels or cloths and place them on the person’s chest, then fan the person.
Apply ice or cold packs to the person’s armpits and chest.
How do you treat cold stress or mild hypothermia?
Cold Stress = 1. Reduce heat loss (e.g., add dry clothing). 2. Give the person a high-calorie food or drink. 3. Increase heat production (e.g., have the person exercise).
Mild Hypothermia = 1. Handle the person gently and keep them horizontal (no standing or walking for at least 30 minutes). 2. Insulate the person or apply a vapour barrier. 3. Apply heat to the person’s upper trunk. 4. Give the person a high-calorie food or drink. 5. Monitor the person until their symptoms improve (for at least 30 minutes). 6. Call EMS/9-1-1 if there is no improvement.
What do we do if the person's condition does not improve or worsens after you have given them sugar?
If the person's condition does not improve within 10 minutes after ingesting sugar, call EMS/911. Administer more sugar if it is safe to do so (ie: they are responsive and able to swallow).
**Bonus Points** - What do you do if they had sugar and their condition got better?
When should you call 911 for someone having a seizure?
For any infant/child, diabetic, pregnant, seizure + injury, multiple seizures, seizures that last more than a few minutes, failure to regain responsiveness after a seizure, if the person asks you to, if the treatment plan directs you to activate EMS, if it is their first time having a seizure or you do not know the person and there is no treatment plan.
If the person is experiencing heat stroke, how can we aggressively cool them down?
Remove the person from the heat and loosen tight clothing.
DO NOT DRY THE SKIN!!!
- Immerse the person’s forearms in cool water.
- Pour water on the person’s clothing and/or on towels or cloths and place them on the person’s chest, then fan the person.
- Apply ice or cold packs to the person’s armpits and chest.
How do you treat moderate or severe hypothermia?
Moderate = Handle the person gently and keep them horizontal (no standing or walking). 2. Do not give the person a drink or food. 3. Insulate the person or apply a vapour barrier. 4. Apply heat to the person’s upper trunk.
Severe = 1. If the person has no obvious vital signs, check for breathing for 60 second. If the person IS breathing, follow the steps for moderate hypothermia. If the person is NOT breathing, start CPR.
** Always call EMS/9-1-1 for moderate/severe hypothermia! **