What type of contrast would be most appropriate for a CT vascular study?
- Gadolinium
- Iodine
- Barium
- Paramagnetic Iron Oxide
Iodine
When would a larger x-ray tube focal spot be most desired?
- A low kVp is needed.
- A sharp penumbra is needed.
- High mAs is needed
- An iodine based contrast agent is used.
- A bucky is not available.
Higher mAs
Larger focal spots help manage the heat generated by high mAs imaging but they do so at the expense of a slightly larger penumbra.
What is this artifact?
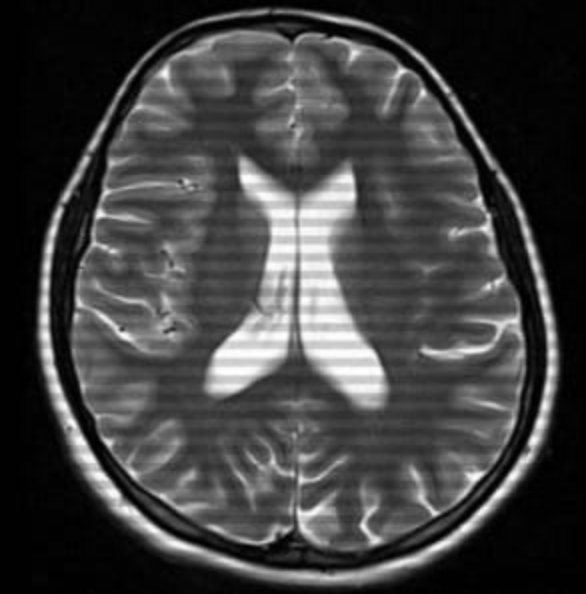
truncation of the Fourier series
What MR pulse sequence do you use for motion management?
Propeller
What are the differences between high f and low f ultrasound waves? What is the typical frequency of ultrasound waves?
high f: better resolution
low f: travel further
1-20Hz
Which of the following is commonly used as IV contrast in diagnostic radiography?
- Gadolinium
- Barium
- Iodine
- Lead
Iodine
Which of the following will decrease CT image noise? (Select all that apply)
- Increase mAs
- Decrease pitch
- Use a contrast agent such as Barium
- Decrease kVp
Increase mAs and Decrease Pitch
Noise will decrease with increased kVp, increased mAs, and decreased pitch. Some Kernels, such as soft tissue, may also reduce perceived image noise by blurring sharp edges.
What is this artifact and how do you reduce it?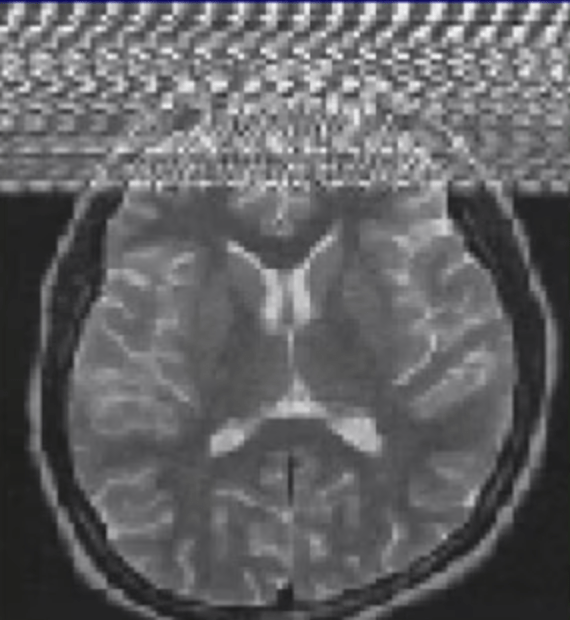
Zipper artifact: from RF feedthrough
Complete RF shielding (door closed and patient equipment far away)
What MRI sequence is most appropriate in reducing intensity of fat in a throasic scan?
STIR : short T1 inversion recovery
How does the far field diameter and near field length change when you increase the transducer diameter? give proportionalities
Far field diameter decreases prop. to sin-1(1/r)
Near field length increases prop. to r^2
What MRI contrast agent is most likely to be used in imaging liver metastasis?
- Barium
- Iodine
- Gadolinium
- Paramagnetic Iron Oxide
Paramagnetic Iron Oxide
Which of the following would not improve soft tissue contrast?
- Increasing the number of information carriers
- Reducing scan kVp
- Reducing scatter
- Increasing voxel size
Increasing the number of information carriers
Increasing the number of information carriers will improve SNR but not contrast.
What is this artifact and how do you fix it?
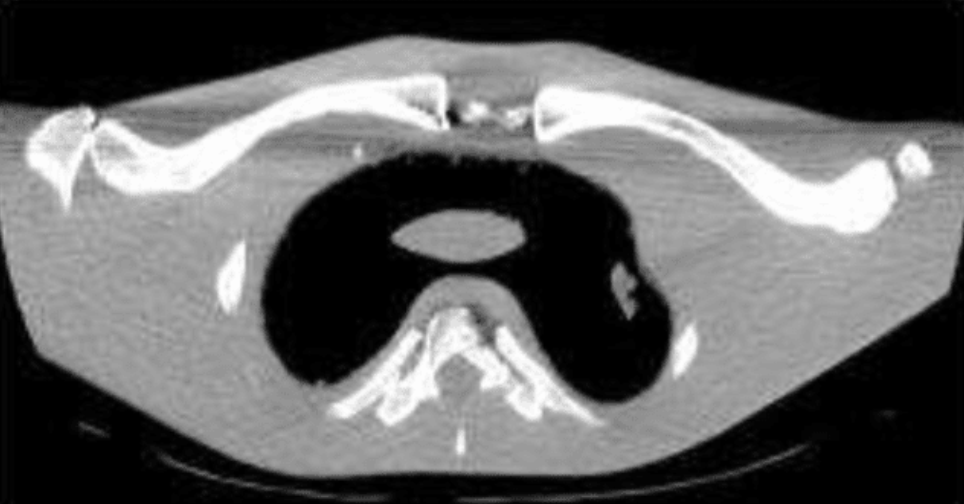
Photon Starvation: an insufficient number of photons reaching the detector
increasing mAs
What weighted MRI is this?
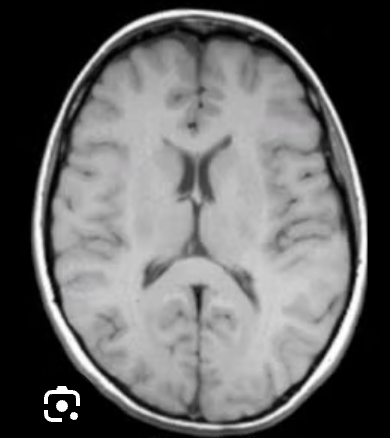
T1
Difference between T1 and T2 (i.e. Longitudinal vs Transverse, decay or regrow to what percent?)
T1: longitudinal relaxation, regrow to 63%
T2: transverse relaxation, decay to 27%
What type of contrast would be most appropriate for a CT gastric study?
- Iodine
- Barium
- Gadolinium
- Paramagnetic Iron Oxide
Barium
Regarding CT imaging, which combination of effects will decrease the dose to the patient?
- Increasing mA by 20% and increasing pitch by 20%
- Changing from axial to helical scanning
- Increasing mAs by 10% while decreasing pitch by 40%
- Decreasing kVp, leaving mA and pitch unchanged
Decreasing kVp, leaving mA and pitch unchanged
- Increasing mAs would increase dose.
- Decreasing pitch would increase dose.
- Increasing dose by 20% while increasing pitch by 20% would offset in effect and give the same dose.
- Axial vs helical scanning does not impact patient dose.
Describe these ultrasound artifacts:
Twinkling
Reverberation
Mirroring
Twinkling: The presence of small strongly reflective objects within the Doppler study.
Reverberation: Repeated reflections between two closely spaced objects.
Mirroring: Multiple beam reflections between the object and the highly reflective surface.
What weighted MRI is this?
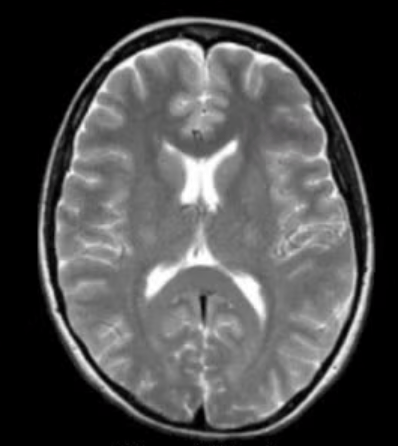
T2
What are the values of these constants?
1. Earth Magnetic Field
2. Attenuation Coeff. through water
3. Speed of sound in water
4. Rose Criterea
1. 6.5e-5 T
2. 0.5 dB/MHx*s
3. 1540 m/s
4. 5
What magnetic property allows Gadolinium contrast to work?
- Ferromagnetism
- Paramagnetism
- Radiomagnetism
- Diamagnetism
Paramagnetism
What is the spatial resolution of
1. Mammography a. 0.01mm b. 0.1mm c. 0.5mm
2. CT a. 0.3mm b. 0.5mm c. 1mm
3. MRI a. 0.5mm b. 1mm c. 2mm
4. PET. a. 3mm b. 4mm c. 5mm
1. b
2. a
3. b
4. c
What is this artifact and how do you fix it?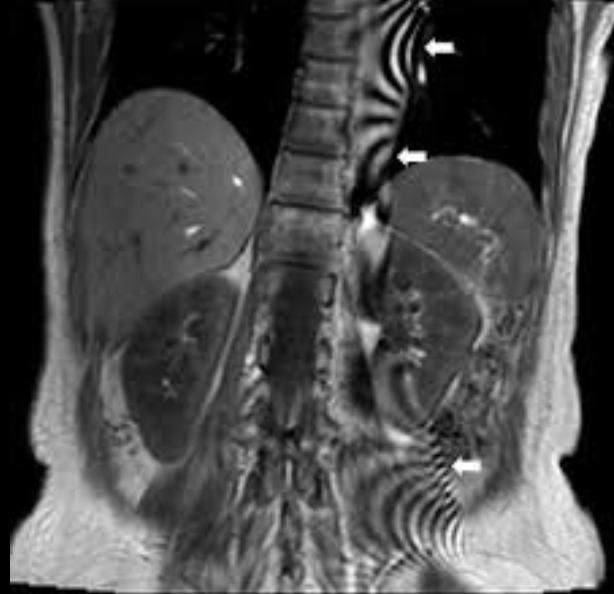
Moiré Fringes Artifact: caused by Non-uniformity of magnetic field.
Improve field uniformity by shimming.
What weighted MRI is this?
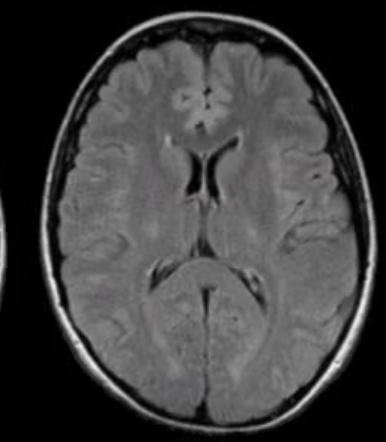
T2 flair
What are the equations/differences between CTDI, CTDI100, CTDIvol, CTDIW, DLP, SSDE
CTDI: integral dose / beam width [1/NT int(D(z)dz)]
CTDI100: integral dose/ beam width over 100mm axial scan [1/NT int{-50->50}(D(z)dz)]
CTDIW: Integral dose through phantom because attenuation changes [1/3CTDI100,cent + 2/3CTDI100,edge]
CTDIvol: normalize dose from helical scan using pitch [1/pitch CTDIW]
DLP: CTDIvol only over scan length
SSDE: size specific dose estimate [fsize* CTDIvol where fsize = effective diameter sqrt(AP * LAT)]