This eye condition is often caused by multiple sclerosis, and presents as painless monocular vision loss.
Optic Neuritis
What is the age at which the USPSTF recommends starting to screen for diabetes in those at risk?
>35 yo
What is the preferred revascularization route in patients with multivessel coronary artery disease.
CABG > PCI
CABG, especially with use of arterial (internal mammary artery) conduits, is indicated in patients with multivessel CAD and no contraindications, because it is associated with enhanced survival compared with medical therapy alone.
An additional indication for CABG > PCI would be severe proximal left coronary artery disease.
What is the screening regimen for lipids?
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends universal lipid screening in adults aged 40 to 75 years to assess for dyslipidemia
These 2 chiefs were in the same residency house.
Justin and Laith
Treat this traumatic condition
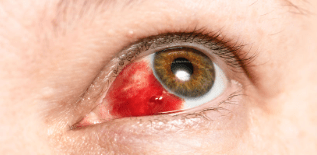
Do nothing. It will resolve over time.
What is best lab to obtain to evaluate for Vit D deficiency?
25-hydroxyvitamin D
What is the most common cause of HFrEF and what is the most common cause of HFpEF?
HFrEF: Ischemia/CAD
HFpEF: Hypertension
How long after initiating statin therapy should you re-check lipids?
4-12 weeks
What are each chiefs' post residency fellowship goals/jobs
Brian: Hospitalist
Justin: PCCM
Kevin: Hem/Onc
Laith: Cards
List 4 ocular emergencies requiring emergent ophthalmology consultation.
Ruptured Globe
Retinal Detachment
Central Retinal Artery Occlusion or Central Retinal Vein Occlusion
Acute Angle Closure Glaucoma
Orbital Cellulitis
Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus
Acute Retinal Necrosis
Corneal Ulcers
Acromegaly is caused by the excessive production of what hormone?
Bonus: Tell me the initial diagnostic test
Growth Hormone
Bonus: Insulin Like Growth Factor-1
Identify this rhythm. Bonus: Tell me its origin location.
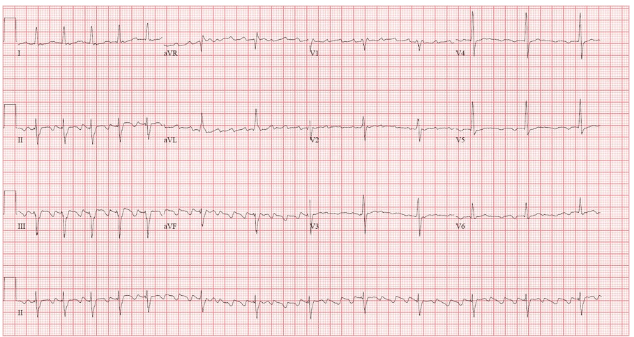
Atrial Flutter
Bonus: Cavotricuspid Isthmus
What lab(s) should you get prior to a patient starting a statin.
LFTs
Measurement of aminotransferase levels should not be repeated during statin therapy in the absence of symptoms of liver injury.
Bonus: What Schoool?
Brian, Kevin, Laith
Bonus: TCOM
What is the largest modifiable risk factor for age-related macular degeneration?
Smoking
Pituitary tumors can cause what visual field disturbance?
Bonus: tell me the structure that becomes compromised causing the visual field disturbance
Bitemporal hemianopsia
Bonus: via compression of the optic chiasm
Beside viral or idiopathic, name 5 causes of pericarditis.
A 52-year-old woman is evaluated for hypertension. Periorbital findings are shown. What is the skin finding?

Xanthomas/Xanthelesma are characteristic skin conditions associated with primary or secondary hyperlipidemias. Xanthomas are yellow or yellow-brown, orange, or reddish papules, plaques, or nodules.
In total, how many kids do all of the chiefs have?
3 (Justin has 2, Brian has 1)
44-year-old woman is evaluated for redness, tearing, and irritation of the right eye that began 1 day ago. She reports no eye pain, photophobia, or change in vision. Her left eye is uninvolved. Visual acuity is 20/20 in both eyes. Pupils are equally round and reactive to light and accommodation.
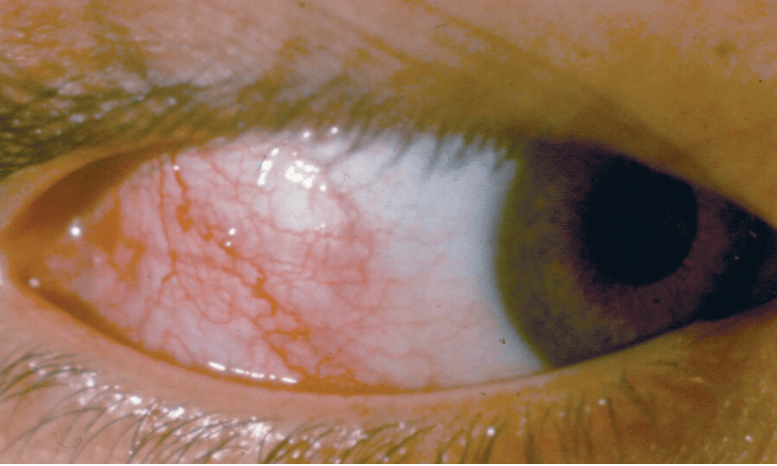
The classic presentation of episcleritis is an abrupt onset of unilateral eye redness due to dilated episcleral blood vessels, irritation, and tearing, with no pain, photophobia, or change in vision.
The cardinal sign of scleritis is edema of the sclera often associated with an underlying violaceous discoloration of the sclera and intense dilation of the episcleral blood vessels, accounting for the red eye. In addition, you can see a ciliary flush. Pain, photophobia, and vision changes are typically absent.
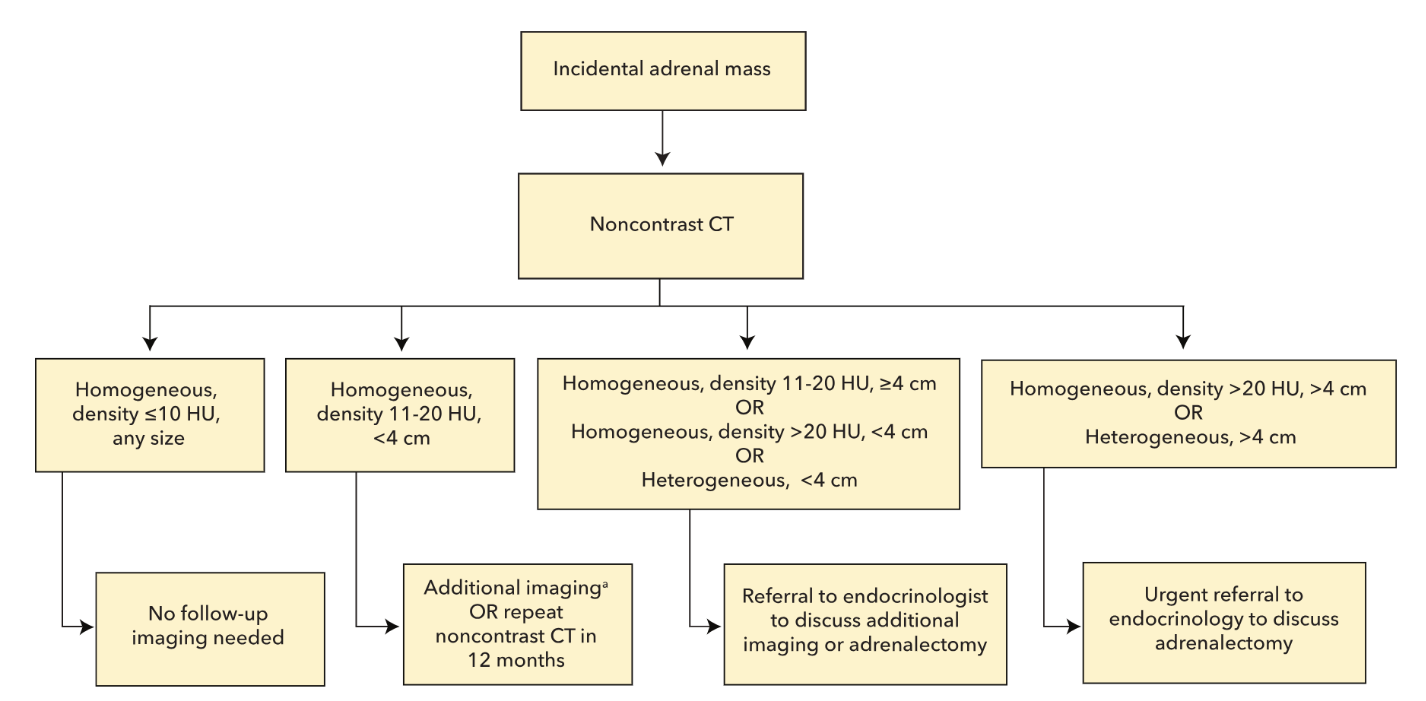
How many Hounsfield units on CT is highly concerning for a pheochromocytoma?
>20
What murmur is the most common postoperative sequela of tetralogy of Fallot repair?
Pulmonary regurgitation
Severe pulmonary regurgitation causes a diastolic murmur heard at the left sternal border that increases in intensity with inspiration, a parasternal lift, and a soft systolic pulmonary outflow murmur.
A 58-year-old man is evaluated at a follow-up appointment. He is feeling well and has no symptoms. Medical history is significant for hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. He is also receiving maximum-dose therapy with atorvastatin and ezetimibe. His baseline LDL cholesterol level before starting atorvastatin and ezetimibe was 220 mg/dL.
Repeat Labs: HDL cholesterol 35, LDL cholesterol 140, Total cholesterol 190, Triglycerides 100.
What is your management of his hyperlipidemia?
Initiation of a PCSK9 Inhibitor
The addition of a proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) monoclonal antibody for primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease can be considered in higher-risk patients aged 40 to 75 years with a baseline LDL cholesterol level of 190 mg/dL (4.92 mmol/L) or higher and who do not achieve a 50% reduction in LDL or an LDL cholesterol level of less than 100 mg/dL (2.59 mmol/L) while receiving maximally tolerated statin and ezetimibe therapy.
These 2 chiefs went to high school, college, and medical school together.
Bonus: Name the 3 schools
Brian and Laith
Belton High School, Texas A&M, TCOM