A cost that is different between two decision alternatives.
The formula for contribution margin is:
Revenue - Variable Costs
Another name for make or buy situations is:
Outsourcing
Costs allocated to different business lines and remain if any line is dropped.
What is the contribution margin per unit?
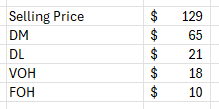
$25 per unit (Sales price minus variable costs)
$129 -$65 -$21 -$18
Costs that do not change regardless of the decision made.
What are irrelevant costs
If a company has excess capacity, this number is used to analyze profitability.
What is contribution margin
Fixed costs that are relevant in a make or buy situation.
What are unavoidable fixed costs
Contribution Margin - Direct Fixed Costs
What is Segment Margin
When choosing a course to register for, which of the following is an irrelevant factor:
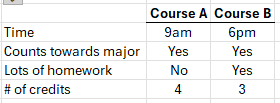
Counts towards major (same regardless of decision)
Costs already incurred and cannot be changed by any decision.
What are sunk costs
What is a qualitative factor of accepting a special order at a loss of profit?
Charitable cause
Relationship building
New customer potential (unplanned advertising)
Being able to use the vacant space to generate income in a make or buy situation
What is opportunity cost
Type of fixed cost tied to a specific line or product
What are direct fixed costs
Which of the following is a sunk cost when deciding on dinner?
Cost of menu items at restarurant of choice
Expected tip
Cost of breakfast earlier today
Gas to get to restaurant
Cost of breakfast - already occurred, cannot be changed.
A non-financial factor in decision making.
What is qualitative
While operating at excess capacity, a special order of 50 units @ $12 each is requested. Normal selling price is $18 with DM of $4, DL of $2, VOH of $3 and FOH of $4.
What amount of profit or loss will be recognized per unit?
$3 profit
$12 - $4 - $2 - $3 = $3 per unit
What is a qualitative consideration of outsourcing?
Quality
Reliability
Reputation
What will happen to Total Operating Income if product A is dropped?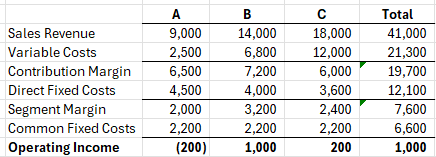
Profit will decrease by $2,000 (segment margin)
Describe the difference between excess capacity and full capacity.
Full Capacity - at production limit given existing resources, in order to produce more, additional cost may be incurred.
Describe an opportunity cost
Forgone benefit of choosing one thing over another.
Lost opportunity
While operating at full capacity, products are sold at $25 with $15 of variable cost. A special order of 100 units at $20 would have what affect on total profit?
Decrease by $500
($25-$20)*100 = $500
Opportunity to purchase 10,000 units @ $10 each
DM = $3
DL = $4
VOH = $2
FOH = $3 (40% avoidable)
Make or Buy? Change in profit?
Buy
Cost to Make = $12
Cost to Buy = $10 + 1.80 = $11.80
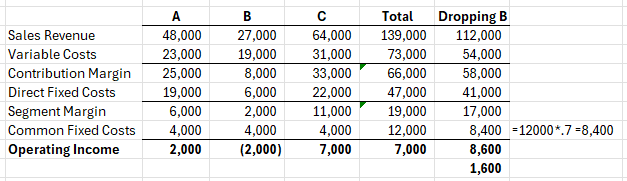
Assuming Common Fixed Costs can be reduced by 30% if product B is dropped, should product b be dropped? What is the affect on profit if product B is dropped?
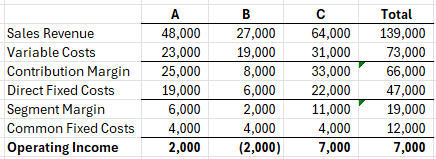
Yes, Increase by $1,600.
Phil's paint is considering adding scents to their gallons of paint, based on financial considerations, should they and what is the change in profit?
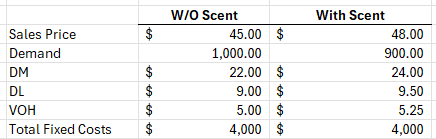
No,
CM of before is $9 per unit x 1,000 units = $9,000
CM of after is $9.25 per unit x 900 units = $8,325
Fixed costs did not change