Acute inflammation of the lungs in which the alveoli and bronchi become plugged with thick fluid.
Causes productive cough, fever, tachypnea, pleuritic chest pain, dyspnea, and systemic malaise, myalgias, and anorexia.
What is pneumonia?
Distinguishing symptoms: fever, tachypnea, and dyspnea.
Infections can be acquired in the community (CAP), the hospital (HAP), or ventilator associated (VAP).
Can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or non-infectious irritants like chemicals, smoke, aspirating food/water/vomit.
Can lead to sepsis and is a major cause of death.
Patho: inflammation leads to migration of WBCs, capillary leak, and accumulation of edema/exudates. Fluid collects around alveolar resulting in impaired gas exchange.
Treatment depends on suspected etiology, symptoms should show improvement after drug therapy started.
Hand washing for 60 seconds and coughing/sneezing into sleeve.
What is patient education for preventing spread of respiratory diseases?
Recommended vaccination annually for this acute viral infection that causes severe muscle aches, fever, chills, fatigue, sore throat, and rhinorrhea.
What is seasonal influenza?
The majority of upper respiratory tract infections are caused by these pathogens; the infections are self-limited and do not require antibiotics.
What are respiratory viruses?
This includes common colds, sinus infections, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, epiglottitis, and laryngitis.
This condition is commonly diagnosed by x-ray as seen below.
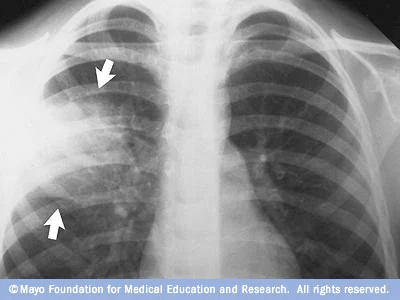
What is pneumonia?
Acute inflammation of the bronchi, most commonly caused by infection and presenting with productive cough, fatigue, and wheezing.
What is acute bronchitis?
There are two types of this vaccine and both are recommended for patients over 65 years old, to be given a year apart.
What is the pneumonia vaccine?
PCV13 and PPSV23
A family of viruses that typically cause the "common cold".
What is coronavirus or rhinovirus?
Inflammation and swelling of the nasal mucosa that can be caused by infection or allergies.
What is rhinitis?
This class of inhaled medications can be used in pneumonia to treat dyspnea and wheezing.
What are bronchodilators?
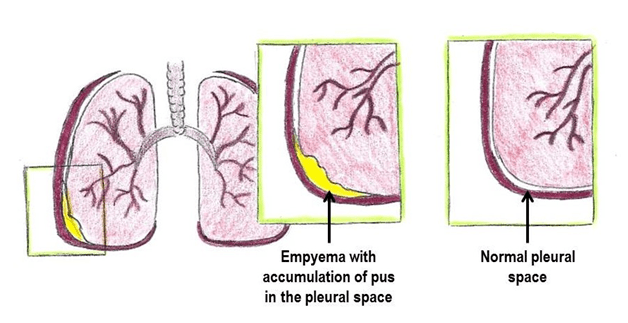
A collection of pus in the space between the lung and the inner surface of the chest wall (pleural space).
What is empyema?
Often requires a chest tube for management and culture & sensitivity for treatment.
Known as “The Lady With the Lamp,” she was a British nurse, social reformer and statistician best known as the founder of modern nursing.
Who is Florence Nightingale?

An infection that is actively spreading and out of control versus a pandemic, which is when an infection affects a large geographic location.
What is an epidemic?
Inflammation or infection of the pharynx, commonly caused by streptococcal bacteria (the medical term for strep throat).
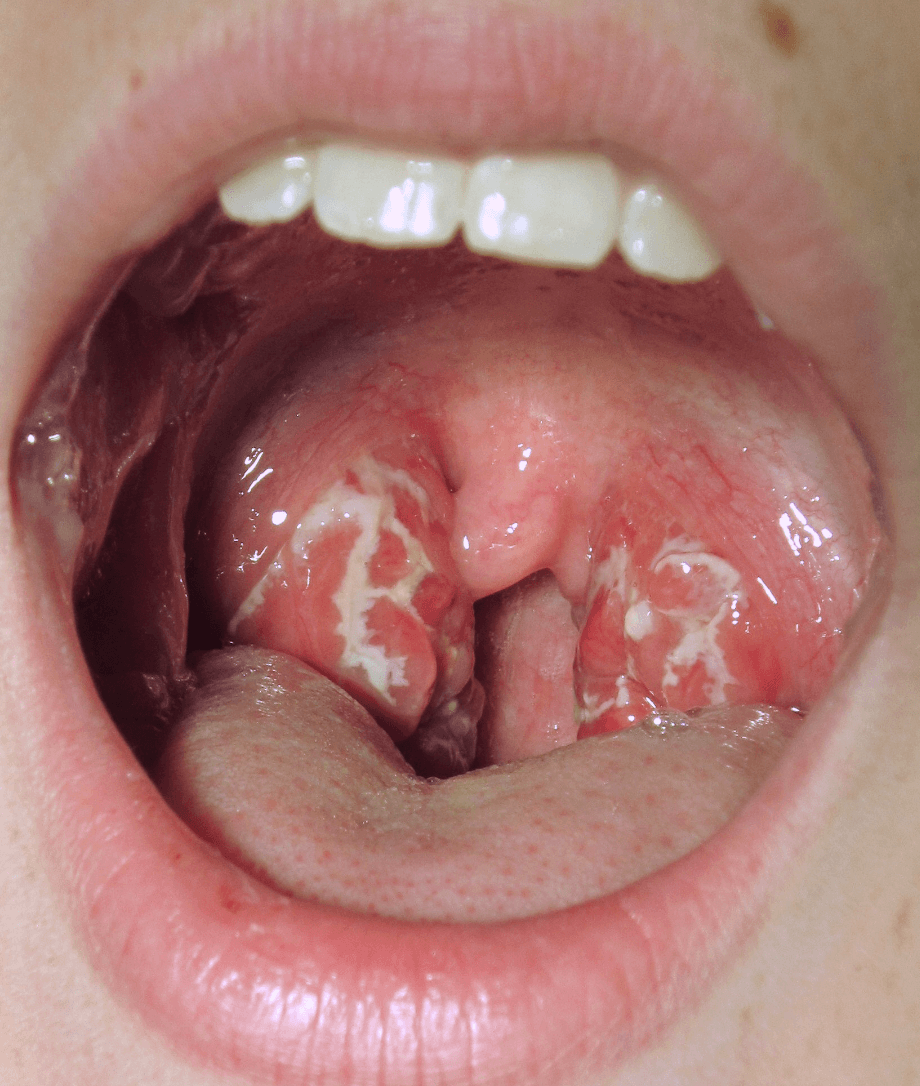
What is Pharyngitis?
Only requires antibiotics if the patient tests positive for strep or the infection lasts longer than 10 days.
Therapeutic interventions include rest, encouraging oral hydration, gargling warm salt water (1/2 teaspoon dissolved in 8oz of water), and OTC analgesic oral meds or topical sprays.
A procedure performed to remove fluid in the pleural space, obtain a specimen for diagnostic testing, and/or relieve dyspnea and improve respiratory compromise.
What is a thoracentesis?
The presence of blood in the pleural space.
What is Hemothorax?
Remember a collection of (non-blood) fluid in the pleural space is called a pleural effusion.
Either condition may require a chest tube.
This common issue associated with respiratory infections is prevented by encouraging oral intake and monitoring intake & output.
What is dehydration?
This newest FDA authorized vaccination decreases likelihood of an infectious respiratory virus that has lead to over a million hospitalizations and deaths since 2019.
What is the COVID-19 vaccination?
This infection in children often leads to a "bark-like" cough and noisy, labored breathing.
What is croup?
In children younger than three years, croup most commonly takes the form of laryngotracheobronchitis, an inflammation involving both the upper and lower respiratory tracts. This inflammation usually starts in the upper airways and descends to the lungs. In older children, only the voice box or the windpipe may be affected.
Patients receiving pharmacotherapy for tuberculosis need close monitoring of this organ due to possible toxicity.
What is the liver?
Combination drug therapy with strict adherence for 6-12 months includes:
-Isoniazid
-Rifampin
-Pyrazinamide
-Ethambutol
These types of patients with tuberculosis can have a negative PPD (purified protein derivative) skin test.
What is immunocompromised or elderly?
Tuberculosis (TB)? is a highly contagious disease transmitted through inhalation or swallowing of droplets contaminated with the TB Bacillus. Patients that are immunocompromised or elderly can get a sputum test or QuantiFERON Gold TB blood test.
This disease is not considered contagious if there are no presenting symptoms or evidence of disease on chest x-ray.
What is tuberculosis (TB)?
Most common bacterial infection worldwide.
Spread by airborne droplets.
It is common to be infected with the bacillus and never develop active TB. A healthy individual can fight off the growth of bacillus, but lesions that form can remain inactive.
This unique symptom, meaning 'loss of smell', is associated with COVID-19.
What is anosmia?
The most serious form of laryngitis in children and is always considered a medical emergency.

What is epiglottitis?
This medication is used to treat influenza and can be prescribed for this condition within 48hour of symptom onset.
What is oseltamivir (Tamiflu)?