What is the smallest unit of matter that makes up an element?
Atom.
What is an element?
A substance that cannot be broken down into simpler chemical substances.
What are the two main types of chemical bonds?
Ionic and covalent bonds.
What property of water allows it to stick to itself?
Cohesion.
What does pH stand for?
Potential Hydrogen
Name the three subatomic particles and their charges.
Proton (+), Neutron (neutral), Electron (-).
What are isotopes? Give an example.
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons, e.g., Carbon-12 and Carbon-14.
Balance the following equation:


What kind of bond forms between water molecules?
Hydrogen bond.
What is the impact of ocean acidification?
It reduces the pH of the ocean, harming marine life.
What determines the atomic number of an element?
The number of protons.
How many protons and neutrons does Carbon-14 have?
6 protons and 8 neutrons.
What is a covalent bond?
A bond formed when two atoms share electrons.
What is a solution?
A mixture where one substance (solute) is dissolved in another (solvent)
If a solution containing 300,000 atoms contains 300 H+ ions, what is the pH of the solution?
pH=3
Where are protons and neutrons located in an atom?
In the nucleus.
How are isotopes used in science?
They are used in radiometric dating and cancer treatment.
How many covalent bonds can hydrogen form?
One
What is capillary action, and how does it relate to water?
The ability of water to move up narrow tubes, like in plant roots, due to cohesion and adhesion.
What is the color change of litmus paper in an acidic solution?
Red
What is the difference between atomic number and atomic mass?
Atomic number is the number of protons; atomic mass is the total of protons and neutrons.
A scientist has a sample of a radioactive substance with a half-life of 10 years. If the original amount of the substance is 100 grams, how much of the substance will remain after 30 years?
After 30 years, 12.5 grams of the substance will remain.
After 10 years:
100 grams ÷ 2 = 50 grams
After 20 years:
50 grams ÷ 2 = 25 grams
After 30 years:
25 grams ÷ 2 = 12.5 grams
What type of bond holds the oxygen and hydrogen atoms together in a water molecule?
Polar covalent bond.
What is the difference between a solvent and a solute?
The solvent dissolves the solute.
What is the typical pH range that pH paper can test?
From 0 to 14.
What is the charge of an atom that loses an electron? What do we call this atom now?
+1 charge and it is called a cation.
A fossil contains 80 grams of carbon-14. The half-life of carbon-14 is 5,730 years. How much carbon-14 will remain in the fossil after 22,920 years
After 22,920 years, 5 grams of carbon-14 will remain in the fossil.
After 1 half-life (5,730 years):
80 grams ÷ 2 = 40 grams
After 2 half-lives (11,460 years):
40 grams ÷ 2 = 20 grams
After 3 half-lives (17,190 years):
20 grams ÷ 2 = 10 grams
After 4 half-lives (22,920 years):
10 grams ÷ 2 = 5 grams
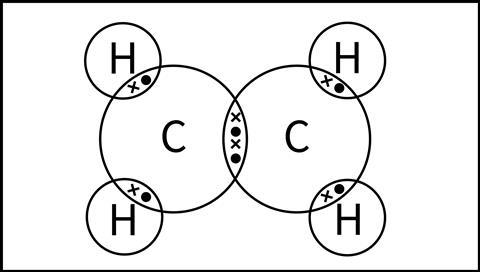
What kind of bond forms between the 2 carbon atoms?
How many double bonds are in this molecule?
How many single bonds?
Draw the Structural Formula
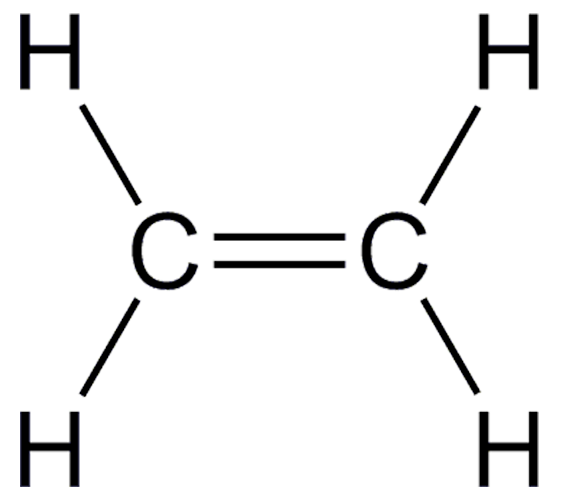
Double bond between the carbons.
One double bond overall.
four single bonds.
How does water dissolve ionic compounds like salt?
The positive side of water attracts the anions, and the negative side attracts the cations.
What happens to the pH when CO₂ dissolves in water, and how can indicators show this change?
The pH decreases, becoming more acidic, and indicators like bromothymol blue can change from blue to yellow, signaling increased acidity.