f(x)=cos(x)
F(x)=sin(x)+k
f(x)=2x+3
f'(x)=2
Bestimmen Sie das Integral int_0^2 f(x)\ dx
int_0^2 f(x)\ dx = 1
Wie lautet der Hauptsatz der Differenzial- und Integralrechnung?
int_a^b f(x)\ dx = F(b)-F(a)
31*13
403
f(x)=3/2x^2
F(x)=1/2x^3+k
f(x)=2e^x
f'(x)=2e^x
Gegeben ist der Graph einer Funktion f. Wo hat der Graph von F eine Wendestelle?
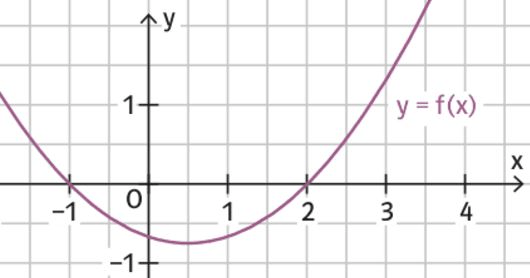
x=1/2
Berechnen Sie das Integral.
int_0^2 x\ dx
1
Wie lautet die nächste Zahl:
25, 50, 54, 49, 98, 102, 97, ...
194
f(x)=e^(2x)-3x^3
F(x)=1/2*e^(2x)-3/4x^4+k
f(x)=-1/2x^2-2x+6
f'(x)=-x-2
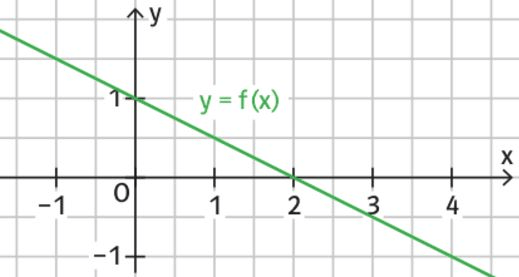
Gegeben ist der Graph von f. Wo hat F eine Extremstelle? Handelt es sich um ein Maximum oder Minimum?
F hat bei x=2 ein Maximum.
Berechnen Sie das Integral.
int_-1^1 x^3\ dx
0
Schreibe 70/4 als Dezimalzahl.
17,5
f(x)=1/((x+1)^2)
F(x)=-1/(x+1)+k
f(x)=0,25*sin(4x+2)-17
f'(x)=cos(4x+2)
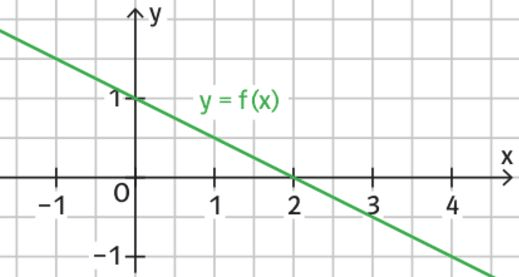
Gegeben ist der Graph von f. In welchem Intervall ist F streng monoton steigend?
Für -1<x<0 und x>2.
Berechnen Sie das Integral.
int_0^pi sin(x)+cos(x)\ dx
2
15% von 240
36
f(x)=2/(sqrt(4x+1))
F(x)=sqrt(4x+1)+k
f(x)=-cos(x/(2pi))+e^(3x)
f'(x)=1/(2pi)sin(x/(2pi))+3e^(3x)
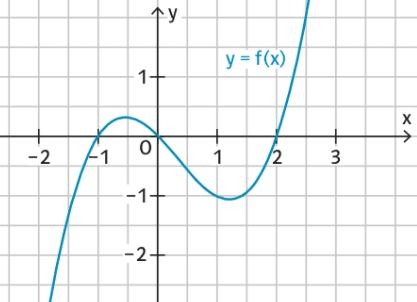
Die Grafik zeigt Graphen von F, f und f'. Ordnen Sie korrekt zu! Eine Funktion passt nicht zu den anderen.
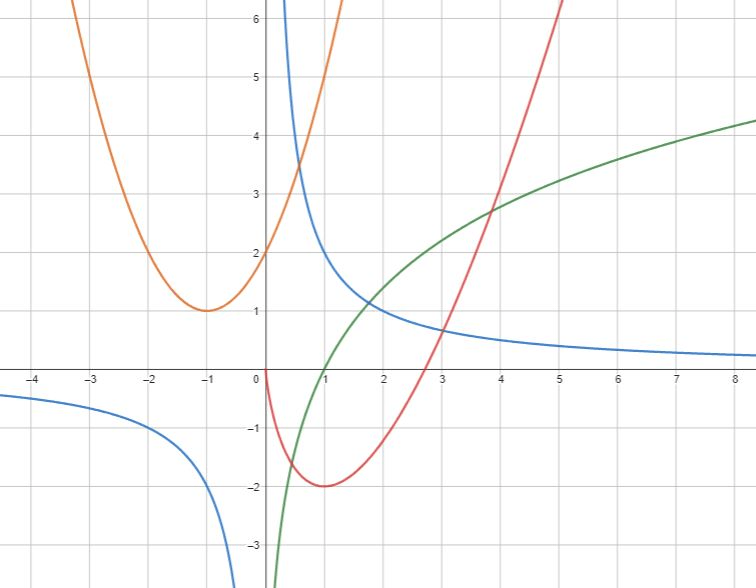
rot: F
grün: f (ln-Funktion)
blau: f' (Hyperbel)
orange: passt nicht (Parabel)
Berechnen Sie das Integral.
int_2^3 1/3x^2\ dx + int_0^2 1/3x^2\ dx
3
512^(1/3)
8