The definition of matter.
Anything that is made of atoms, has mass, and takes up space.
The definition of the Law of Conservation of Mass.
In a physical or chemical change, mass is neither created nor destroyed.
Definition of kinetic molecular theory.
Matter is made up of particles and the particles are always moving.
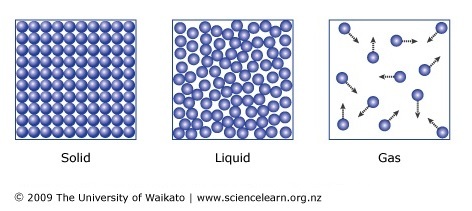
The particles and movement of the particles in a solid, liquid, and gas.
The relationships between the following variables (direct or inverse):
- pressure and volume
- volume and temperature
- pressure and temperature
- pressure and volume = inverse
- volume and temperature = direct
- pressure and temperature = direct

State of matter when the temperature is 400 K and the pressure is 0.5 atm.
Gas.
The difference between a pure substance and a mixture.
A pure substance only has one type of particle while mixtures have more than one type of particle.
An example of the Law of Conservation of Energy.
Potential energy is converted to kinetic energy as you ski down a hill, but energy is not lost.
The shape and size of a crystal in comparison to the unit cell.
Larger but the same shape as the unit cell.
Diffusion versus effusion.

Two real-life examples of Boyle's Law, Charles's Law, or Gay-Lussac's Law. You must identify the variables involved in the laws you are providing examples of.
Boyle's Law (P and V): As the plunger on a syringe is pulled, increasing the volume, the pressure decreases, drawing in liquid
Charles's Law (V and T): a hot air balloon inflates as the gas inside is heated
Gay-Lussac's Law (P and T): the pressure inside an Instant Pot increases as the temperature is increased, cooking your food faster
 Location of the triple point (letter, temperature and pressure) and a definition.
Location of the triple point (letter, temperature and pressure) and a definition.
D, 273.2 K, 0.006 atm
The point where solid, liquid, and gas coexist in equilibrium.
The difference between a compound and a mixture.
Compounds have two or more elements chemically combined while mixtures have two or more pure substances physically combined.
Two physical properties and two chemical properties of iron.
Physical properties: size, color, magnetism, hardness
Chemical: ability to rust, ability to react with acid
A definition of kinetic energy and how it relates to particles at the same temperature.
Kinetic energy: energy of motion
Particles at the same temperature will have the same kinetic energy (kinetic energy and temperature are directly related).
An example of how you could decrease the pressure in a room.
Picture should show: increasing the amount of space, decreasing the number of particles, or decreasing the temperature.
If the initial temperature of 3.0 L of a gas is 298 K, at what temperature will the volume increase to 9.5 L?
940 K
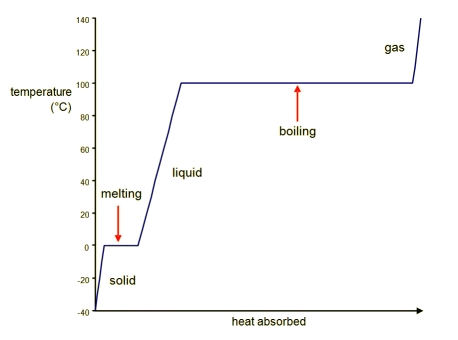
Draw the heating curve for water. Label the axes, phases of matter, and phase changes.
An example of an element, a compound, a homogeneous mixture, and a heterogeneous mixture.
Element: carbon
Compound: H2O
Homogeneous mixture: air
Heterogeneous mixture: fruit salad
The difference between intensive and extensive properties plus an example of both for a pencil.
Intensive does not depend on the amount of substance (yellow color). Extensive depends on the amount of substance (mass, length).
Three assumptions about gases in kinetic molecular theory.
1. Gases are small, hard, spheres with insignificant volume
2. Gases are in constant, rapid, random motion
3. Collisions between gas particles are perfectly elastic
Illustration and description of the movement of the particles in a solution, colloid, and suspension

A gas is in a flexible 450 mL container, at a pressure of 1.0 atm and a temperature of 30 oC. If the temperature is decreased to -20 oC, and the pressure is increased to 5.5 atm, what will the volume of the container be?
0.07 L (70 mL)
What is specific heat? Describe the difference between a substance with high specific heat and one with low specific heat.
Specific heat is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1g a substance by 1 degree Celsius. A substance with high specific heat heats up slowly and holds heat (insulator), while a substance with low specific heat heats up quickly and cools down quickly (conductor).
Three separation methods and and an example of when you would use each one.
Filtration- to separate a heterogeneous mixture of a liquid and solid (ex: sand and water)
Distillation- to separate a homogeneous mixture of two liquids with different boiling points (ex: water and alcohol)
Chromatography- to separate compounds with different polarity (ex: colored ink in a marker)
Three physical changes and three chemical changes.
Physical- breaking a toothpick, melting ice, blowing up a balloon.
Chemical- bleaching paper, hard boiling an egg, mixing vinegar and baking soda
The difference between a solution and a colloid, how you can tell the difference, and an example of both.
Solutions are homogeneous mixtures while colloids are heterogeneous mixtures.
Solutions will not exhibit the Tyndall effect while colloids will.
Salt water is a solution while jello is a colloid.
The velocity of helium gas (He) versus fluorine gas (F2) at the same temperature and the equation explaining why.
Picture should show He moving faster than F2 because of the equation KE = 1/2 mv2
What is the volume of a gas canister containing 3.55 moles of hydrogen gas at STP?
AND What are the two assumptions about ideal gases?
79.5 L
- the volume of the gas particles is negligible
- the gas particles do not experience any attractive intermolecular forces
Rocks can be used to store heat in solar-heated homes. If the specific heat of the rocks is 0.821 J/g-C, what temperature change would 50,000 g of rocks undergo if they emitted 450,000 J of heat?
11 degrees