Living things in the environment such as:
- Animals
- Plants
- Fungi
- Bacteria
Biotic
These organisms produce food energy for themselves and all other organisms on Earth
Use energy from the Sun (photosynthesis) and nutrients in the soil/water to grow
Producers
Accidental or planned introduction of a non-native species into a community.
Bioinvasion
When a liquid changes into vapour.
Evaporation
When a species no longer exists anywhere on earth
Extinct
Non-living things in the environment such as:
- Air
- Water
- Soil
- Sunlight
- Minerals and Nutrients
Abiotic
The process by which producers create all of the energy for the ecosystem.
Photosynthesis
More than one living thing trying to reach the same goal
Competition
When water that is taken up through a plant’s roots evaporates from its leaves, stem, and flowers.
Transpiration
Organisms that are so rare that they are in danger of becoming extinct
Endangered
What are the 4 basic needs of living things?
Food, water, suitable habitat, exchange of gases.
These are the 3 types of consumers.
- Herbivore
- Omnivore
- Carnivore
Animals get their food by killing and eating other organisms
Predation
Carnivore
When vapour changes into a liquid. Warm air contains water vapour, which condenses into clouds, fog, or dew.
Condensation
Species that has been removed from a certain part of their habitat:
Extirpated
White fur in snowy areas, camouflage, webbed feet or flippers to swim fast, long beaks for getting insects are all examples of this inherited characteristic that helps an organism survive in its environment.
Adaptation
Organisms that get matter and energy they need from wastes and dead plants and animals
Decomposers & Scavangers
A niche:
The role an organism plays
When water vapour that forms from the condensation inside of clouds falls as rain, sleet, snow, or hail.
Precipitation
DDT damaged the eggshells of what organism:
Peregrine Falcon
A symbiotic relationship between two different organisms in which both benefit.

Mutualism
Movement of pollutant through the levels of a food chain so that greater quantities are present up the food chain.
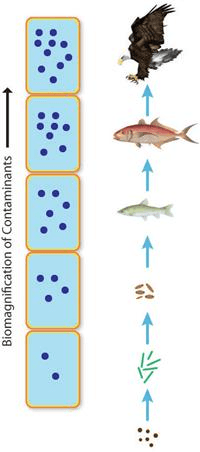
Bioaccumulation
What type of consumer would the FOX be:
:strip_icc()/pet-fox-diet-1238708_FINAL-e211c63562ab47269b8cd9f3a950d49f.jpg)
Omnivore
Identify one of the processes in this carbon cycle that releases carbon into the atmosphere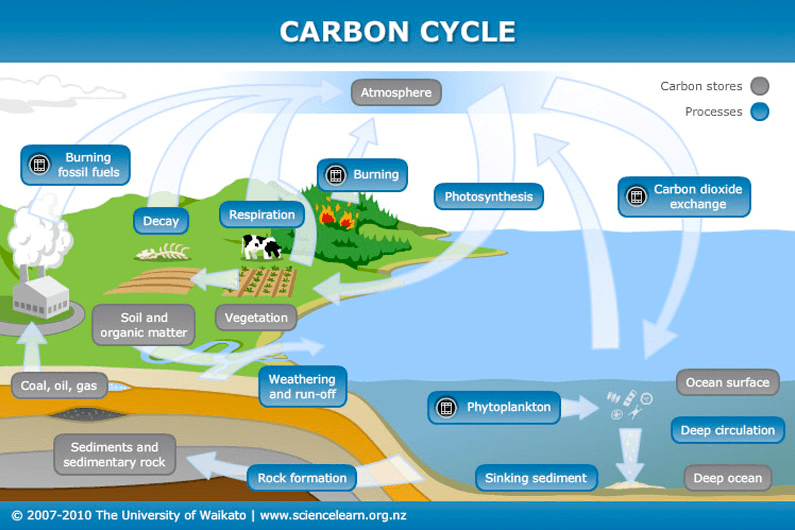
- Burning fossil fuels
- animal decay
- respiration
- forest fires
Affected small bugs eaten by geckos. Geckos suffered nerve damage and moved more slowly. Cats started hunted slow moving geckos instead of rats and died from DDT poisoning. Rat population increased and so did the diseases they carry.
An example of:
An example of the Negative Effects of DDT
A symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits and the other partner neither loses or gains (neutral).

Commensalism
This organism has the largest population in this food pyramid:
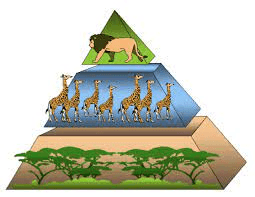
Trees and vegetation.
The most important R
Reduce
The cycle shown in this diagram.
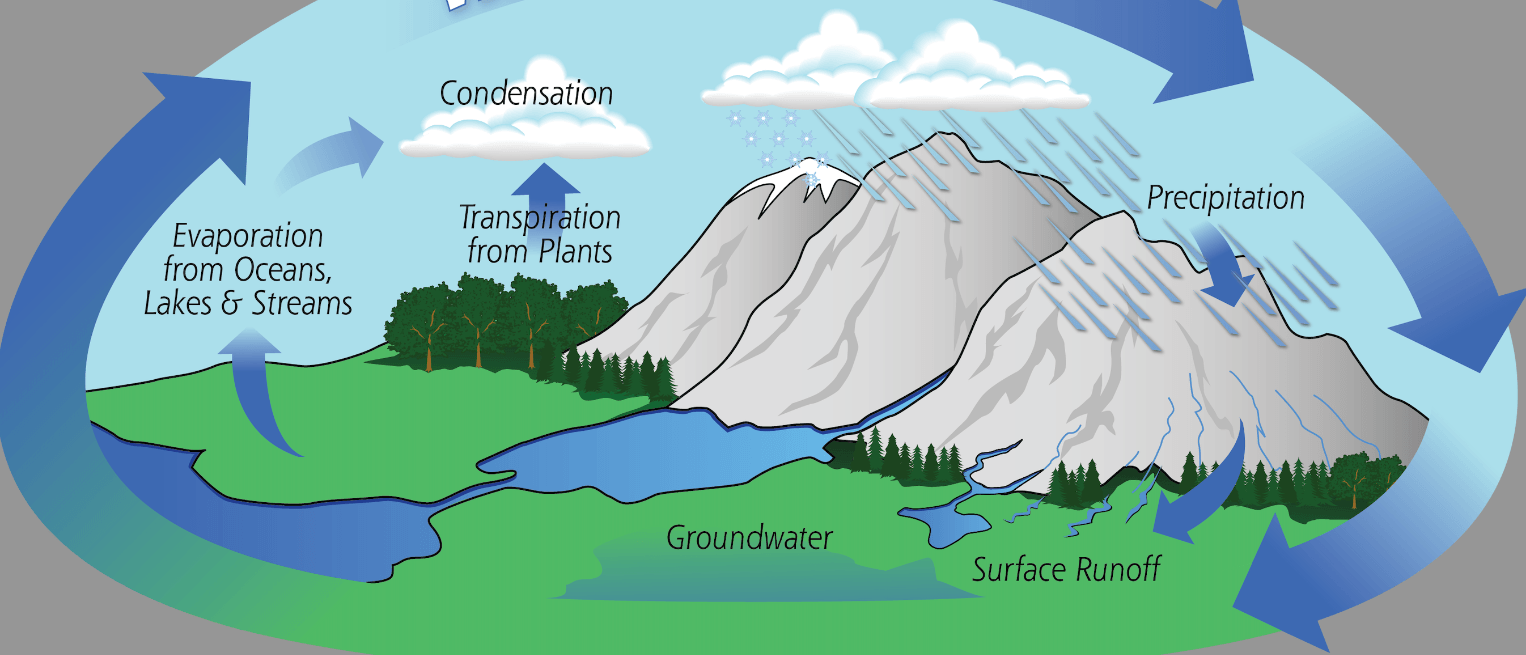
The water cycle
The Great Auk is now:
Extinct
A symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits and the other is harmed.


Parasitism
This organism has the lowest population in this food pyramid: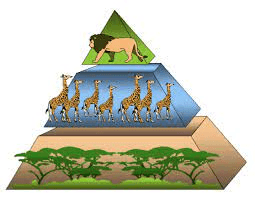
Lion
The starting point for information that ecologists use when studying an ecosystem.
Baseline Data
This type of precipitation has a pH value below 5.6 because sulfur and nitrogen pollutants reacted with water vapour in the atmosphere.
Acid rain
Describe a way humans can impact or change an ecosystem.
Be specific
Your Example: