When FHR is less than 110 beats/minute for 10 minutes or longer?
What is bradycardia?
What is uterine tachysystole?*
>5 contractions in 10mins averaged over 30minutes. No matter what the FHR tracing shows.
What is the main goal of EFM? *
what is to assess fetal wellbeing. Identify a fetus who is or isn't well oxygenated
What is the meaning of extrinsic factors for a fetus? Example?*
Extrinsic Influences include anything that is OUTSIDE the fetus.
Example- Amniotic fluid, Placenta etc
Vagus nerve stimulation in a healthy infant will cause what to happen with the fetal heart rate due to the release of acetylcholine?*
What is a decreased in fetal Heart rate.
Example- intervention used for SVT in an infant
When FHR is more than 160 beats/minute for 10 minutes or longer?
What is tachycardia?
When reviewing the contractions, what fours things should the nurse be documenting?*
What is frequency, duration and intensity, resting tone*
What is the normal FHR of a term pregnancy?*
What is 110 - 160 bpm?
An acceleration that occurs after a variable is caused by?*
Occlusion of the umbilical vein. Due to the decreased in fetal venous return, that triggers the baroreceptor causing a temporary increased in the fetal heart rate.
what is the appropriate intervention for this tracing?
Increase Pitocin to help labor, decrease Pitocin to eliminate tachysystole or reposition from side to side?
what is Reposition from side to side
Why is oxygen not needed at this time?
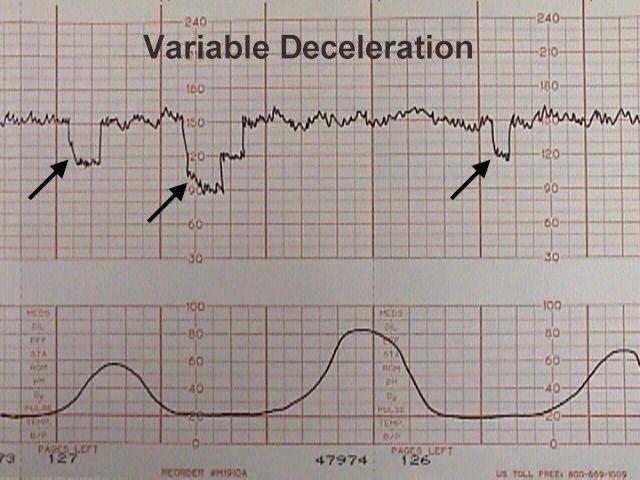
What are caused by conditions that restrict flow through the umbilical cord; these fall and rise abruptly with the onset and relief of cord compression?*
What is a variable deceleration?
What is used to detect pressure created by tensing of the uterine muscle? *
what is Tocodynamometer?
IUPC- detects pressure created by the actual strength of the uterine muscle.
What is your variability?

What is moderate?
what part of the placenta does maternal-fetal oxygen transfer take place*
What is the intervillous space?
You have a tracing with recurrent late decelerations what is you primary physiologic goal?*
What is Maximizing oxygen to the fetus
Interventions include: Reposition and start bolus. If continues and on Pitocin- Decreased Pitocin, If continues to have late decelerations- turn off Pitocin if decreased variability then oxygen 8-10L.
What is variability? *
Variability is defined as the fluctuations in the baseline that are irregular in AMPLITUDE AND FREQUENCY
What is the correct interpretation of this pattern?

Sinusoidal, recurrent lates or accelerations?
what is recurrent late decelerations
What category is a sinusoidal baseline?*
what is category 3, seen with fetal anemia such as with an abruption.
Cord blood gas values:
pH 6.90, PCO2- 86mmHg, pO2- 4mmHg, BE- -18.6 mEq/L*
what is Mixed acidemia
What is it called when you have periods where you are measuring the maternal and fetal heart during the tracing
*Commonly seem while pushing and can cause unexpected adverse fetal outcome. *
What is signal ambiguity.
Intervention- Place mother on pulse to verify maternal vs fetal. Typically wouldn't expect to see fetal accelerations while actively pushing.
What is the process or steps when assessing a FHR tracing?*
What is baseline, variability, Accelerations, Decelerations, Category
You have a patient being induced with Pitocin at 14mU/min. This is you tracing average for 30mins.
What is the most appropriate intervention at this time.
what is reposition patient, decreased Pitocin infusion and start bolus
If continues even once Pitocin has been decreased turn Pitocin off. If decreased variability 02.
Which fetal pattern would you expect to see with a tight nuchal cord x2 ?*
What are variables decelerations.
T/F- Freshly oxygenated blood enters the fetus from the umbilical vein then shunted through the ductus venosus to the inferior vena cava? *
What is true.
The Ductus Venosus has the most highly oxygenated blood in all of fetal circulation.
Why is supporting maternal coping an appropriate physiologic goal?
No matter what your tracing looks like.
what is to increased uterine blood flow by decreasing maternal catecholamine production.