GI
Please explain the main difference between AKI and CKD.
Resolution of kidney injury can occur with treatment in AKI, however kidney disease/failure is a life long condition.
These changes in bloodwork are associated with _______ _________:
- increased NH3
- low BUN
- low glucose
- low albumin
- elevated ALT, AST, ALP
- elevated bilirubin
Liver dysfunction
Explain the difference between vomit and regurgitation.
The main difference between regurgitation and vomiting is that regurgitation is a passive process, while vomiting is an active process:
- Regurgitation: The passive expulsion of food, fluid, or other material from the esophagus or pharynx. Regurgitated material usually looks the same as when it was eaten, and it may be accompanied by liquid.
- Vomiting: The forceful expulsion of stomach contents from the body. Vomiting is usually accompanied by nausea, abdominal heaving, drooling, and an apprehensive appearance. Vomiting is an active process that involves a coordinated closure of the nasopharynx and glottis to protect the airway. Vomiting is usually more forceful and larger in amount than regurgitation.
A complete history and thorough examination can usually differentiate between regurgitation and vomiting.
What is hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid glands fail to produce adequate amounts of the hormones T4 (thyroxine) and T3 (triiodothyronine).
- Primary hypothyroidism: idiopathic thyroid gland atrophy, or immune-mediated lymphocytic thyroiditis
- Diagnosis: T4, fT4, TSH, along with elevated cholesterol and mild, regenerative anemia.
What does 'IMHA' stand for?
Immune mediated hemolytic anemia
(Formerly known as AIHA - autoimmune hemolytic anemia)
Name a common cause for AKI.
Infectious disease
Urinary tract obstruction
Certain medications
Neurologic problems caused by poor liver function, and which causes these clinical signs, is called _____________.
- Dullness
- Inability to respond to basic commands
- Circling, head pressing, aimless wandering, weakness, and poor coordination
- Blindness
- Excessive drooling (Ptyalism)
- Behavior changes
- Collapse
- Seizures
- Coma
Hepatic encephalopathy
A neurobehavioral syndrome affiliated with either critical liver failure or liver shunt. The development is not completely understood. We often see elevated levels of ammonia with this disease.
Are the following clinical symptoms associated with small bowel or large bowel diarrhea?
- Melena
- Flatulence
- Inappetence
- Weight loss
Small bowel (small intestine)
Describe 3 clinical signs of hypothyroidism.
- Lethargy/dull mentation
- Inactivity/unwillingness to exercise
- Weight gain
- Cold intolerance or heat seeking
- Symmetric, non-pruritic hair loss
- Post-clipping alopecia
- Dry, dull hair coat
- Scaling
- Hyperpigmentation
- Recurrent pyoderma or otitis externa
- Lipid corneal deposits
- Laryngeal paralysis
- Megaesophagus or esophageal dysmotility
- Bradycardia
Explain the disease process of IMHA.
Normally, a red blood cell is removed from circulation and recycled when it is no longer functional. When old RBCs circulate through the spleen, liver, and bone marrow, they are plucked from circulation and destroyed through extravascular hemolysis. This releases the iron, which is then sent to the liver for recycling in the form of a yellow pigment called bilirubin.
The spleen uses immunological cues on the surface of the RBCs to determine which cells should be plucked out of circulation.
When the immune system marks too many cells for removal, this is when IMHA begins.
Excessive ______ is a warning sign of poor kidney function.
"Thirst"
A pet with insufficient kidney function will not be able to make concentrated urine and will need to drink extra water to process the body's waste chemicals.
Specific gravity is a measure of how concentrated a urine sample is. Water SG is 1.000, a dilute urine sample is < 1.020 or 1.010, and a well concentrated urine sample is 1.030-1.040.
In patients with portosystemic shunting or liver failure, ammonia concentrations escalate predominantly because of...
Poor circulation to the liver, which decreases the liver's ability to detoxify the ammonia levels.
Metronidazole is often used to decrease population of ammonia-producing gut microbes, and lactulose acidifies the gut environment to restrict ammonia absorption.
- Mucus
- Hematochezia
- Tenesmus
- Urgency
- Normal appetite
Large bowel diarrhea
What is hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism is the condition that results from an excess of thyroid hormones. Diagnosis is based on clinical signs and elevated thyroid levels.
What does ITP stand for?
Immune mediated thrombocytopenia
What blood analyte would be low in a case of glomerulonephritis?
Albumin
Albumin is a carrier molecule for water insoluble substances, and also is important in keeping water in the bloodstream. Without enough water, blood sludges and clots abnormally. The water will also leak into other body cavities, such as the chest and abdomen.
A portosystemic shunt can either be acquired or congenital. What is a portosystemic shunt?
The diseased liver resists blood flow into the organ, so new blood vessels develop to bypass the liver altogether, connecting the blood stream to the rest of the body (like finding a detour around a traffic jam). Acquired shunts are formed over time after a liver injury, and congenital shunts are a birth defect.
Acute hemorrhagic diarrhea syndrome is characterized by acute _______ and _______.
Vomiting and Diarrhea
AHDS diagnosis is based on clinical signs and a PCV > 60%. Most commonly seen in young (5 years) dogs, small and toy breed dogs.
List 3 clinical signs of hyperthyroidism.
- Hyperactivity
- Excessive vocalization
- Weight loss despite a good appetite
- Polyphagia
- Vomiting
- Voluminous stool
- PU/PD
- Palpable thyroid nodule
- Tachycardia/tachypnea
- Dry or greasy haircoat
What is Evan's syndrome?
ITP and IMHA
___________ is an inflammation of the kidney ("upper urinary tract infection"), commonly showing no symptoms at first, caused by a bacterial invasion. They may cause lesions that destroy the kidneys, causing kidney failure.
Pyelonephritis
Extrahepatic bile duct obstruction is the blockage of the normal flow of bile from the liver to the _________.
Intestinal tract.
Many primary conditions obstruct the CBD:
Inflammation in the surrounding area (eg. pancreatitis, duodenitis, duodenal foreign body), cholelithiasis, GB mucocele, cholecystitis, neoplasia, bile duct malformations, parasites, extrinsic compression, fibrosis, and bile duct structure.
Clinical signs (acute EHBDO): lethargy, cyclic fever, jaundice, elevated T.Bili (within 4 hours of obstruction taking place), inappetence or polyphagia (due to fat maldigestion from the lack of bile acids).
Please explain how miralax helps in cases of constipation?
Miralax (polyethylene glycol) acts by pulling water from the body into the intestinal tract during stool formation, leading to a softer stool.
What is the treatment of choice for a curative option for hyperthyroidism in cats?
Radioiodine therapy:
Radioiodine is concentrated within the thyroid gland, where it selectively irradiates and destroys the hyperfunctional thyroid tissue.
We are getting a transfer from VEG for thrombocytopenia. When the pet arrives, what is one of the first things you would assess?
- mucus membranes, belly, and pinnae for evidence of petechiae and/or bleeding
- Pulses (weak, bounding, snappy)
- Heart rate (tachycardia, heart murmur)
Amyloidosis refers to a group of diseases characterized by abnormal deposition of an insoluble, fibrous, proteinaceous substance (amyloid) in tissue. Name one possible cause of this disease.
Chronic persistent inflammatory diseases
Cancers
Amyloidosis may be difficult to diagnose based on clinical signs because these will depend on the location and the organs affected.
There is no specific treatment that can prevent the development of amyloid, or promote resorption of amyloid. Elimination of the source of chronic inflammation may slow amyloid deposition.
This is commonly seen in shar peis and abbysinian cats.
Fill in the blanks:
The gallbladder functions to store _____ between meals. When the patient eats, the fatty acids and amino acids trigger the release of cholecystokinin, stimulating _________ contraction. When it contracts, stored bile empties into the duodenum where it aids in digestion and absorption of dietary _____.
The gallbladder functions to store bile between meals. When the patient eats, the fatty acids and amino acids trigger the release of cholecystokinin, stimulating gallbladder contraction. When it contracts, stored bile empties into the duodenum where it aids in digestion and absorption of dietary fat.
When does constipation become obstipation?
Obstipation occurs when constipation becomes a more permanent and continuous problem. Obstipation is a more severe form of constipation that occurs when a pet is unable to pass feces due to a buildup of hard, dry stool. Obstipation is often associated with a serious, permanent, or irreversible medical condition.
What is pancreatitis?
Pancreatitis is an inflammatory condition that is common in dogs and cats. It can be acute or chronic and subclinical or associated with various clinical signs.
Name the condition that causes joint pain, lameness, and swelling in multiple joints caused by an inflammatory response of the immune system.
IMPA - Immune mediated polyarthritis
Clinical signs:
- Periodic walking issues - stiffness, difficulty standing to walk/reluctance to walk
- Swollen, warm, painful joints
- Hyporexia/anorexia
- PU/PD
- Lymphadenopathy, fever, lethargy
Name this disorder:
An inherited disorder in which small, closed, liquid-filled sacs develop in the tissue of the kidney.
Polycystic kidney disease
These cysts multiply over time, eventually overwhelming the kidneys and often leading to potential kidney failure. This most frequently is seen in Persian cats.
What is the difference between cholangitis and cholangiohepatitis?
Cholangitis is inflammation of the biliary tree.
Cholangiohepatitis is inflammation of the biliary tree and the surrounding liver tissue.
What imaging is most commonly diagnostic for megaesophagus?
Radiographs!

What are the most common tests to diagnose pancreatitis?
- clinical signs
- imaging (radiographs, ultrasound)
- serum lipase immunoreactivity levels (PLI)
What is myasthenia gravis?
Myasthenia gravis is the condition where the neuromuscular junctions are diseased. The acetylcholine message from the nerve trying to stimulate the muscle is quickly blunted because of damage to the nerve/muscle interface. This can be congenital or acquired (immune mediated).
What disease causes the following symptoms:
- Weight loss
- Lethargy
- Hypertension
- PU/PD
- Anorexia
- Nausea/vomiting
- Pitting edema
Protein Losing Nephropathy (PLN)
The most severe complication of PLN is thromboembolic disease (antithrombin III, a protein that stops blood clots from forming when they shouldn't, is lost in the urine). This makes them prone to clots, and may be fatal if one reaches the lungs or brain.
What is cholecystitis? What is the most common treatment of choice?
Inflammation of the gallbladder (a common complication of cholelithiasis, extrahepatic bile duct obstruction, and other diseases). Usually treated by performing a cholecystectomy in most cases.
Clinical signs: Abdominal pain (sometimes only postprandial), fever, vomiting, ileus, and sometimes jaundice/hyperbilirubinemia.
Diagnosis: Abdominal X-rays, AUS, bloodwork (elevated T.Bili, and can even evaluate concentration of bilirubin within abdominal effusion and compare to blood levels)
Treatment also includes a combination of metronidazole, unasyn, and baytril to provide broad-spectrum antibiotics against enteric opportunists.
What is PLE?
Protein Losing Enteropathy: A group of diseases that cause the loss of proteins from the bloodstream into the GI tract.
Name this syndrome:
A syndrome caused by insufficient synthesis and secretion of digestive enzymes by the exocrine portion of the pancreas. The most common clinical signs are polyphagia, weight loss, and a large volume of orange-colored, "fatty", loose stools.
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
Treatment: Supplementation with pancreatic enzymes
- Powdered pancreatic enzymes: start with 1 tsp/10kg per meal for dogs, or 1 tsp per meal for cats. Once clinical signs have resolved, taper the dose to the lowest effective. Dose can vary between enzyme batches.
-Oral bleeding is a side effect of pancreatic enzymes. Soaking the powder in water mixed with food help reduce bleeding.
- +/- B12 supplementation
Describe the clinical signs of myasthenia gravis.
- Muscle weakness affecting the eyes, muscles of facial expression
- Muscle weakness of the throat/esophagus, causing difficulty swallowing, voice change, laryngeal paralysis, megaesophagus, and complications like aspiration pneumonia
- Muscle weakness of the limbs, leading to early exercise fatigue
Name this birth defect that causes one or both ureters to connect to an abnormal location (tunneling through the bladder wall, or into the urethra).
Ectopic ureters
Intramural (tunneling through bladder wall)
Extramural (bypassing the bladder and connecting to the urethra)
Symptoms:
- Urine leakage/dribbling
- Difficulty house training; lots of accidents
- UTI
- Licking genital area
- Rash on genital area
- Urine staining and genital area persistently wet
Diagnose this ultrasound image:
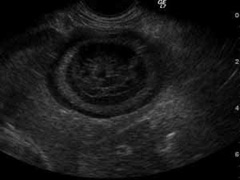
Gallbladder mucocele.
A gallbladder mucocele is a non-inflammatory condition where the gallbladder becomes distended with abnormal bile. Complete removal is the treatment of choice (cholecystectomy).
Nursing care post-op involves:
- Monitor cardiovascular status closely to identify complications like hypovolemic shock or sepsis
- Provide sufficient analgesia; regular pain scores
- Maintain fluid and acid-base balance
- Provide nutritional support and maintain GI motility
What dog breeds most commonly get PLE?
Soft-coated wheaten terrier
Yorkshire terrier
Maltese
Chinese Shar-Pei
Rottweiler
Basenji
Irish setter
Norwegian Lundehund
Explain the difference between Cushing's disease and Addison's disease.
Cushing's = Hyperadrenocorticism due to an ACTH-secreting tumor of the pituitary gland
Addison's = Hypoadrenocorticism, a lack of glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, or both.
Explain autoagglutination. Why does this happen? How does this affect test results?
Autoagglutination is the spontaneous clumping of RBCs. The immune destruction of red cells causes them to clump together due to the antibody coatings sticking together. This can also form clots, causing a thrombosis.
May affect blood typing/crossmatch results
This condition is caused by a 'defect' in the way a cat handles stress. Symptoms include hematuria, stranguria, inappropriate urination, urinary blockage, licking the urinary opening.
Feline Idiopathic Cystitis
The urinary bladder is lines with glycoproteins calls PSGAGs. This material insulated the bladder from the urine it contains. Urine can vary greatly in pH and can contain abrasive crystals in addition to assorted toxins and irritants that the kidneys have removed from the bloodstream and concentrated. All of these unpleasant materials are present in the urine, so it is a good thing to have a layer of insulation protecting the actual tissue of the bladder.
Explain copper storage disease as you would to a client; what is copper storage disease? How is it diagnosed?
Excessive amounts of copper accumulate in the liver due to the inability to get rid of it, too much in the diet, or both.
It is diagnosed by a liver biopsy and copper quantification test.
What is the name for dilation of the lymphatic vessels in the GI tract?
Lymphangiectasia

Explain the diagnostics used to diagnose addison's disease and cushing's disease.
Addison's - ACTH Stim test
Cushing's - LDDST
What is a coomb's test?
also known as an antiglobulin test, is a laboratory procedure that detects antibodies that may attack red blood cells.