the ability of a country to produce a greater quantity of a good, using the same amount of resources
absolute advantage
it occurs when many companies offer competing products or services that are similar, but not perfect, substitutes
monopolistic competition
According to this concept, government should increase the supply of a state's gold and silver with exports rather than to deplete it through imports
Mercantilism
State the two purposes of tariff
to provide revenue and to protect particular domestic sectors
measure of the cost of not being able to produce something else with the resources used
opportunity cost
Who is the founder of New trade theories?
Paul Krugman
the term for absence of trade
autarky
a general prohibition of most trade with the sanctioned country
embargo
it shows the maximum amount of the two products that can be produced by the county with certain amount of labor
Production possibilities frontier curve
What happens to the price after trade within the trade theory of external economies of scale?
Precise answer:
The price after trade is lower than the price in the both of the countries before trade
What is the title of the main work of Adam Smith
Wealth of Nations
What is the Most Favored Nation (MFN) Tariff?
The Most Favored Nation (MFN) tariff is the import duty rate a country sets, which applies to all its trading partners equally, treating them as its most favored in terms of trade.
The table shows the unit labor requirement to produce 1 unit of product.
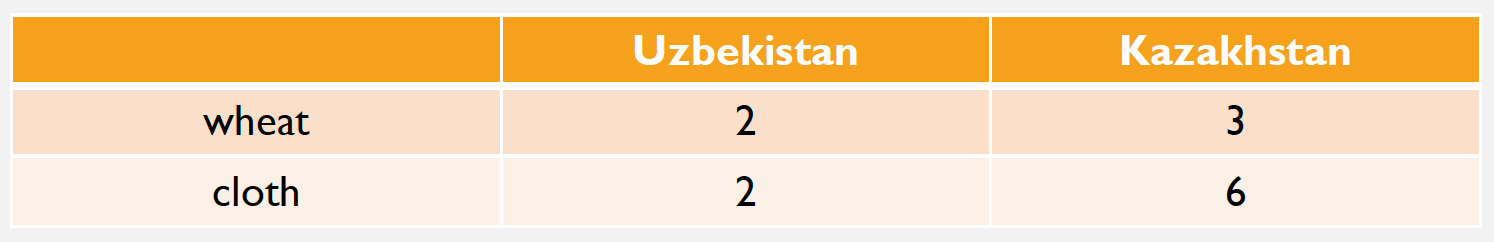
What is the opportunity cost of producing cloth in Kazakhstan?
2 kg of wheat
What is intra-industry trade
the country both imports and exports the same thing
What is intra industry trade?
the same types of goods or services are both imported and exported. For example, Uzbekistan both exports and imports textile goods.
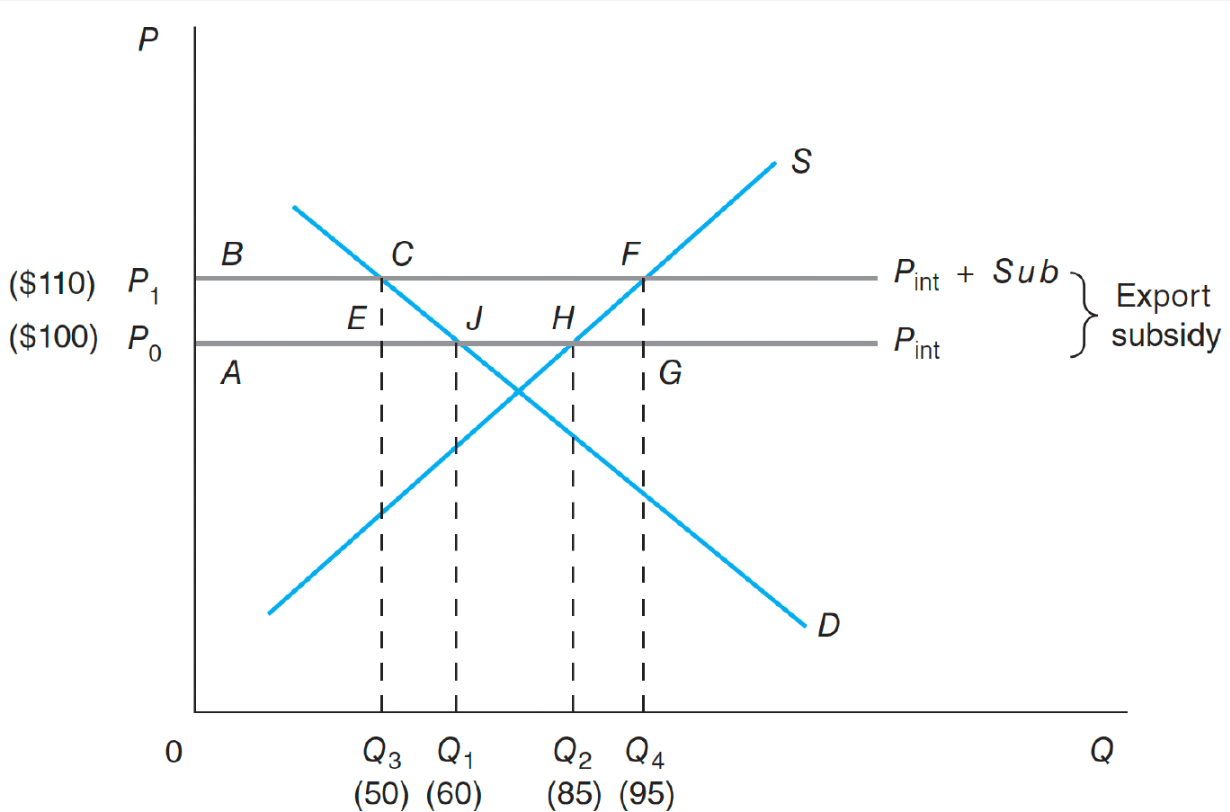 Calculate deadweight loss
Calculate deadweight loss
(110-100)(60-50)/2+(110-100)(95-85)/2=100
What are the two main assumptions of Heckscher-Ohlin model?
1. factor intensity of the product
2. factor abundance of the country
Explain the difference between external and internal economies of scale
•External economies of scale occur when the cost per unit depends on the size of the industry.
•Internal economies of scale occur when the cost per unit depends on the size of an individual firm.
Laplandiyaning qulupnay bozorida talab va taklif egri chiziqlari quyidagicha: S=60+20P va D=1060-20P
Import narxi 10 dollarga teng bo'lsa, import hajmini hisoblang
Importga talab: MD= D-S = 1060-15P - (60+20P)
=1060-20P-60-20P=1000-40P
P=10 => MD=1000-40*10=600
Country Macrology has only three imported goods with the following tariff rates: cheese 10 percent; shirts 20 percent; and computers 30 percent. It imports $2 billion worth of computers, $2 billion worth of shirts, and $1 billion worth of cheese.
Calculate weighted and unweighted average tariff rates.
Unweighted: (10+20+30)/3=20
Weighted: (10*1+20*2+30*2)/(1+2+2)=22