The acronym for assessing a client for symptoms of a stroke.
FAST
A client reports a decrease is his ability to smell, the nurse knows to assess this cranial nerve during the physical assessment.
What is CNI Olfactory nerve? (This is a sensory nerve responsible for smell.)
A chronic recurring abnormal brain electrical activity resulting in two or more seizures.
What is epilepsy?
The term for headaches.
What is cephalgia?
A warning of an impending stroke.
What is a transient ischemic attack (TIA)?
The stroke severity indicated when a client has a Score between 21-42 on the NIHSS Stroke scale.
What is a severe stroke?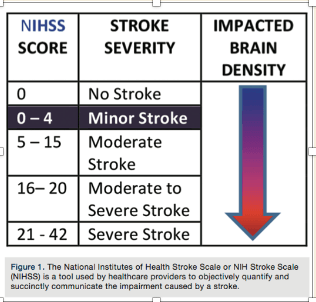
A client reports having trouble hearing. This is the cranial nerve the nurse will most likely assess in the physical examination.
What is CN VIII, acoustic nerve. (This is a sensory nerve responsible for both hearing and balance.)
Seizure that involves both hemispheres of brain and manifest as staring into space with subtle body movements.
What is non-motor (absence seizures)generalized seizures?
Patient education for managing migraines.
What is educate patient on identifying triggers, promoting stress reduction techniques, encouraging healthy lifestyle and health promotion activities and providing comfort measures including going into a quiet, dark room to alleviate light and sound stimuli (b/c they are sensitive to light, sound and smell)
A genetically engineered medication that breaks up clots, mimicking a substance made naturally by the body.
What is tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA)?
A client has had injury to the cerebellum. This area is the primary area for assessment?
What is coordination?
This cranial nerve signals to the lateral rectus muscle in the eye and when it contracts it moves the eye away from the nose. (It abducts the eye.)
What is CN VI abducens nerve?
A seizure that manifests with impaired consciousness/awareness and automatisms (i.e. smacking of lips).
What is a complex partial seizure?
Infection of the meninges, also a complication that can occur with intraventricular catheter in place to measure ICP.
What is meningitis?
Unaware of persons or objects on side of visual loss; neglect of one side of body
What is Homonymous Hemianopsia?
Older adults may have these head or hand tremors; repetitive movements of the lips, jaw or tongue.
What is dyskinesia?
A nurse is assessing this cranial nerve and the client is unable to blink and has weakness of the messeter muscle; so having difficulty chewing.
What is CNV, trigeminal nerve? (This is both a motor and a sensory nerve. Responsible for facial sensation and mastication)
The primary goal for nursing management of a client having a seizure.
What is to prevent patient from injury?
When a client awakens to vigorous shake or painful stimuli but returns to unresponsive sleep.
What is stuporous?
A patient who suffered a stroke one month ago is experiencing hearing problems along with issues learning and showing emotion, this lobe of the brain has more than likely been impacted.
What is the temporal lobe? (It is responsible for hearing, learning, and feelings/emotions.)
Asking the client to stand erect with arms at side and feet together and noting any unsteadiness or swaying. Then with the client in the same body position, ask the client to close the eyes for 20 seconds, while again noting any unsteadiness or swaying.
What is the Romberg test?
A client has dysphagia. These two cranial nerves are a priority to assess.
CN IX, glossopharyngeal nerve and CN X, vagus nerve (An abnormal finding when assessing CN IX is an absent gag reflex; An abnormal finding when assessing CN X is dysphagia)
Most dramatic type of seizure with body stiffening and shaking and incontinence.
What is tonic-clonic seizure?
This is what a client would "look" like if he or she were having increased intracranial pressure (ICP).
Client would have irritability, restlessness, deteriorating level of consciousness, headache, dilated pupils, deterioration in motor functioning and abnormal posturing (decebreate, decorticate, flaccidity)
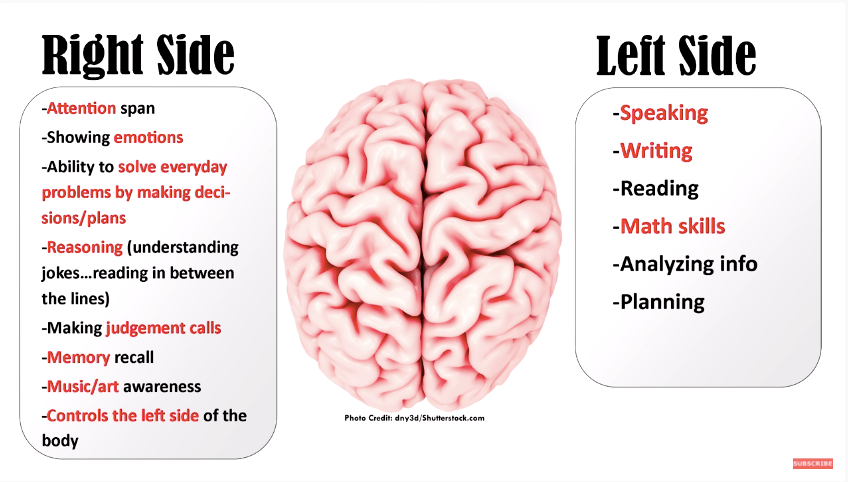
A patient is confused on date, time and place & has a very short attention span. The nurse suspects that patient to have had injury to this brain hemisphere?
What is the Right side of the Brain?