The SI (metric) base unit for length
Meter
The three parts of an atom.
Proton, neutron, and electron
Neutrons.
Mendeleev arranged his table by increasing atomic mass, but today we arrange it by this.
Atomic number
The number of valence electrons in an atom increases as you move this direction on the periodic table.
Left to right.
The unit that is larger than a liter by a factor of 3.
Kiloliter
The subatomic particles that are inside the nucleus.
Protons and neutrons.
This subatomic particle is the same for all isotopes of an element
Protons
These elements, found between metals and nonmetals, share properties of both.
Metalloids
Atomic radius gets larger when you move this direction in a group on the periodic table.
Down
The equivalent to 987 mm in meters.
0.987 meters
The only part of the atom that does not contribute to its mass.
Electron
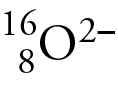
The mass number of this oxygen isotope.
16.
The vertical columns on the periodic table are called this.
Groups
As you move left to right across the periodic table, ionization energy generally does this.
Increases
476000000 in scientific notation
4.76 x 10^8
In order to create a neutral atom, these two subatomic particles must be equal in value.
Protons and Electrons
The isotope of carbon with 8 neutrons.
Carbon-14
All elements in the same group have this in common.
Number of valence electrons.
These elements in Group 18 usually don’t have electronegativity values because they do not chemically bond.
Noble Gases
The wavelength of red light is about 6.5 × 10⁻⁷ meters. Express this in nanometers (nm) (10-9 m).
650 nm
An atom has 17 protons, 18 neutrons, and 17 electrons. Identify the element and its charge.
Chlorine; neutral
An atom has 15 protons, 16 neutrons, and 15 electrons. Write the isotope’s name and symbol in standard notation.
Phosphorous-31
Although both belong to Group 1, hydrogen is often placed separately from the alkali metals. Explain why this is.
It does not share the same metallic properties with the other alkali metals in this group.
Explain why atomic radius increases down a group, but decreases across a period.
As you add electron shells down a group, the radius gets larger; as you add an electron to the shell across a period, they are pulled in more by added protons.