Usually relates to the arrangement of its internal components.
Structure
Resistance to localized plastic deformation at surface
Hardness
A material in which atoms are situated in a repeating or periodic array over large atomic distances.
What is Newton's 1st Law of Motion?
An object will remain in its original state of motion if there is no unbalanced force acting on it.
A child applies a force of 200 N to a couch causing the couch to displace 10 meters. What is the work done on the couch?
W=Fdcos(\theta)
W=2000 J
A trait (magnitude) of response to a specific imposed stimulus
Properties
Deflection under stress
Stiffness
A material that is not crystalline or lacks periodic atomic order/packing.
Amorphous
The forces of action and reaction between two objects are equal, collinear, and opposite!
1.A person pulls a box with a rope, which makes an angle of 45º to the floor. The person is pulling the rope with 200 N causing the couch to move 10 meters. What is the work being done on the box?
W=Fdcos(\theta)
W=1414 J
Degree of overall functionality of material.
Performance
Elastic Deformation is reversible, while Plastic Deformation is permanent.
What defect is this?

Vacancy
What is Newton's Second Law of Motion?
The acceleration of the movement of an object is proportional to the resultant force, and is also in the same direction of the resultant force. F=ma.
An elevator with a mass of 2500 kg is lifted by its motor a distance of 50 meters within 6 seconds. What is the power rating of the motor in Watts?
P=(WORK)/t
P=204,375 W or 204 KW
Series of operations that transforms industrial materials from a raw material state into finished parts or products.
Processing
What is the difference between Strength and Toughness?
Strength is the stress needed to cause permanent deformation; toughness is the energy necessary to fracture, area under the stress strain curve.
What defect is this?

Substitutional
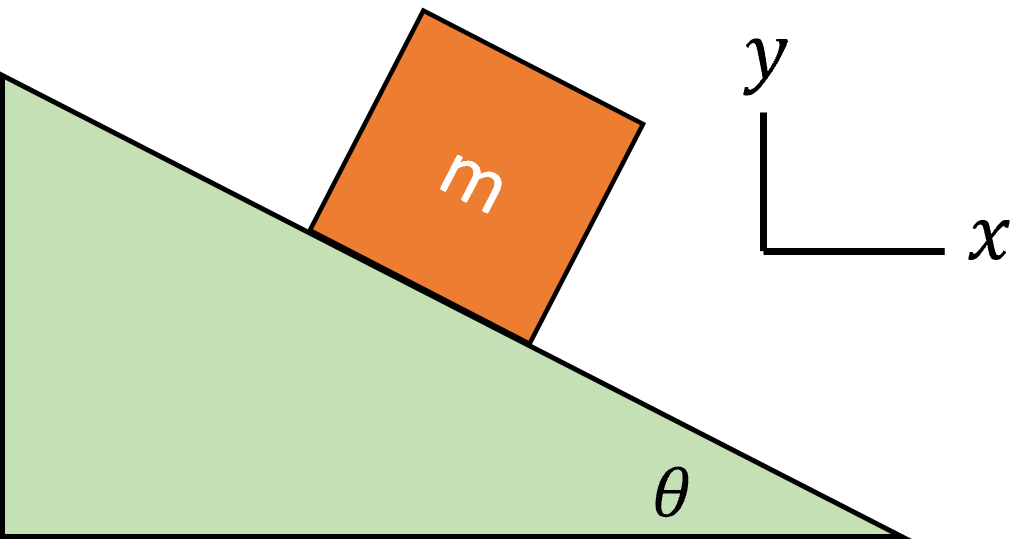
Draw the Free Body Diagram. Consider Friction.
A pendulum with a mass of 100kg reaches a maximum height of 3m. What is its velocity at the bottommost point in its path?
KE=1/2mv^2, PE=mgh, KE_1+PE_1=KE_2+PE_2
7.67m/s
Difference Between Materials Science and Materials Engineering?
Material Science: Determines relationship between structure and properties of materials. R&D new materials.
Material Engineering: With application in mind, develops new products/components. Develops new materials processing techniques, to suit application
A material property that involves the materials physical response to stress & strain, typically by external forces.
Mechanical Properties
What are the 3 “solid materials” and what are the main bonding types (primary & secondary) associated with them?
Metals: Metal Bonds
Polymers: Covalent Bonds and Van der Waals
Ceramics: Ionic Bonds
What is the difference between statics and dynamics.
Dynamics: Velocity changes, sum of forces: F=ma
A Cart rolling down an incline for 6s, has an acceleration of 5m/s2. If the car has an initial velocity of 3m/s, what is the final speed?
v_f =v_0 + at
33m/s
Highest Elongation: A
Stiffest: C
Strongest: B
Toughest: A
Based on Stress-Strain Curve below, rank the toughness and stiffness of Materials A, B and C.

C) Toughness A<B<C; Stiffness A>B>C
What kind of fracture is this?

Ductile Fracture
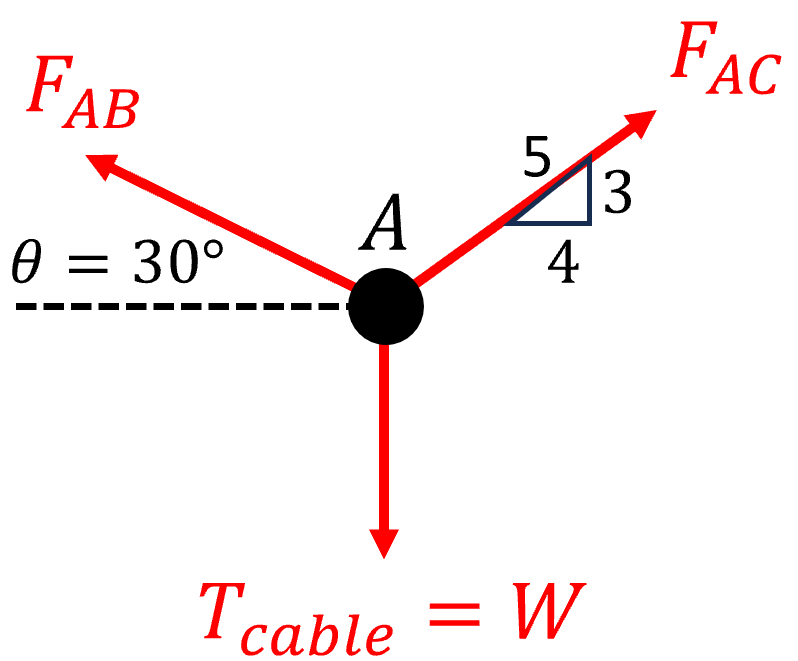
Draw the Free body Diagrams for Point A and the Crate. What is the Tension in the Cable directly holding the Create?
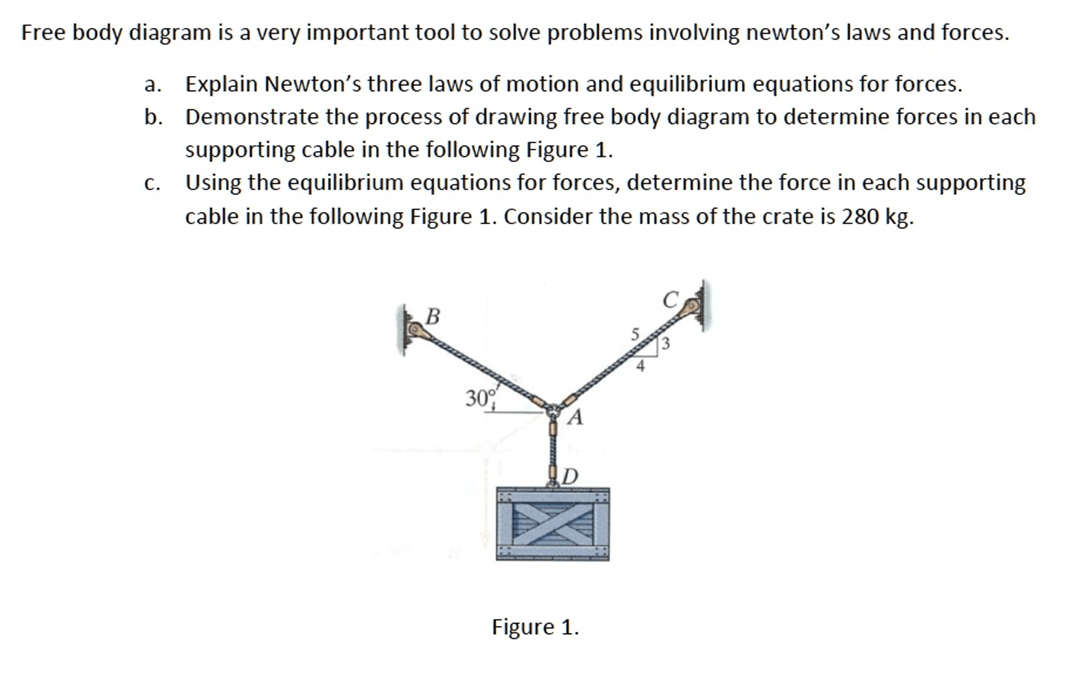
Tension in Cable AD=2747 N
Driving along a steady speed of 26m/s and suddenly see a car stop ahead from you. Breaks can produce acceleration of -2.5m/s² but it takes time to get the foot from the gas to the brake pedal. How much time do you have till the car comes to rest, and how much distance will it take to stop?
v_f=v_i+at
v_f^2=v_i^2+2aDeltax
t = 10.4 s
x=135.2 m
