One of these d orbitals lies on the x, y, or z axes
What is dz2 or dx2-y2?
This element is the most electronegative
What is fluorine?
A head-to-head overlap of orbitals characterizes this type of bond
What is a sigma bond?
This term means a substance has gained electrons
What is reduction?
This logarithmic scale typically ranges from 1 to 14
What is the pH scale?
Coordination compounds are characterized by this type of bond
What is coordinate covalent / dative?
The Na+ ion has this number of electrons
What is 10?
This element has the largest atomic radius
What is francium?
Two parallel p orbitals make this type of bond
What are pi bonds?
Electrons flow in this direction in an electrochemical cell
What is from anode to cathode?
This classification defines an acid as a proton donor
What is a Brønsted-Lowry acid?
This chemist is referred to as the father of coordination compounds
Who is Alfred Werner?
There are seven of this type of orbital
What are f orbitals?
This lamp analogy helps explain the periodic trend of...
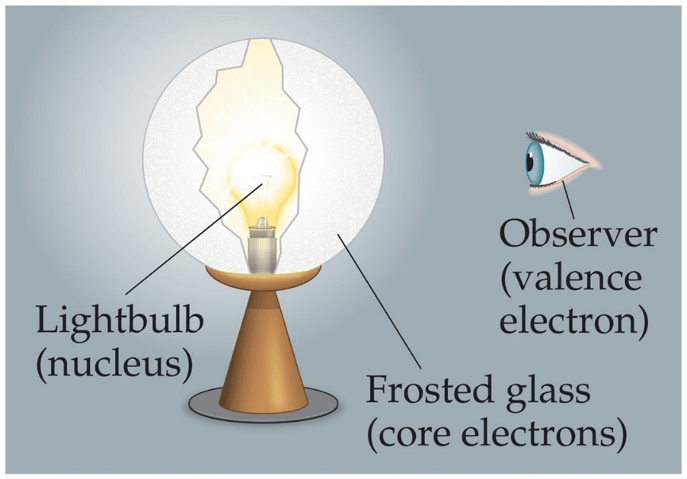
What is effective nuclear charge?
This molecular geometry is characterized by 120 and 90 degree bond angles
What is trigonal bipyramidal?
In a spontaneous reaction, this value is negative
What is Gibbs free energy?
This classification defines an acid as an electron pair acceptor
What is a Lewis acid?
In tetrahedral geometry, this set of d orbitals is lower in energy
What is the eg set?
These two first row transition metals have anomalous electron configurations
What are Cr and Cu?
What are the chalcogens?
Valence bond theory predicts the hybridization of SeF6 is...
What is d2sp3?
The oxidation state of Mn in MnO4- is...
What is +7?
At 25 °C, this constant is equal to 1 xx 10^-14
What is Kw, the autoionization constant for water?
Name the compound: CoBr2Cl(NH3)3
What is triamminedibromochlorocobalt(III)?
This type of atomic orbital is described by the angular momentum quantum number 1
What are the p orbitals?
These three periodic trends increase up and to the right on the periodic table
What are electronegativity, electron affinity, and ionization energy?
These atomic orbitals form the molecular orbital...
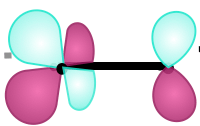
What is π*?
In an electrochemical cell, this component is required to complete the circuit from anode to cathode
What is the salt bridge/porous disc?
This theory can be used to qualitatively predict reaction equilibria and naturally occurring compounds
What is hard/soft acid/base theory?
For a compound that appears violet, its orbital splitting can be described as...
What is high spin / weak field / small delta?