True or False (and Why or Why Not): Once a nerve cell is grown, it is static, maintainting the same state and connections for its lifetime.
False: Neurons grow or shrink / retract their dendrites / dendritic spines based on experience and the necessity of a connection. With age, the fatty myelin that wraps around axons deteriorates. The number of synapses between neurons also changes, which can affect learning and memory.
Which of these is NOT a function of the midbrain?
A) Emotion
B) Sleep
C) Motor Control
D) Temperature
A) Emotion
The midbrain is mainly involved in sleep/arousal, temperature, and motor control. The reticular formation is a major player in the physiology of comas and also drives the thalamus, which is the relay station of all incoming motor and sensory information.
What is required for neurotransmitter release from vesicles
A) Chloride
B) Magnesium
C) Calcium
D) Potassium
C) Calcium

Caffeine stimulates the release of what?
A) Adenosine
B) Monoamines
C) Catecholamines
D) Indolamines
C) Catecholamines
Caffeine blocks adenosine release and adenosine typically inhibits catecholamines. Therefore caffeine will stimulate catecholamines. Monoamines include catecholamines and indolamines. Indoleamines are serotonin.
Two types of functional neuroimaging we have discussed include:
A) fMRI; MRI
B) CT; MRI
C) PET; CT
D) PET; fMRI
D) PET ; fMRI
- Positron emission tomography (PET)
- Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)
- Electroencephalography (EEG)
- Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
- Functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS)
- Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)
- Functional ultrasound imaging (fUS)
What makes up the blood-brain barrier?
A) Microglia
B) Meninges
C) Astrocytes
D) Both B & C
C) Astrocytes
Astrocytes help in delivering the nutrients neurons require for function from the blood, such as oxygen, while also preventing the neurons from making direct contact with the blood to avoid damage to the neurons. The meninges (Dura, Arachnoid, Pia) are also involved in the blood brain barrier, as they cover the brain and help separate the brain from the blood
In the brain, how is gray and white matter arranged?
A) Gray matter is more central, white matter is more in the periphery
B) Gray matter is more peripheral, white matter is more central
C) Gray matter and white matter are equally distributed throughout the brain
D) The brain only consists of gray matter
B)
In the brain, white matter is more central, and gray matter is more peripheral. It is important to realize that this arrangement is opposite in the spinal cord:
Brain: white matter is central, gray matter is peripheral
Spinal cord: white matter is peripheral, gray matter is central
True or False (and Why or Why Not): Potassium leak channels are always open and contribute to maintaining the resting membrane potential.
True! They do not open and close like voltage-gated potassium channels!! K+ leak channels help to maintain the resting membrane potential. An example includes when hyperpolarization (undershoot) occurs after an action potential where K+ is able to rush in through the leak channels to make the cell more positive and help re-establish resting membrane potential. This is a situation of K+ ions flowing inward along their electrical gradient instead of outward due to diffusion (since K+ is normally higher inside the cell). The Na+/K+ pump also helps to maintain the resting membrane potential as more positive ions are pumped out than pumped in (3 Na+ out and 2 K+ in).
All of the following will occur with consistent drug exposure EXCEPT:
A) Buildup of delta FosB
B) Withdrawal symptoms
C) Tolerance
D) Increased dopamine in the ventral tegmental area
B)
Withdrawal symptoms will only occur if the person stops taking the drug, not if they are consistently taking the drug.
Delta FosB builds up within neurons with each drug exposure, and will continue to be activated for several years even if the person stops taking drugs. It remodels the nucleus accumbens, and enhances things like craving, which leads to a reinforcement of addiction (hard to stop)
Tolerance occurs with repeated use as the body adjusts to the presence of the drug and its effects, which is why addicts will have to take more and more of the substance over time to get the same desired effect
The ventral tegmental area (VTA) is part of the mesolimbocortical dopamine system, which is the major reward system of our brain. Abused drugs will increase dopamine in the VTA
What type of imaging and view/cut is this?
A) MRI scan/ horizontal
B) MRI scan/ coronal
C) CT scan/horizontal
D) CT scan/ coronal
C) CT Scan / horizontal
Cells in the notochord promote differentiation of cells in the spinal cord into:
A) Sonic Hedgehog
B) Motor neurons
C) Sensory neurons
D) All of the above
B) Motor Neurons
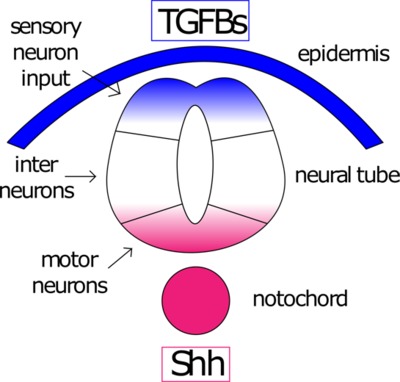
In the spinal cord, how is gray and white matter arranged?
A) Gray matter is more central, white matter is more in the periphery
B) Gray matter is more peripheral, white matter is more central
C) Gray matter and white matter are equally distributed throughout the spinal cord
D) The spinal cord only consists of white matter
A)
Myelinated axons are what make up white matter. The somas of neurons makes up the gray matter. In the spinal cord, gray matter will be more central, and white matter will be more in the periphery.
A sushi enthusiast goes to a japanese restaurant and has fugu, moments later he collapses. What mechanism of action has occurred on a cellular level?
A) Tetrodotoxin activated nerve action by binding to voltage gated K channels
B) Tetrodotoxin blocks nerve action by binding to voltage gated K channels
C) Tetrodotoxin activated nerve action by binding to voltage gated Na channels
D) Tetrodotoxin blocks nerve action by binding to voltage gated Na channel
D) Tetrodotoxin blocks nerve action by binding to voltage gated Na channel
There will be minute differences between questions, make sure to differentiate between them and think through them!
A person is injected with Curare prior to an abdominal surgery. Which of the following things would most likely occur?
A) His breathing rate would increase
B) His heart would slow down
C) He would fall asleep
D) He would be unable to move his arms and legs
D) He would be unable to move his arms and legs
Why? Curare is a ACh antagonist- it blocks the nicotinic receptors (which are ionotropic and excitatory), causing paralysis by blocking NMJ activity. It is commonly used as an anesthetic prior to abdominal surgery.
Put the stages of CNS development in order.
- Neuronal cell death
- Cell migration
- Synaptogenesis
- Neurogenesis
- Synapse Refinement
- Differentiation
Neurogenesis: Mitosis will generate precursor stem cells
Cell migration: The precursor cells will go to their final destinations by going along radial glial cells
Differentiation: Cells differentiate into either neurons or glial cells
Synaptogenesis: Synaptic connections form
Neuronal Cell Death: Nerve cells die via programmed cell death mechanisms
Synapse refinement: Synapses will start to “fine tune” based on experience → some weaken, some strengthen
When a neuron is at rest, what is the force that will push sodium out of the cell?
A) Electrostatic potential
B) Graded potential
C) Concentration potential
D) Sodium potassium pump
D) Sodium potassium pump
Remember: 3-2-1 NOKIA → 3 Na+ Out, 2 K+ in, 1 ATP required
At rest, there will be more sodium outside the neuron than inside, and more potassium inside the neuron than outside. So, to push sodium out of the cell, sodium needs to go against its concentration potential.
Key takeaway: At rest, the sodium potassium pump constantly works to maintain the resting potential by pumping 3 Na+ out and 2 K+ in.
Since ganglion refers to cell bodies in the (CNS/PNS), preganglionic neurons must be in the (CNS/PNS), and postganglionic neurons must be in the (CNS/PNS).
Thus, (preganglionic/postganglionic) neurons make up the spinal cord, a component of the (CNS/PNS), and innervate the (sympathetic/parasympathetic) chain.
Since ganglion refers to cell bodies in the (CNS/PNS), preganglionic neurons must be in the (CNS/PNS), and postganglionic neurons must be in the (CNS/PNS).
Thus, (preganglionic/postganglionic) neurons make up the spinal cord, a component of the (CNS/PNS), and innervate the (sympathetic/parasympathetic) chain.
What would you treat with a D2 antagonist?
A) Depression
B) Schizophrenia
C) Narcolepsy
D) Migraine
B) Schizophrenia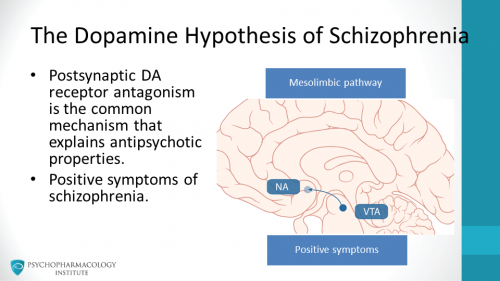
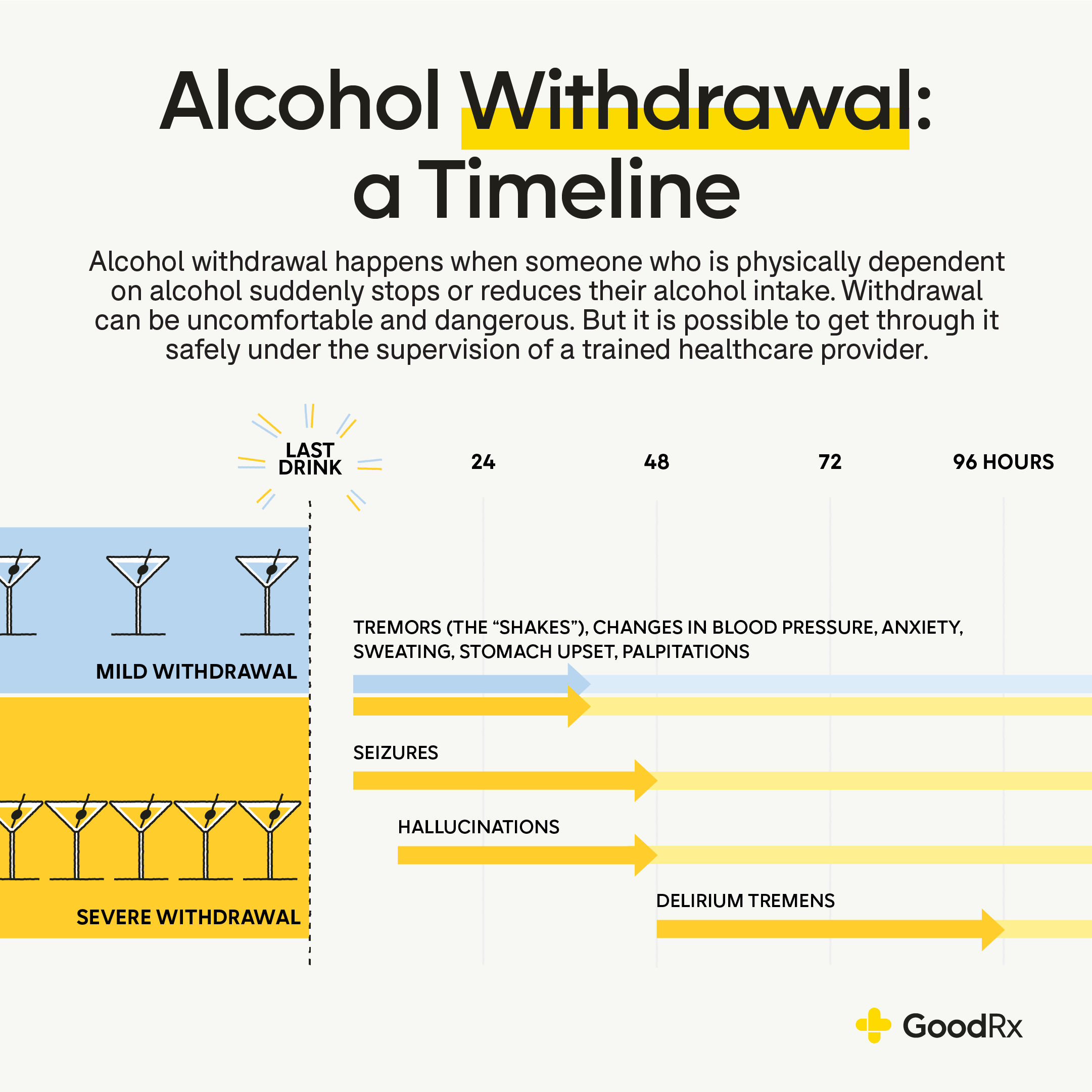
You are an extreme alcoholic and your friends force you to go cold turkey. After about 50 hours you begin having seizures. This is because your nervous system has:
A) up regulated glutamate receptors
B) up regulated acetylcholine receptors
C) down regulated glycine receptors
D) up regulated GABA receptors
A) up regulated glutamate receptors
Select ALL of the following that are correct about the neuronal membrane:
A) It is made of a lipid bilayer with hydrophobic heads and hydrophilic tails.
B) All substances require channels to move from one side to another.
C) It is normally impermeable to water.
D) Some proteins embedded in the membrane use ATP to move substances across it.
C & D
C) It is normally impermeable to water.
D) Some proteins embedded in the membrane use ATP to move substances across it.
A -- It is made of a lipid bilayer with hydrophobic TAILS and hydrophilic HEADS, not the other way around.
B -- SOME substances require channels to move from one side to another, such as water, ions, and large molecules.
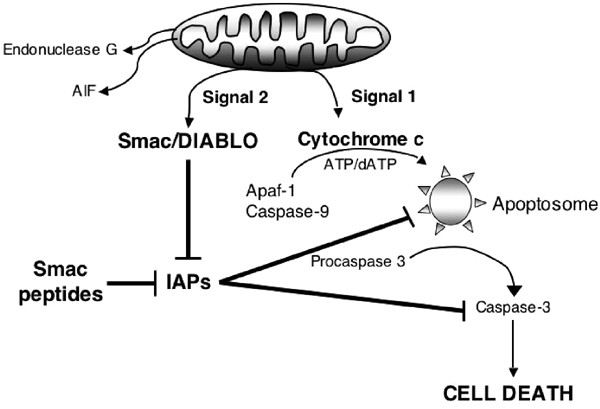
How does Diablo promote apoptosis?
A) Binds to and inhibits IAPs, leading to increased caspase activity
B) Binds to and activates IAPs, leading to increased caspase activity
C) Binds to and activates IAPs, leading to decreased caspase activity
D) Binds to and inhibits IAPs, leading to decreased caspase activity
A)
DIABLO (direct inhibitor of apoptosis-binding protein) is a proapoptogenic mitochondrial protein that is released to the cytosol in response to diverse apoptotic stimuli, including commonly used chemotherapeutic drugs.
If a patient has a lesion ventral to the occipital lobe, what effects might the lesion cause?
A) Vision loss
B) Abnormal gait
C) Abnormal hearing
D) Loss of Cognitive Function
B) Abnormal gait
The area that the question is asking about is the cerebellum which works with motor function. Vision is associated with the occipital lobe. The area in purple is the occipital lobe and the area in brown is the cerebellum.
Excitotoxicity is caused by an excess release of what?
A) GABA
B) Glutamate
C) Carbon Monoxide
D) Serotonin
E) A and B
B) Glutamate 
Barbituate’s block _____ channels and activate ________ channels
A) Potassium / Magnesium
B) Sodium / Potassium
C) Sodium / Chloride
D) Chloride / Sodium
Barbituate’s block SODIUM channels and activate CHLORIDE channels
What are 3 main differences between a graded potential and an action potential?
Graded potentials start at the dendrites and will diminish as it spreads throughout the cell body. They do not usually set off voltage gated ion channels on their own. If the sum of the graded potentials cause the membrane at axon hillock to reach around -40mV (threshold), an action potential will be fired.
Action potentials start at the axon hillock and are "all or nothing" so they do not dissipate away. They always have the same amplitude and pattern for a particular cell, where the intensity of a signal is based on an increased frequency of fired action potentials, not a difference in the action potentials themselves.