What is the most common type of cell that makes up the brain?
(+50 points: Is gray or white matter more common?)
Neurons!
(+50 points: White matter)
.jpg?width=960&name=gray%20matter,%20white%20matter%20(1).jpg)
Is phrenology (the study of the conformation of the skull and head as a measure of intelligence) an accurate field in psychology?
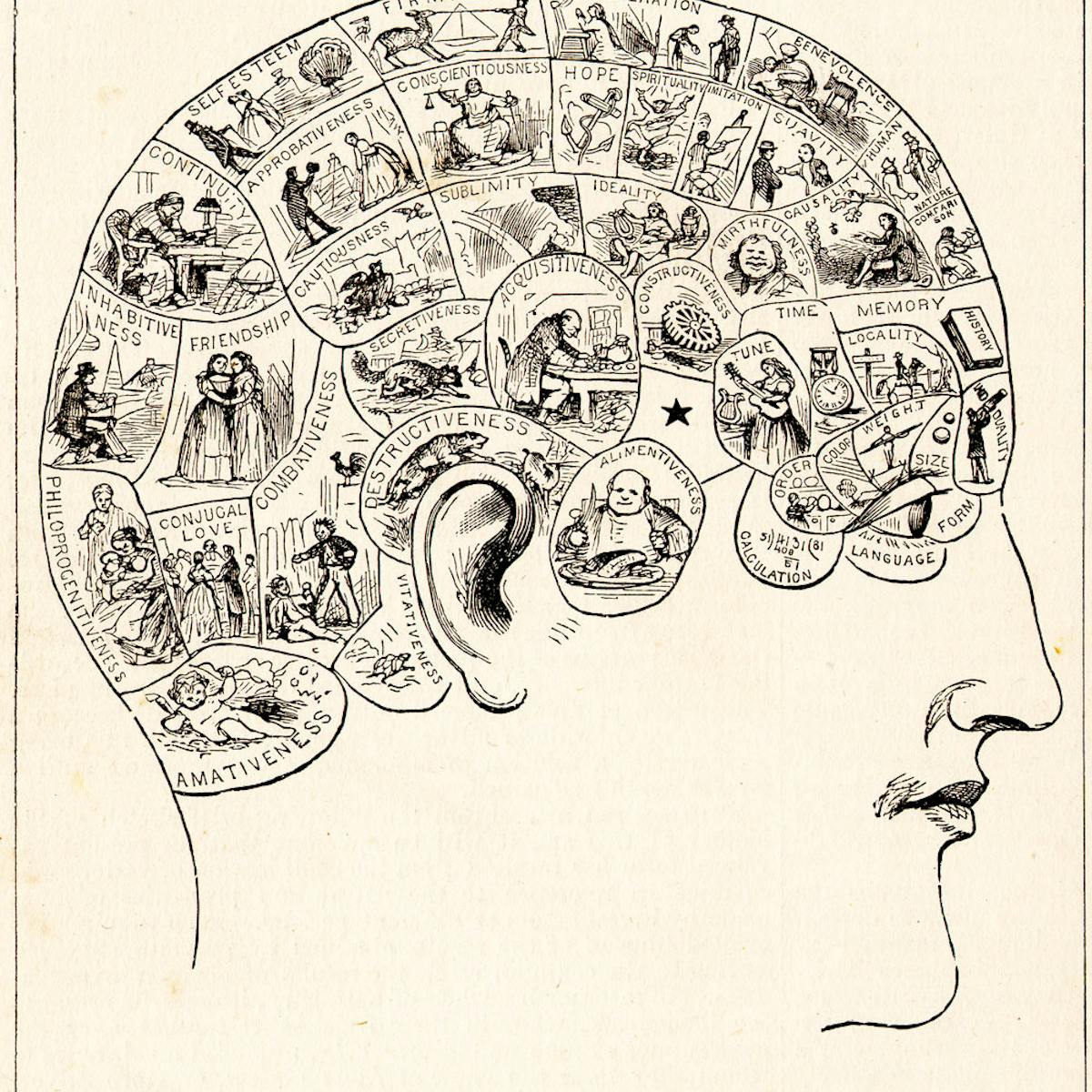
NO!
Having arbitrarily selected the place of a faculty, Franz Joseph Gall (1758-1828) examined the heads of his friends and casts of persons with that peculiarity in common, and in them he sought for the distinctive feature of their characteristic trait. Some of his earlier studies were made among inmates of jails and lunatic asylums, and some of the traits that he presumed to detect were “criminal.”
Who does this skull belong to?

Phineas Gage.
~His left frontal lobe was severely damaged when a railroad tamping iron (giant metal stick) misfired, shooting through the skull of young Phineas. His family and close friends reported that his behavior became listless and aggressive. He was fully conscious during his accident, and died years later.
What is persuasion?
Persuasion is the process by which a person’s attitudes or behavior are influenced by other people.
Memory is the ability to take in information, encode it, store it, and retrieve at a later time. What are the two KINDS of memory?
Short-term memory (aka working memory) & long term memory
Long-term memory can be subdivided further into explicit/declarative memory, which is consciously recalled AND implicit/procedural memory, which is automatic and resistant to forgetting.
Name any two parts of the brain.
Parietal Lobe, Frontal Lobe, Temporal Lobe, Occipital Lobe, Cerebellum, Brain Stem
What is psychology?
The study of the human mind and behavior?
~Psychologists try to understand, define, and predict human behavior and all of the various processes associated with the mind.~
Dr. William Beecher Scoville, a Hartford neurosurgeon, stood above an awake H.M. and skillfully suctioned out the seahorse-shaped brain structure called the hippocampus that lay within each temporal lobe.
What was the other outcome of this drastic surgery?

Henry Molaison’s surgery involved the removal of large parts of the hippocampus on both sides of his brain and the result was that he was ALMOST ENTIRELY UNABLE TO STORE any new information in LONG-TERM MEMORY.
~Up until then, it had not been known that the hippocampus was essential for making memories, and that if we lose both of them we will suffer a global amnesia. Once this was realized, the findings were widely publicized so that this operation to remove both hippocampi would never be done again.~
The human brain is powerful but subject to limitations. Cognitive biases are often a result of your brain's attempt to simplify information processing. Biases often work as rules of thumb that help you make sense of the world and reach decisions with relative speed. Why can cognitive biases be bad?
Poor decisions and bad judgements. These biases can change the way you think, what you remember, what you listen to/what you ignore, you can make an illogical snap-decision that is too fast and excludes something or misses the entire idea.
When you are making judgments and decisions about the world around you, you like to think that you are objective, logical, and capable of taking in and evaluating all the information that is available to you. Unfortunately, these biases sometimes trip us up, leading to poor decisions and bad judgments.
What is gratitude, and what is one thing it can do for each of us?
Gratitude is the quality of being thankful. It is a readiness to show appreciation for and to return kindness.
It can help relieve stress and pain.
It can improve our health over time.
It can help those with depression, causing structural changes in the same part of the brain that were active in the experiment.
We all know about Aristotle's 5 senses (see, taste, hear, smell, touch). What is another sense beyond these 5 that all humans have?
Proprioception (the sense that lets us perceive the location, movement, and action of parts of our bodies).
Interoception (the sense responsible for understanding and feeling what is going on inside our bodies).
How long has psychology been around?
Studies of the mind and behavior of humans has been an ongoing phenomenon, even prior to the term "psychology" being used. The first example was an Ancient Egyptian manuscript describing the symptoms of clinical depression in 1500 BC. The term was coined in the late 15th century, early 16th century AD.
So, about 3,500 years!
What happened to Oliver Sacks?
He suffered from prosopagnosia, or "face blindness."
Face recognition is one of the most important social perception skills. Damage to any of the face processing regions of the brain inhibits our ability to identify and store patterns for thousands of individual faces. For those with prosopagnosia, the new method for recognizing faces depends on the less sensitive object-recognition system.
What do these pictures show an example of?
Scarcity, which is one of the techniques of persuasion. Essentially, people want more of those things they can have less of.
~When British Airways announced in 2003 that they would no longer be operating the twice daily London—New York Concorde flight because it had become uneconomical to run, sales the very next day took off.~
What is empathy and why is it important?
Empathy is the ability to recognize, understand, and share the thoughts and feelings of another person, animal, or fictional character. Developing empathy is crucial for establishing relationships and behaving compassionately.
Give 3 examples of different kinds of nonverbal communication.
Nonverbal communication types include facial expressions, gestures, paralinguistics such as loudness or tone of voice, body language, proxemics or personal space, eye gaze, haptics (touch), appearance, and artifacts.
How does one gather scientific data on behavior and the human mind?
Through the Scientific Method, using naturalistic observation & experiments.
Who is Koko and why is her behavior noteworthy?
Koko is a gorilla, who led to major revelations in the field of psychology regarding animal empathy and communication.
Research and work with Koko, and other gorillas, has revealed that great apes have language skills similar to small children.
300 points: What is the experiment Ivan Pavlov did with dogs?
200 points: What did we learn from it?
in Pavlov's classic experiment, the smell of food was the naturally occurring stimulus that was paired with the previously neutral ringing of the bell. Once an association had been made between the two, the sound of the bell alone could lead to a response.
He discovered what is called "classical conditioning," which is a learning process in which an association is made between a previously neutral stimulus and a stimulus that naturally evokes a response.
Why are emotions important? Give two reasons.
Meaningful/connected relationships, internal/moral compass, affect our mood and behaviors, help in decision making, give us meaning/purpose in our lives.
Feeling emotions is a large part of being human, and is what brightens and deepens our lives and relationships with those around us.
400 points: What is the name of the neurotransmitter known as the "feel-good/cuddle hormone"?
100 points: What does this neurotransmitter do for us?
Oxytocin: Face-to-face interaction releases this feel-good hormone that amplifies empathy. When we interact face-to-face oxytocin is released in our bodies and we experience heightened empathy, and we may understand the other person better.
What is the APA? What do they do?
American Psychological Association; they gather scientific, psychological data from around the world.
What is significant about Kim Noble?
She has what is called "dissociative identity disorder," which used to be called "multiple personalities."
Usually, in those suffering from DID, the dominant personalities have some awareness of the other characters: maybe they hear voices or they can see what is going in even when they’re not in control.
But with Kim’s condition, there is no ‘seepage’ between the personalities. They operate independently of each other — sharing the same body but none of the same experiences. Today, there are more than 20 alter egos who can appear at any given moment. Alongside the sensible, no-nonsense Patricia, there’s Abi, who’s single and desperately looking for love, Bonny, a mother with a young daughter, and Salome, a devout Roman Catholic. There’s a little boy called Diabalus who only writes in Latin, and a depressed twenty-something called Ken.
Name three examples of cognitive bias.
Confirmation bias, anchoring, overconfidence bias, gambler's fallacy, fundamental attribution error, hindsight bias, and more...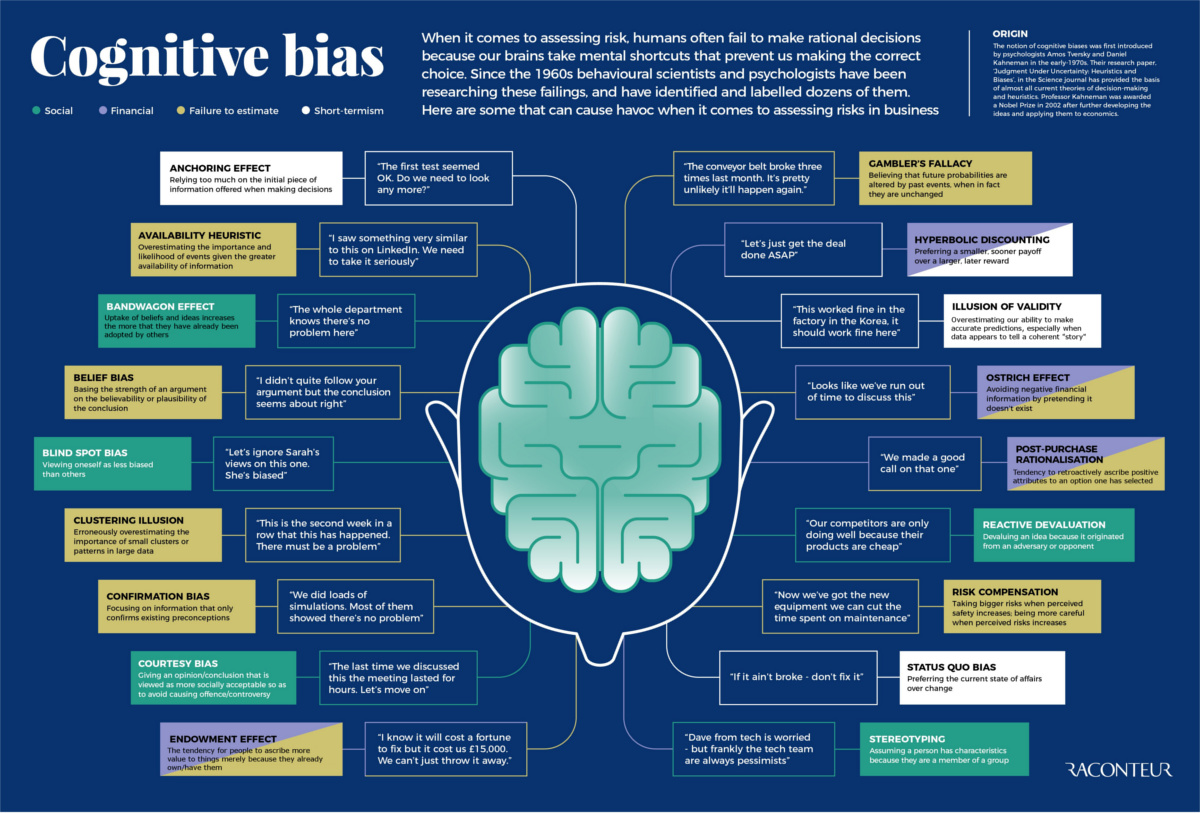
Give four of the many areas of Gardner's theory of Multiple Intelligences.
Visual-spatial, Naturalistic, Musical, Logical-mathematical, Interpersonal, Bodily-kinesthetic, Linguistic-verbal, Intrapersonal.
