The nervous system is made up of 3 different systems. Name all 3.
What are the Central, Peripheral, and Autonomic Nervous Systems
______________ are glial cells that are responsible for the formation and maintenance of myelin in the CNS vs. _____________ are responsible for formation and maintenance of myelin in the PNS.
What are Oligodendrocytes & Schwann cells.
Identify anterior vs posterior. Additionally, identify if this is the R or L hemisphere.
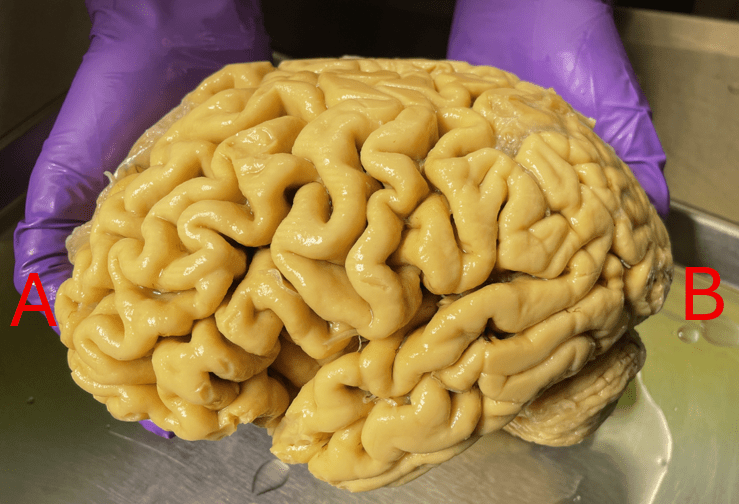
A: anterior
B: posterior
Left hemisphere
Name the structure labeled "A"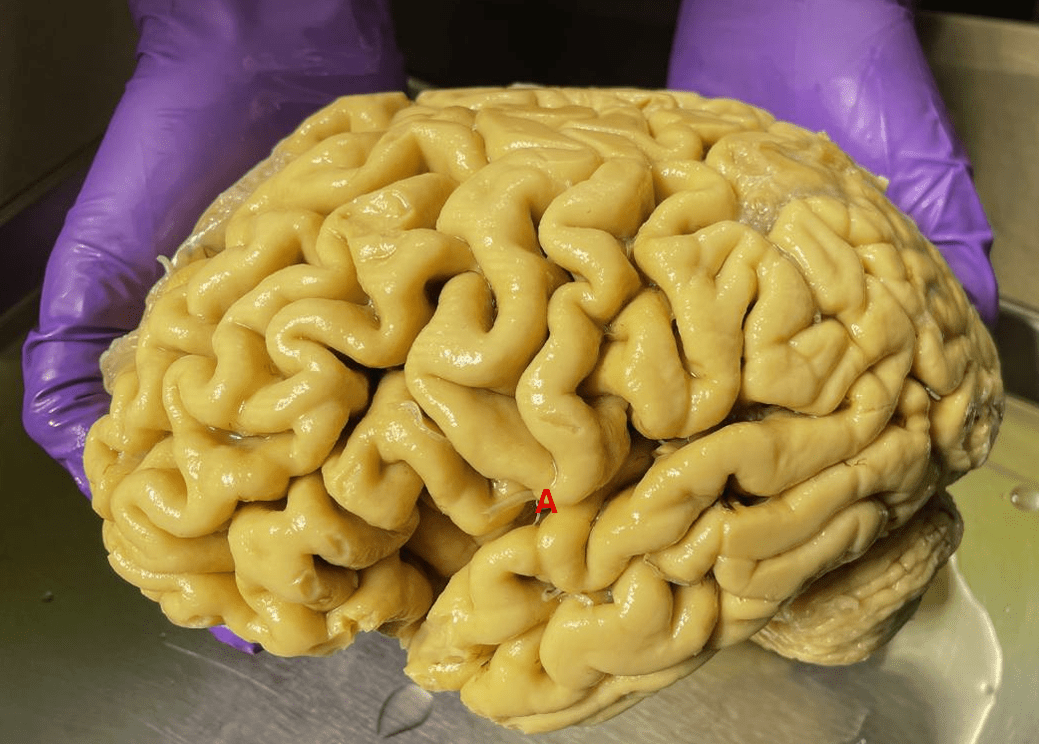
What is the lateral fissure
Where in the neuron determines if a message/impulse is sent?
What is the cell body.
Due to the presence of neuronal cell bodies, most of the synapses in the CNS occur in the ______ matter.
What is the gray matter.
Ependymal cells create the lining of fluid filled spaces in the __________ and __________.
What are the brain and spinal cord
This is a mid-sagittal view of the brain. Identify which letters are anterior vs. posterior. 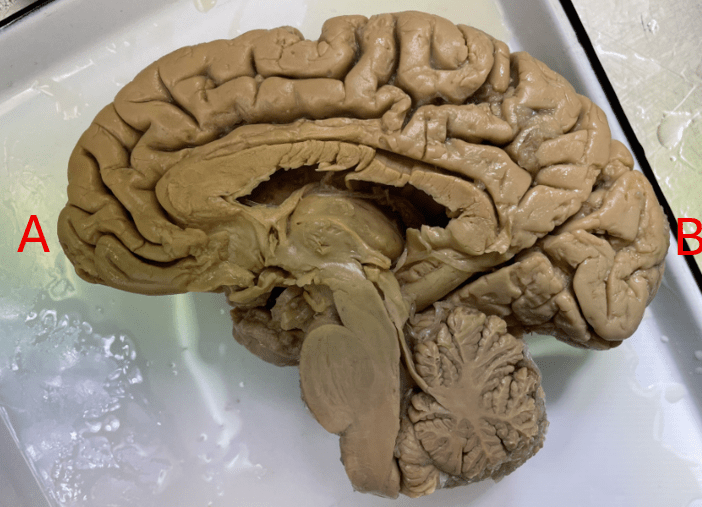
A: anterior
B: posterior
Name the layer of meninges labeled here: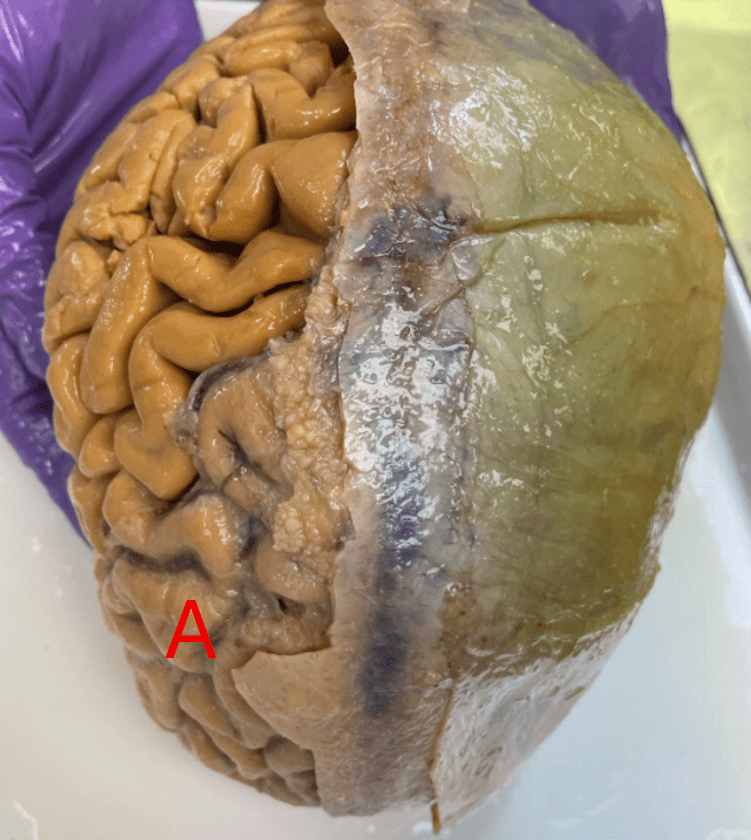
What is arachnoid mater
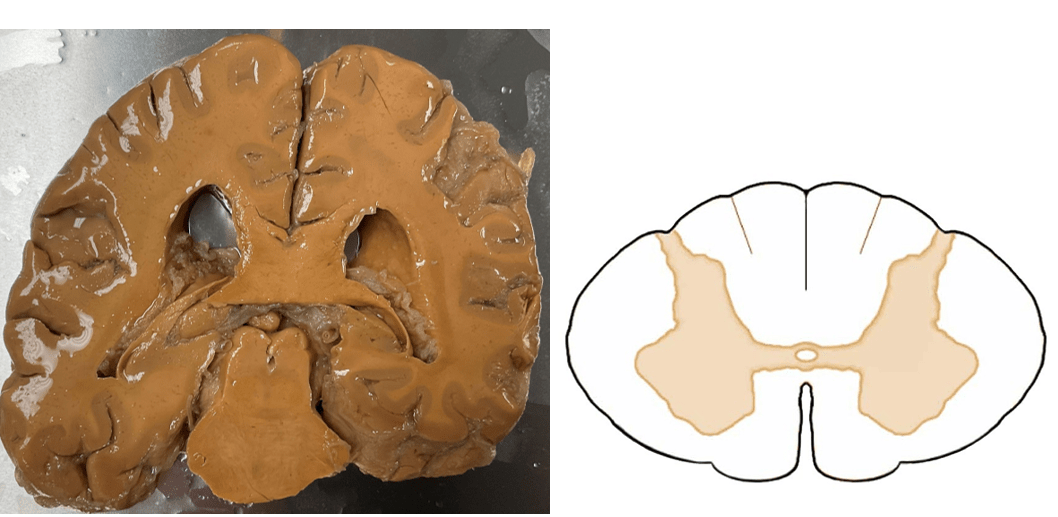
In the spinal cord cross section below, identify structures A, B, and C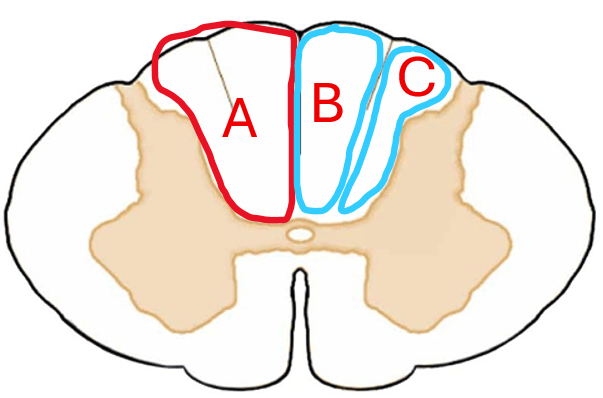
A: posterior funiculus
B: gracile fasciculus
C: cuneate fasciculus
Cranial nerves are a part of the _____________ nervous system.
What is the peripheral nervous system.
Mr. Smith arrives to your outpatient clinic s/p resection of L parietal lobe astrocytoma. He presents with R hemiparesis due to involvement of ______ (upper or lower) motor neurons.
What are Upper Motor Neurons
Is this the right or left hemisphere?
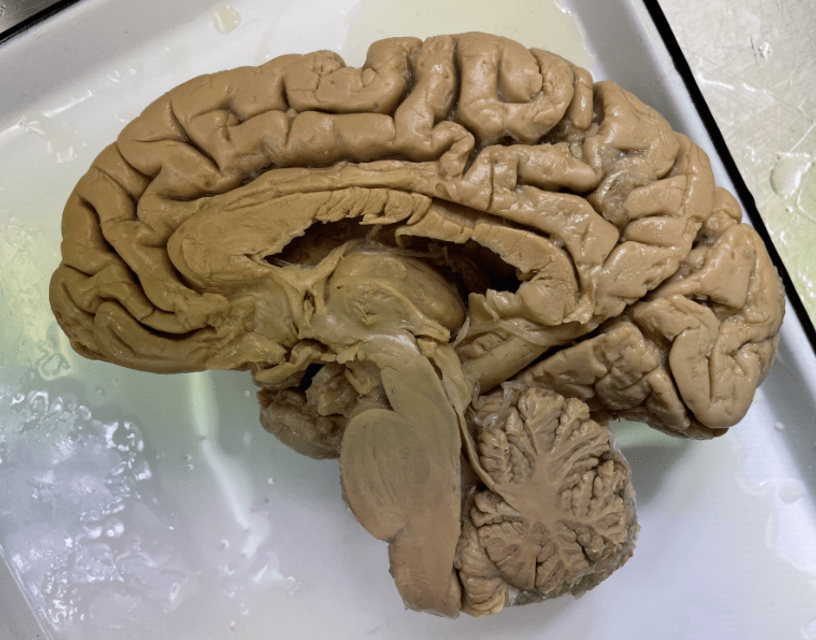
What is the right hemisphere?
A portion of the parietal and frontal lobes is resected. Identify the structure that lies on the superior surface of the lateral fissure, marked "A".
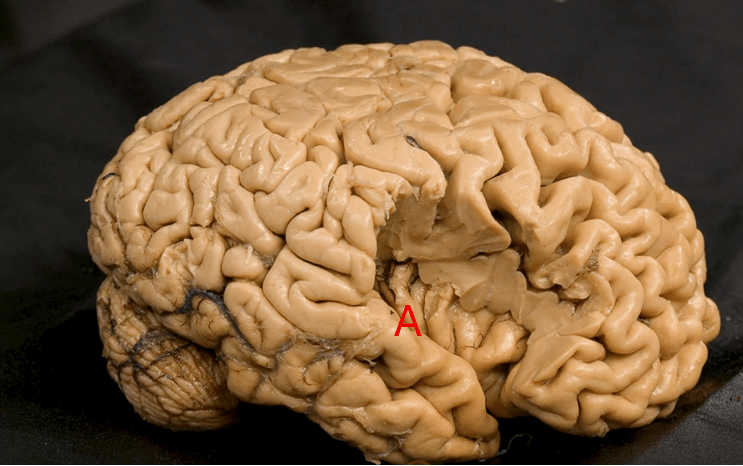
What is the transverse temporal gyri
A neuron receives a signal from an axon. The type of _____________ released into the synaptic cleft will determine if the signal inhibits or excites the neuron.
What is neurotransmitter.
Upper motor neuron cell bodies are located in the _________________ and connect to either the brain stem motor nuclei or the ____________.
What are the cerebral cortex & anterior horn of SC.
Ms. Adams arrives to your clinic with a diagnosis of relapse remitting multiple sclerosis (MS), which is a disease that causes destruction of ____________ (these cells) causing _____________ (this phenomenon).
What is oligodendrocytes & demyelination
Is this an anterior or posterior view?
What is posterior?
Name the sulcus labeled "A" and the two lobes it separates.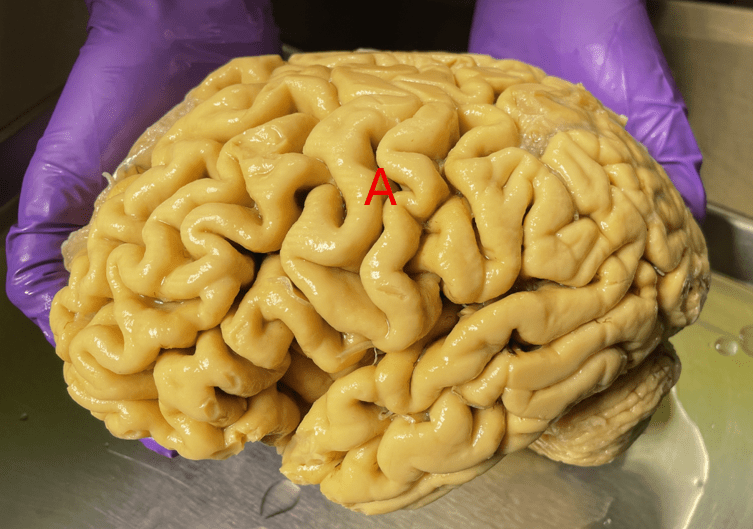
What is the central sulcus, which separates the frontal and parietal lobes.
The type of neuron that transmit signals to our skeletal muscle fibers are _________ neurons.
What is multipolar
George arrives to your outpatient clinic with orthopedic injuries related to his poliomyelitis diagnosis. In Polio, the anterior horn cells of the spinal cord are destroyed, causing flaccid paralysis. Is polio considered an upper or lower motor neuron lesion?
What is a Lower Motor Neuron lesion.
35 y.o Mary is admitted to acute care with progressive weakness and numbness starting in her legs that has now progressed to her arms and hands. She is diagnosed with acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (AIDP) which is a autoimmune condition affecting the __________ nervous system, particularly the _________ cells.
What are peripheral & Schwann.
This is an ______ view of the brain. Orient yourself and identify which letter correlates with anterior, posterior, right, and left.
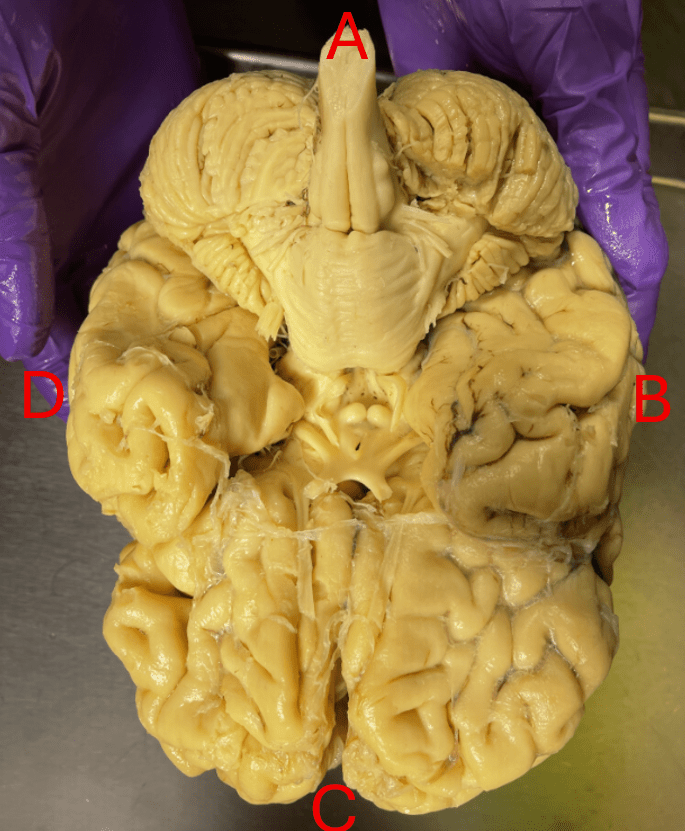
What is inferior view.
A: posterior
B: right
C: anterior
D: left
Name this structure, identify R vs. L.
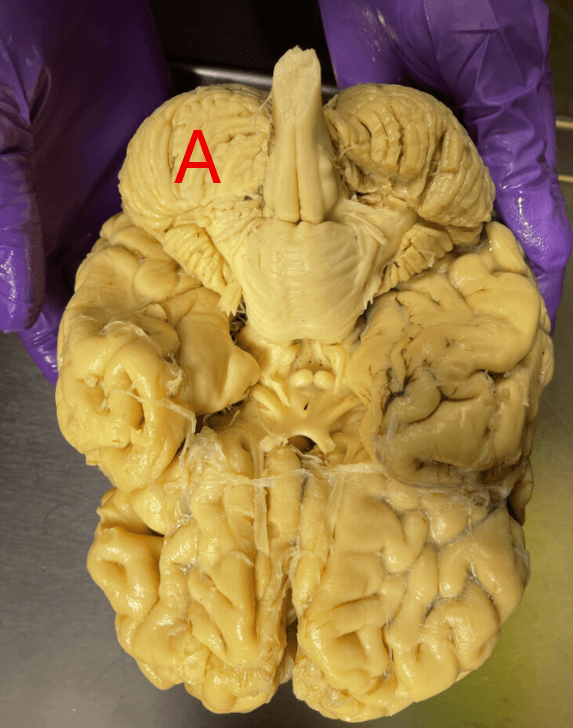
What is the left cerebellar hemisphere
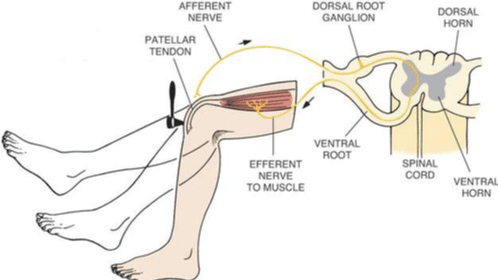
During a deep tendon reflex test, a reflex circuit immediately occurs to create the motor response, causing the knee to extend. Simultaneously, a relay circuit is transmitting information to the brain to provide us sensory information about the input. If a person has no motor response to the test, this may indicate a lesion to the ________(upper or lower) motor neurons.
What is lower