Simply stated, statistics is the study of __________________.
Data
Which of the following is NOT a categorical variable?
Color of a person’s eyes
Model of a truck
Breed of a dog
Weight of a horse in pounds
Weight of a horse in pounds
Bivariate data involves the analysis of _________________.
Two types of variables
The number of times an observation occurs in a data set is known as what?
Frequency
In probability and statistics, what do we call the imitation of chance behavior based on a mathematical model?
Simulation
Which of the following is NOT part of the statistical process?
Collecting Data
Viewing Websites
Summarizing Data
Drawing conclusions
Viewing Websites
Variables that are quantities, counts, or measurements are what type of data?
quantitative
Which of the following type of graphs is NOT representative of univariate data?
Scatter plot
Box-and-whisker plot
Histogram
Stem-and-leaf plot
scatter plot
23 out of 92 students got to school each day by car. What is the relative frquecy of students riding the car
25 %
In probability, models are used to represent what?
Random Event
A certain college with a total enrollment of 5000 students wants to know what proportion of its students use the library at least 10 hours a week. The college asked 100 students whether they spend at least 10 hours per week in the library or not.
The individuals of the study are ____________________.
100 Students
Of the data Mr. Jones collects from his Algebra 2 class, which piece of data is a categorical variable?
County of Residence
Number of people in family
Numerical GPA in previous school year
Numerical Grade in Algebra 1
County of Residence
One of the main purposes of bivariate data is to
how are the two variable relate
In statistics, relative frequencies are used in order to provide
____________________ in the scenario being studied.
Context
Which of the following is not a “Chance Device”?
Dice
Cards
A Coin
A Highway
A Highway
A certain college with a total enrollment of 5000 students wants to know
what proportion of its students use the library at least 10 hours a week.
The college asked 100 students whether they spend at least 10 hours per
week in the library or not.
What is the population?
5000
_____________________________ data is most often represented by bar
graphs and pie charts
Categorical
All of the following are an example of univariate data except what?
The amount of time a student studies and the student’s grades
Number of students in a class that are males
Number of cars in a parking lot that are red
The number of people who enter a grocery store
The amount of time a student studies and the student’s grades
Two-way tables are an effective way to organize and compare two categorical _________________________.
Variable
Simulated probabilities get closer to true probabilities as the number of trials ____________________.
Increases
Organizing, graphing, and summarizing information from all individuals in
a sample are the methods of ________________ statistics;
Descriptive
What type of number can continuous data be?
any numbers
Which of the following is not an example of continuous data?
The height of a man
The weight of a dog
The number of desks in a room
The time it takes to run a mile
Number of desks in the clasroom
What is the marginal relative frequency of females in the study?
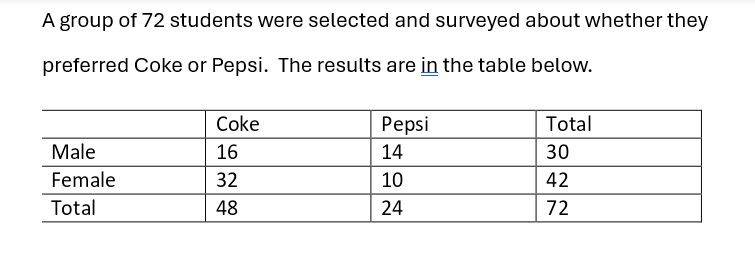
58.3 %
Discrete and continuous are types of what variables?
Quantitative
drawing
conclusions regarding the population based on the study of the sample is_______________ statistics.
Inferential
What are the 2 types of quantitative data?
Discrete and continuous
Which of the following is not a categorical variable?
Eye color
Gender
Dog breed
Number of cards in a deck of cards
Number of cards in a deck of cards
what is the relative frequency
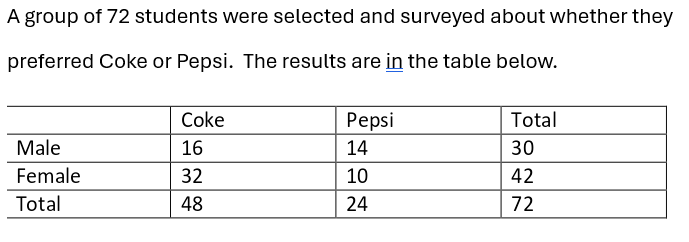
15.4 %
ratio of the frequency in a cell and the total number of data
values
Joint relative Frequency