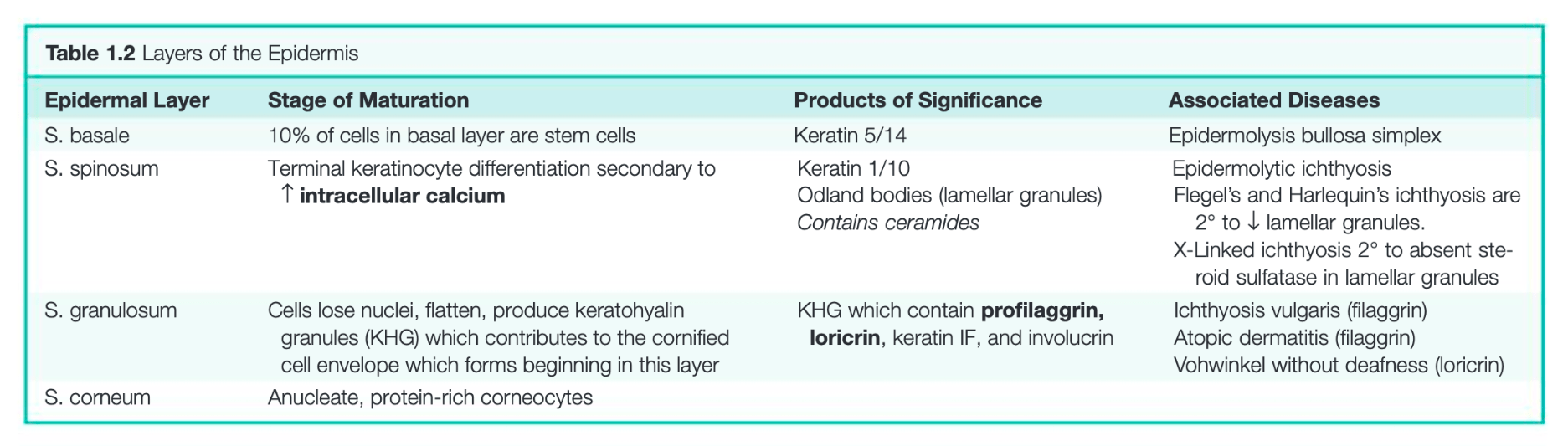
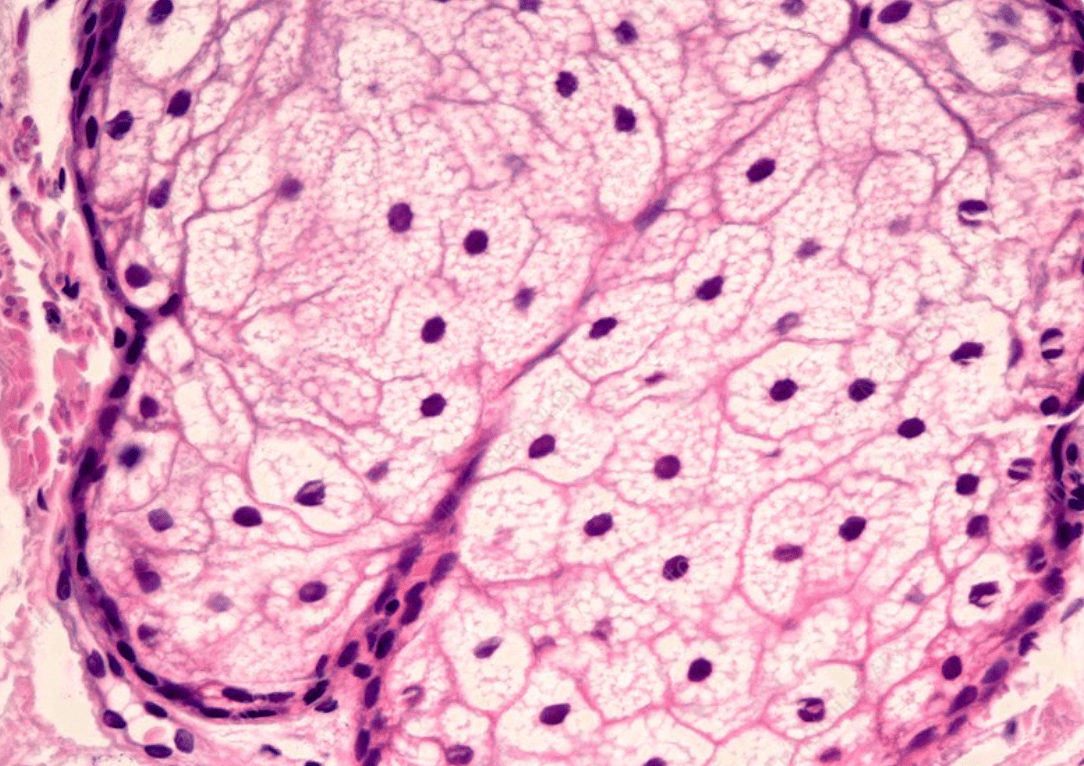
Epidermis: Corneum, Lucidum, Granulosum, Spinosum, Basale
Dermis: Papillary, Reticular
Hypodermis: SubQ fat
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/1932/xLpKWxhLwspEm6QvkDKcTw_skin-histology_med_mag_english.jpg)
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/1806/6mQ27thRTtY0sA1QtDAg_skin-histology_low_mag_english.jpg)
Time from: (a) basale to corneum, (b) basale to desquamation
(a) 14 days
(b) 28 days
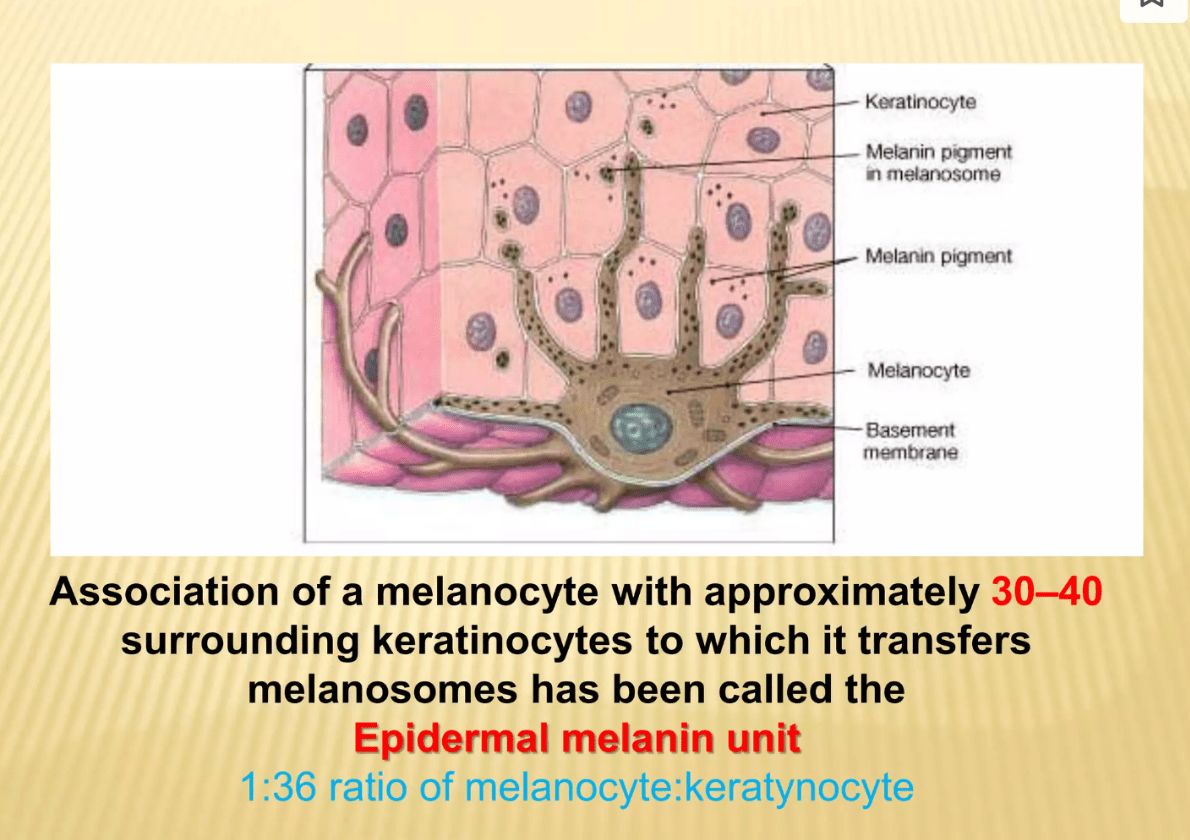
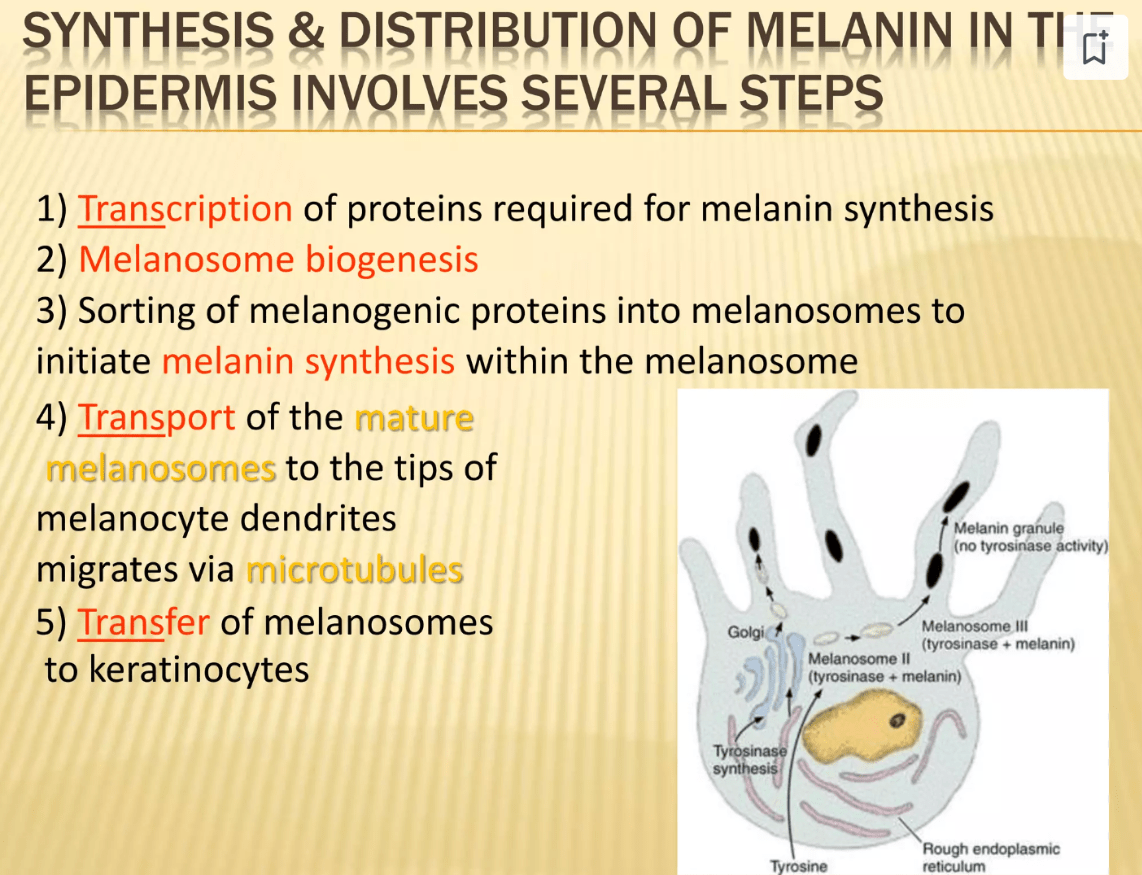
How many keratinocytes in the "epidermal melanin unit"
36 keratinocytes with 1 melanocyte in 3D!
- 10:1 in 2D
Which enzyme in epidermis associated with proliferative state?
Bonus: inhibited by what 3 things?
Ornithine decarboxylase
Inhibited by (a) corticosteroids, (b) retinoids, (c) vitamin D
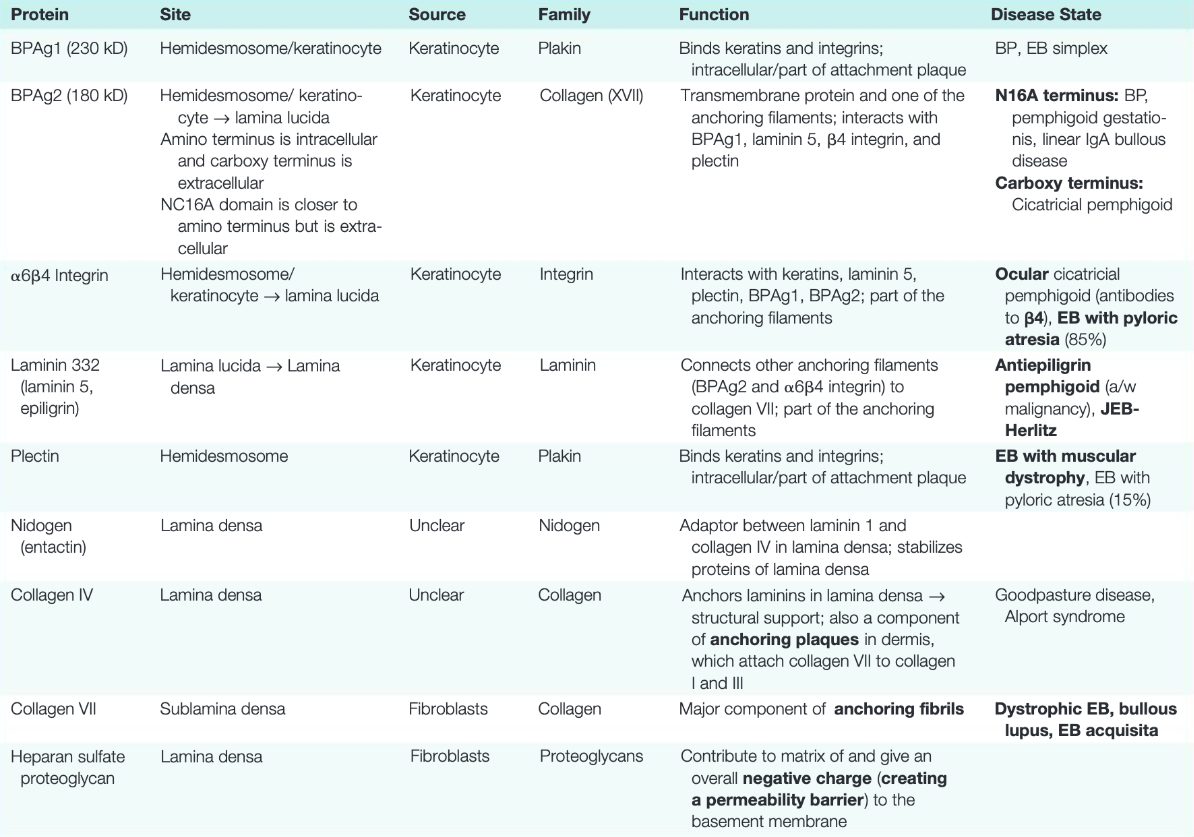
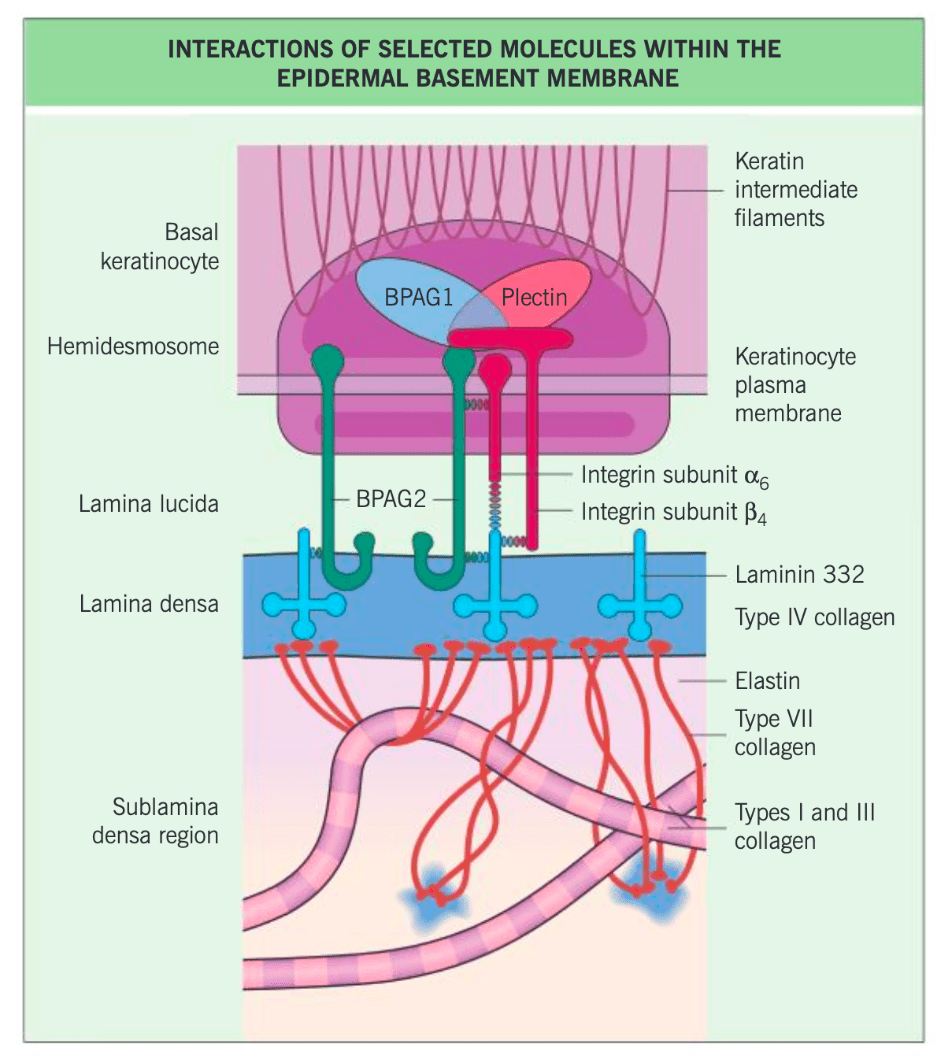
What is the target antigen in this condition with ocular-predominant symptoms?
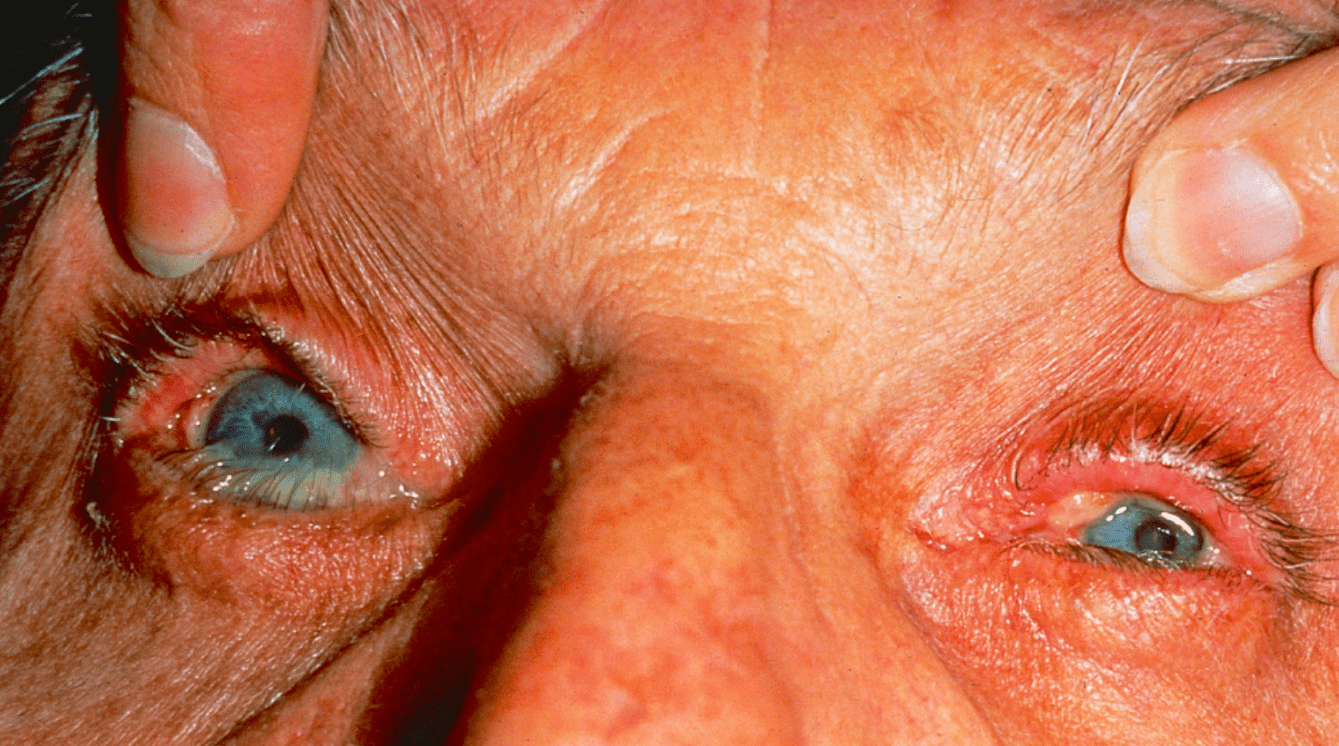
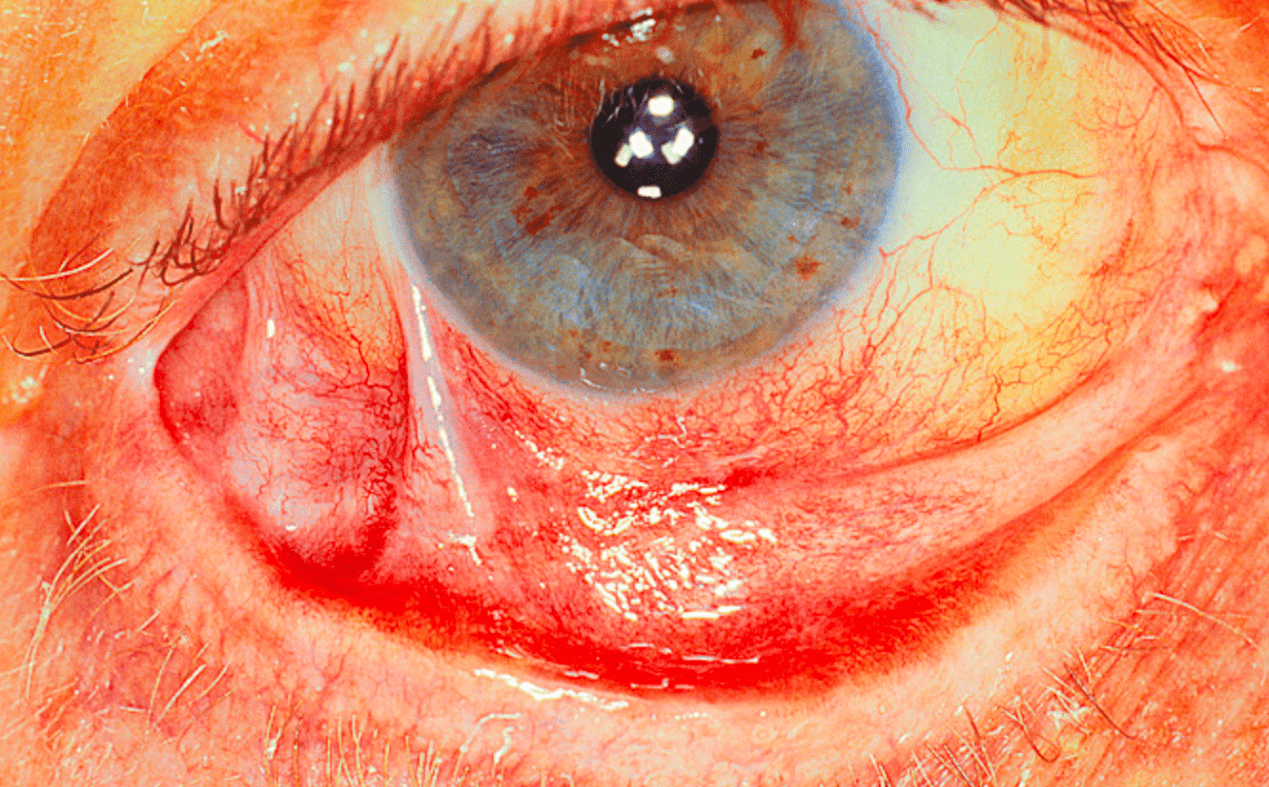
β4 subunit of α6β4 integrin
(β = sunglasses = eye involvement)
Variants of MMP
- Anti-epiligrin MMP
- target = laminin 332 (laminin 5, epiligrin)
- salt-split skin shows dermal staining
- strongly a/w underlying solid organ malignancy (#1 = adenocarcinoma)
- Ocular MMP
- target = β4 subunit of α6β4 integrin
- nearly exclusive ocular involvement
- Anti-BP antigen MMP
- target = BP180 (BPAg2, C-terminus)
- skin and mucosal involvement
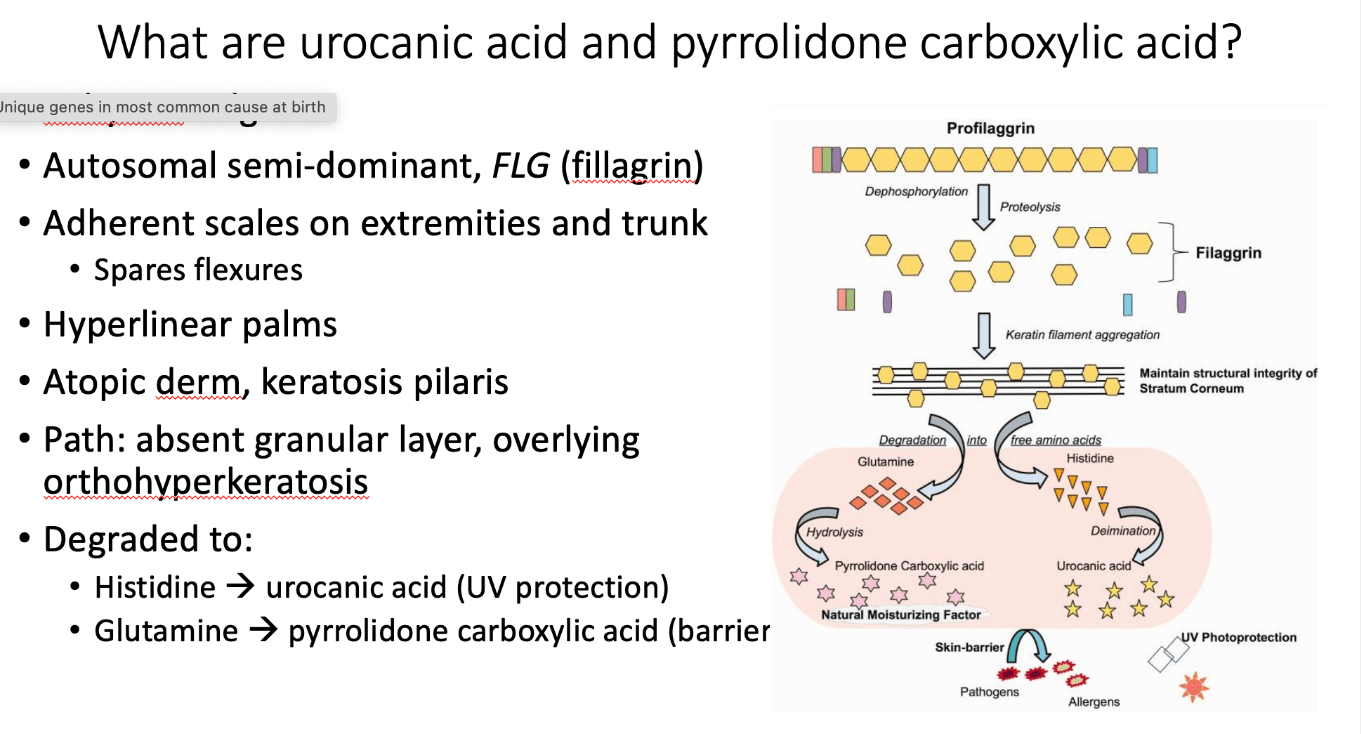
What is the function of the mutated gene?
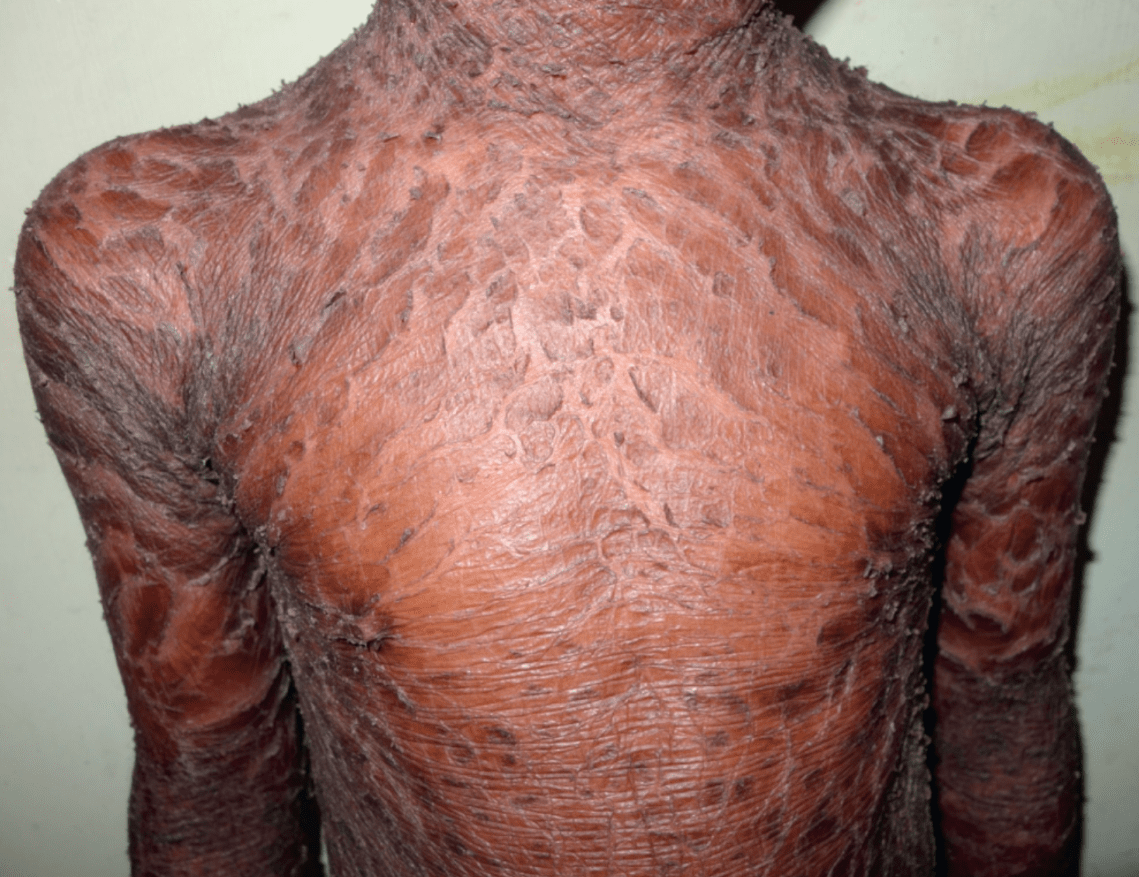
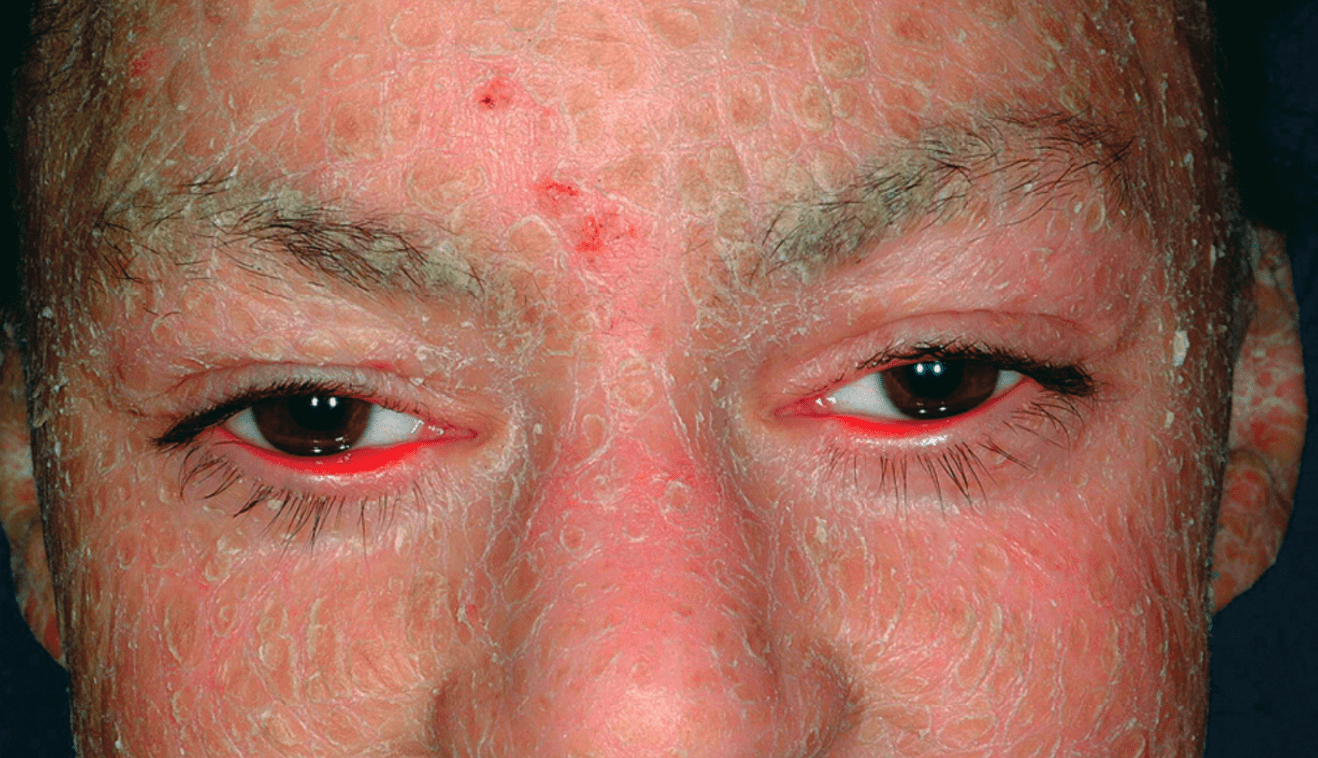
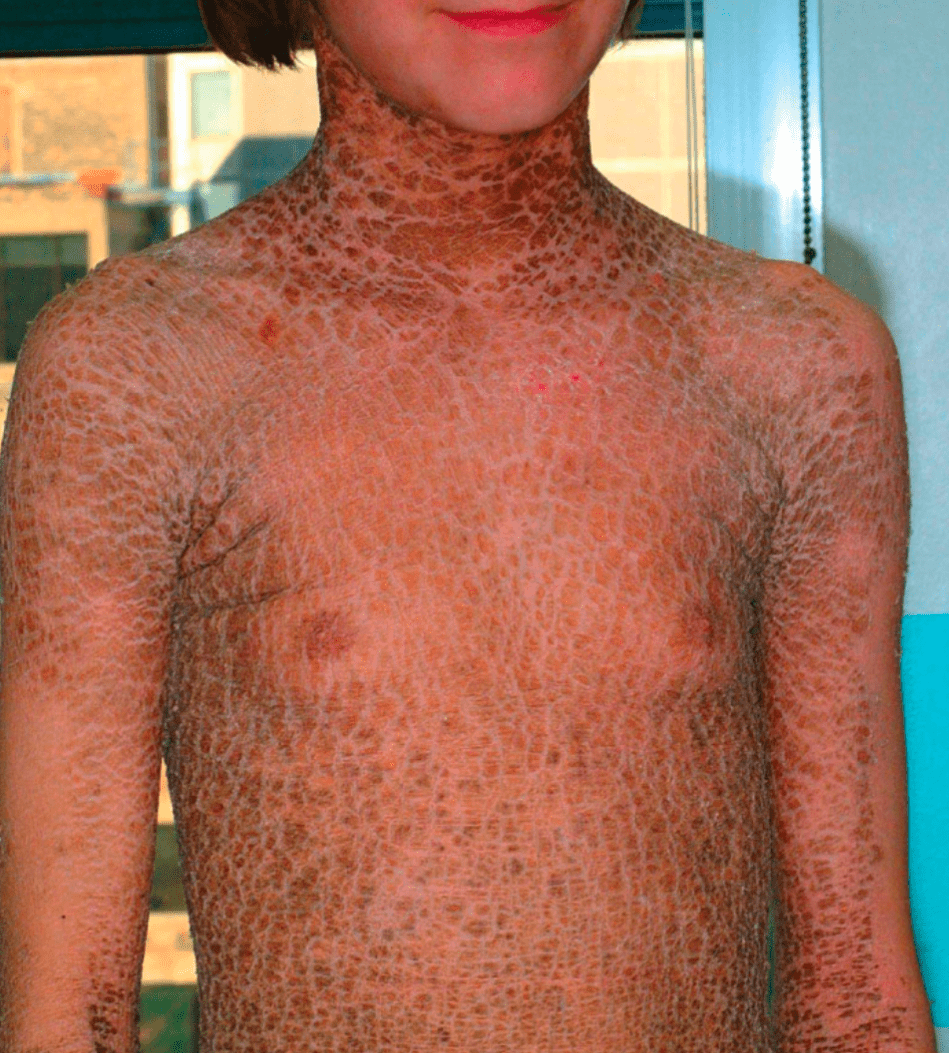
Cross-linking of loricrin, KRT2/11, proline-rich proteins, and filaggrin in the granular layer
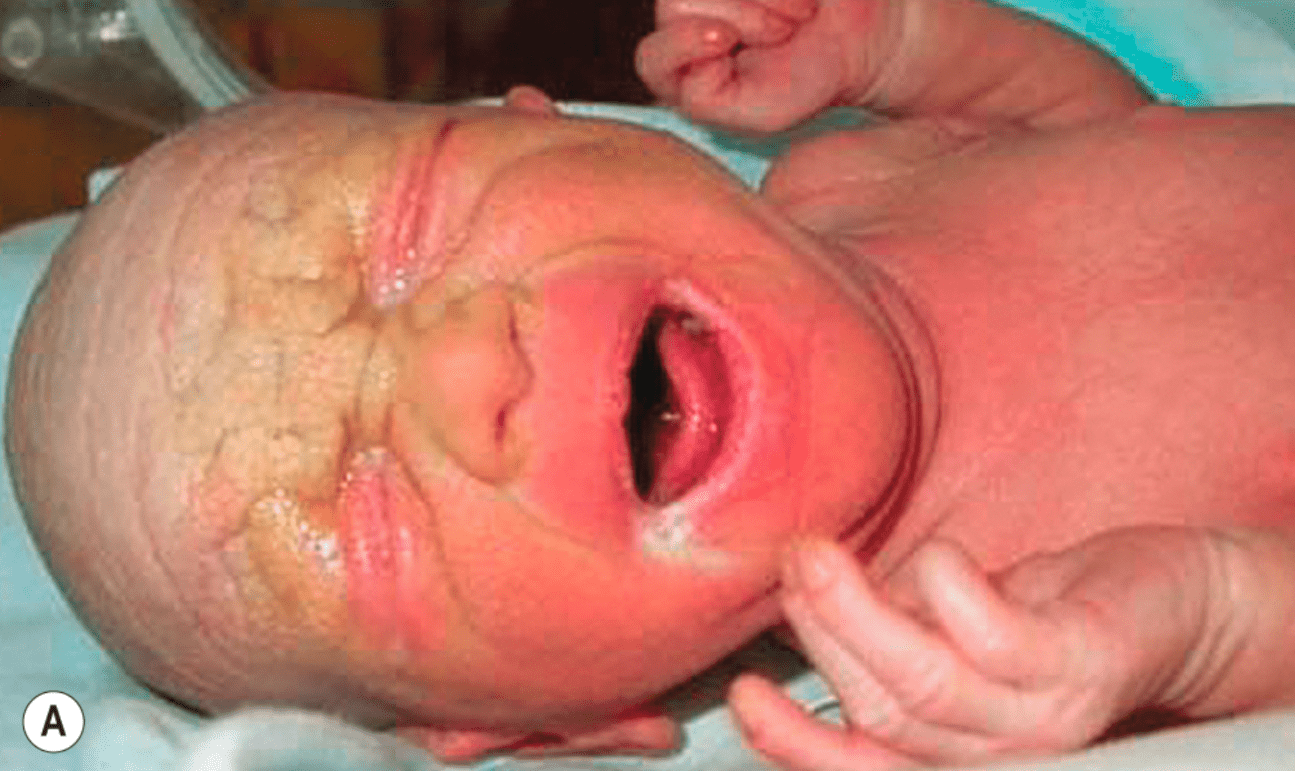
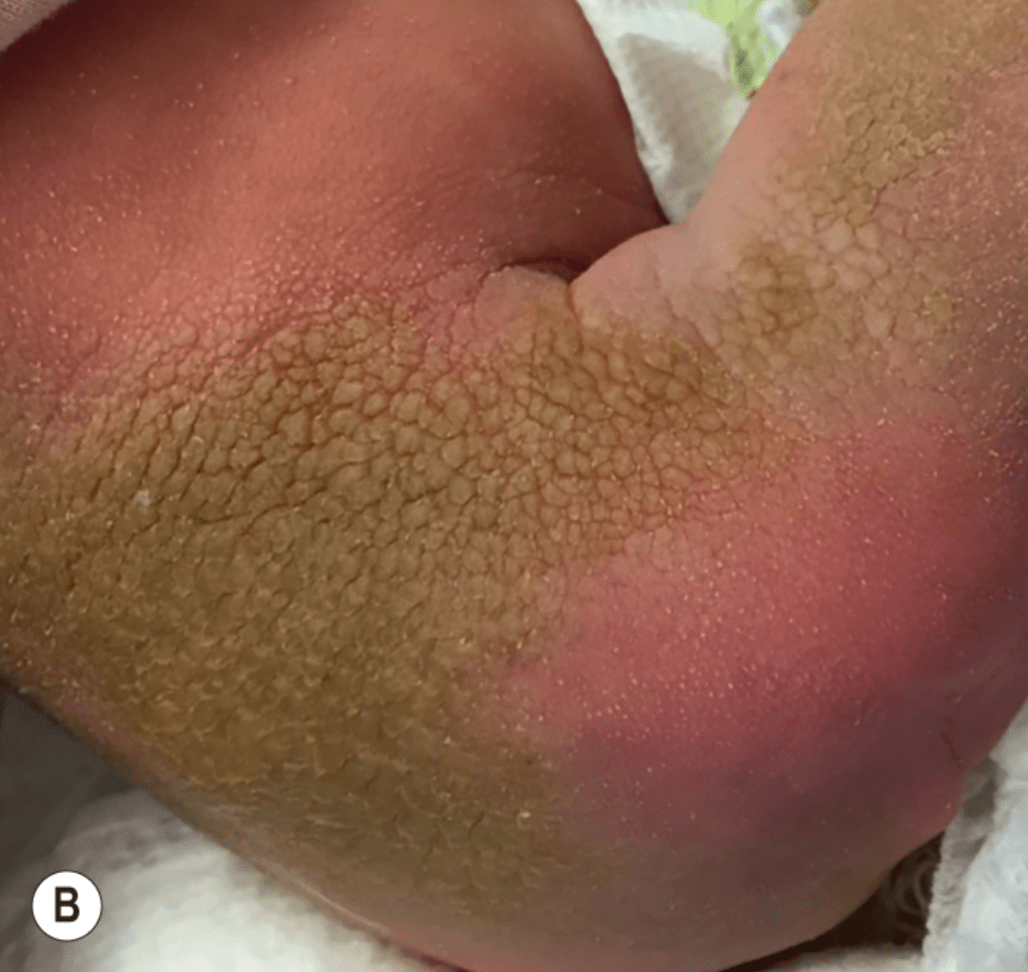
TGM1 mutation = lamellar ichthyosis
- collodion membrane, plate-like scale, ectropion, alopecia
- improvement with tazarotene
Four cell types in the basal layer
(1) Keratinocytes (terminally differentiated, stem cells, transient amplifying cells)
(2) Melanocytes (neural crest)
(3) Langerhans cells (major APCs)
(4) Merkel cells (mechanoreceptors)

What is the major component of:
(a) Odland bodies (lamellar granules) in spinous layer
(b) Cornified cell envelope in granular layer
(a) Ceramide - most important lipid in epidermal barrier function
(b) Loricrin - cross-linked to involucrin
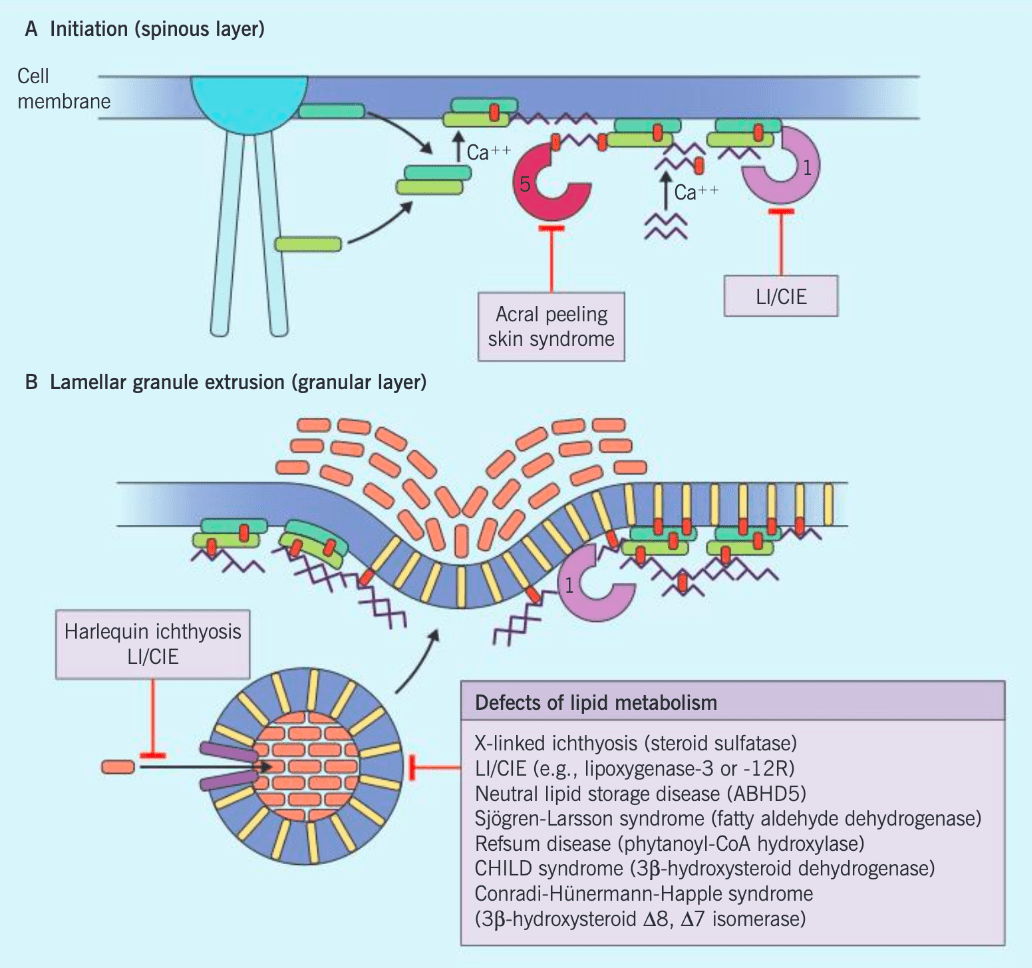
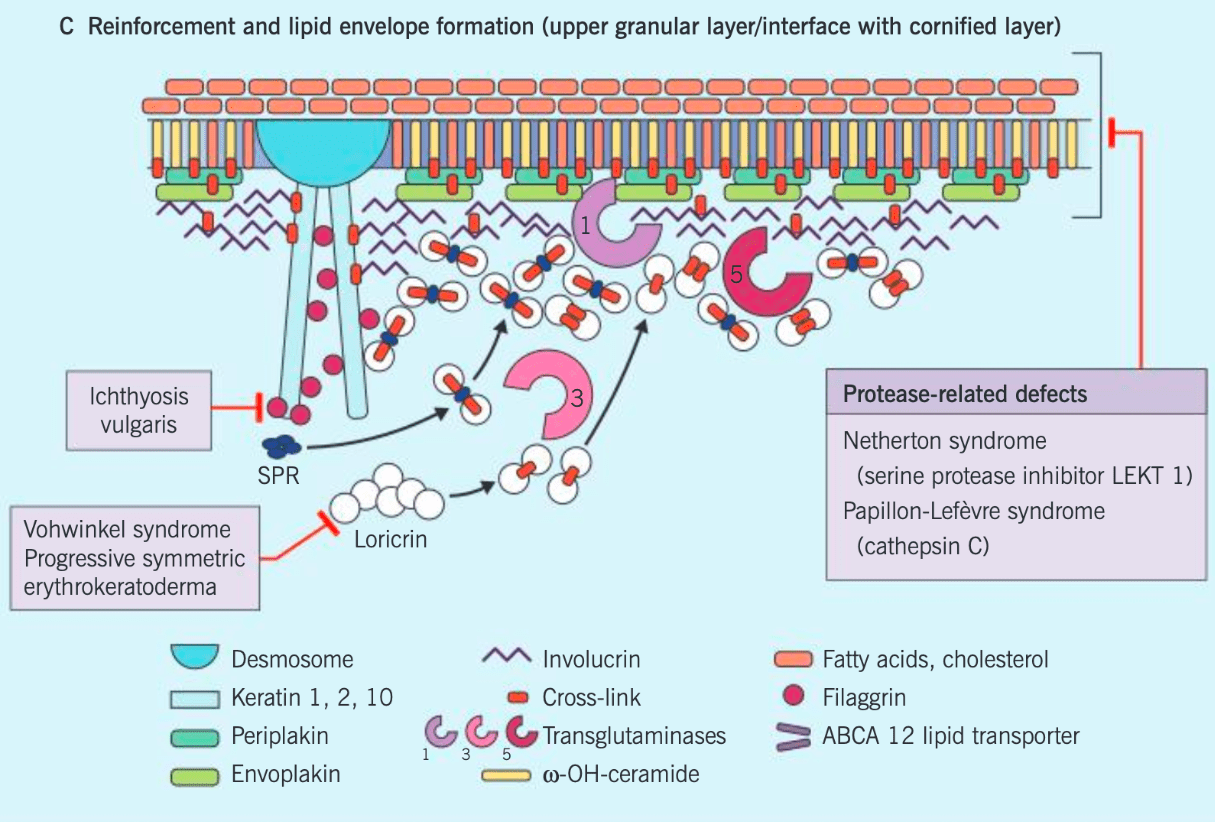
Steps in cornified cell envelope formation:
(a) Formation of a cross-linked scaffold composed of envoplakin, periplakin, and involucrin along the inner surface of the cell membrane
(b) Extrusion of lamellar granules
(c) Reinforcement via loricrin cross-linking and translocation to cell periphery
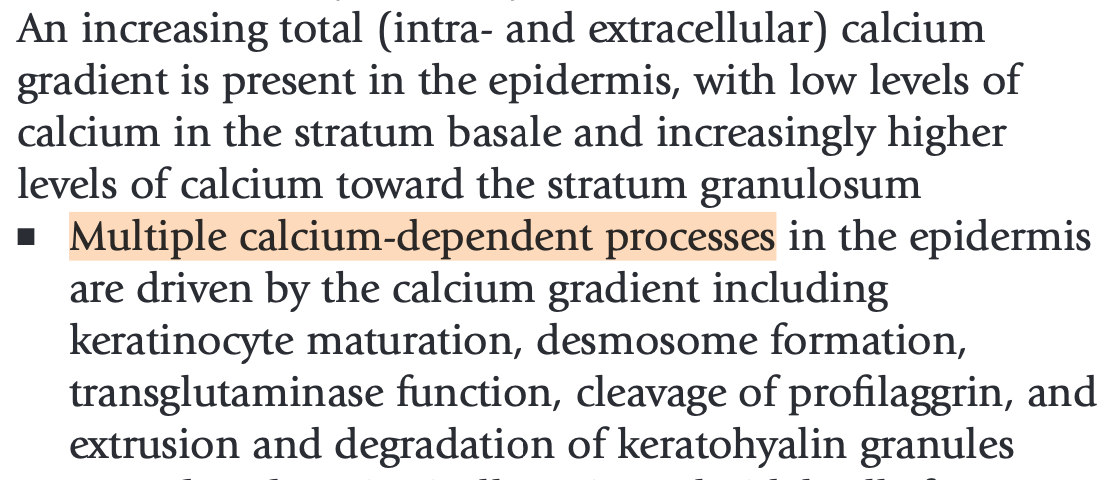
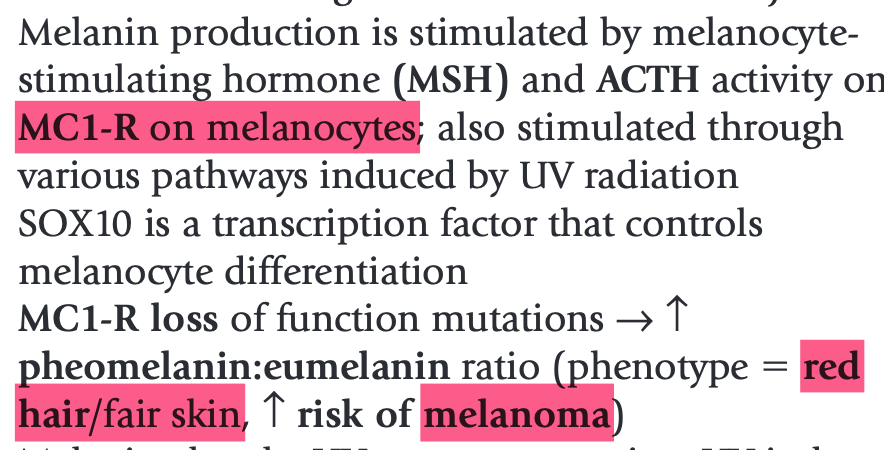
What are the important metal elements in the epidermis involved in:
(a) keratinocyte differentiation
(b) melanin synthesis
Bonus for (a): conditions with ATPase mutations leading to abnormal transport
(a) calcium
-- Bonus: Hailey-Hailey (APC2C1, golgi), Darier (APC2A2/SERCA, ER)
(b) copper (tyrosinase co-enzyme)
-- Bonus: also involved in elastin crosslinking (lysyl oxidase coenzyme); reduced activity in Menke's Dz
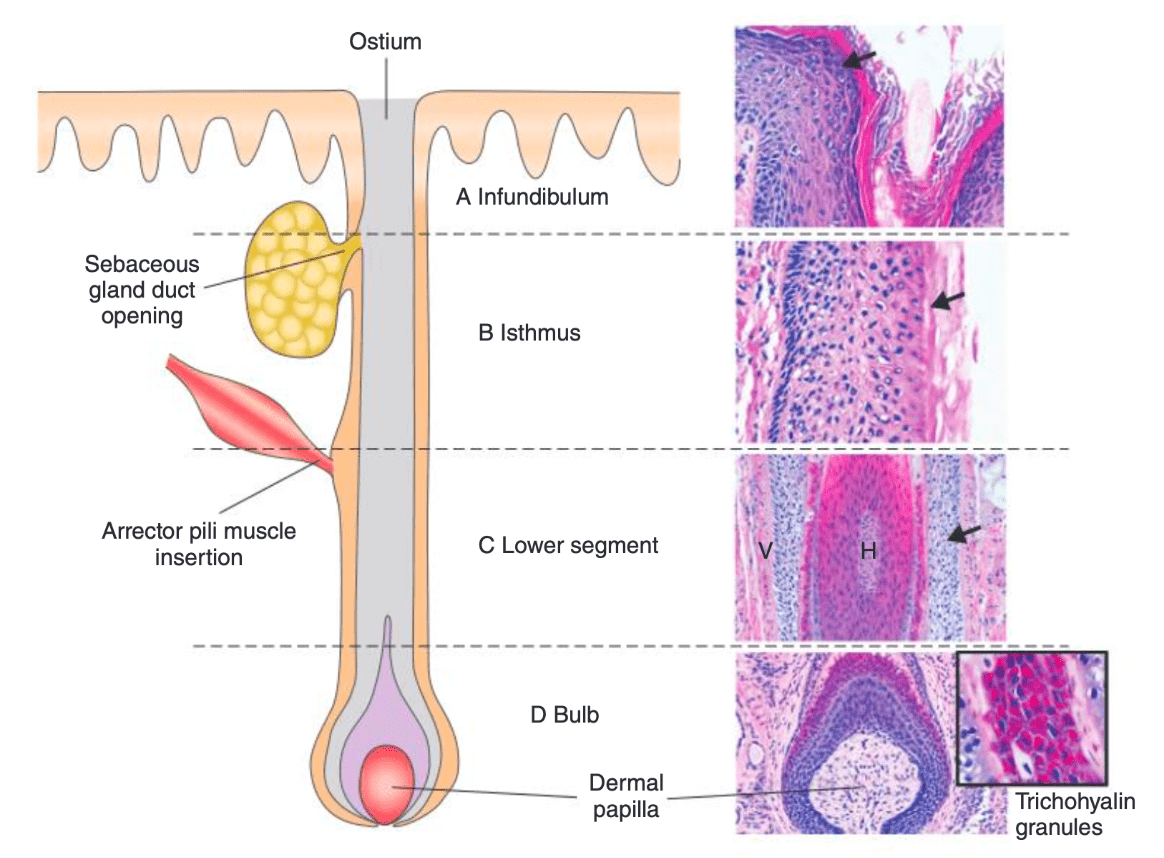
What are the boundaries of the normal part of the hair from which this lesion is derived?
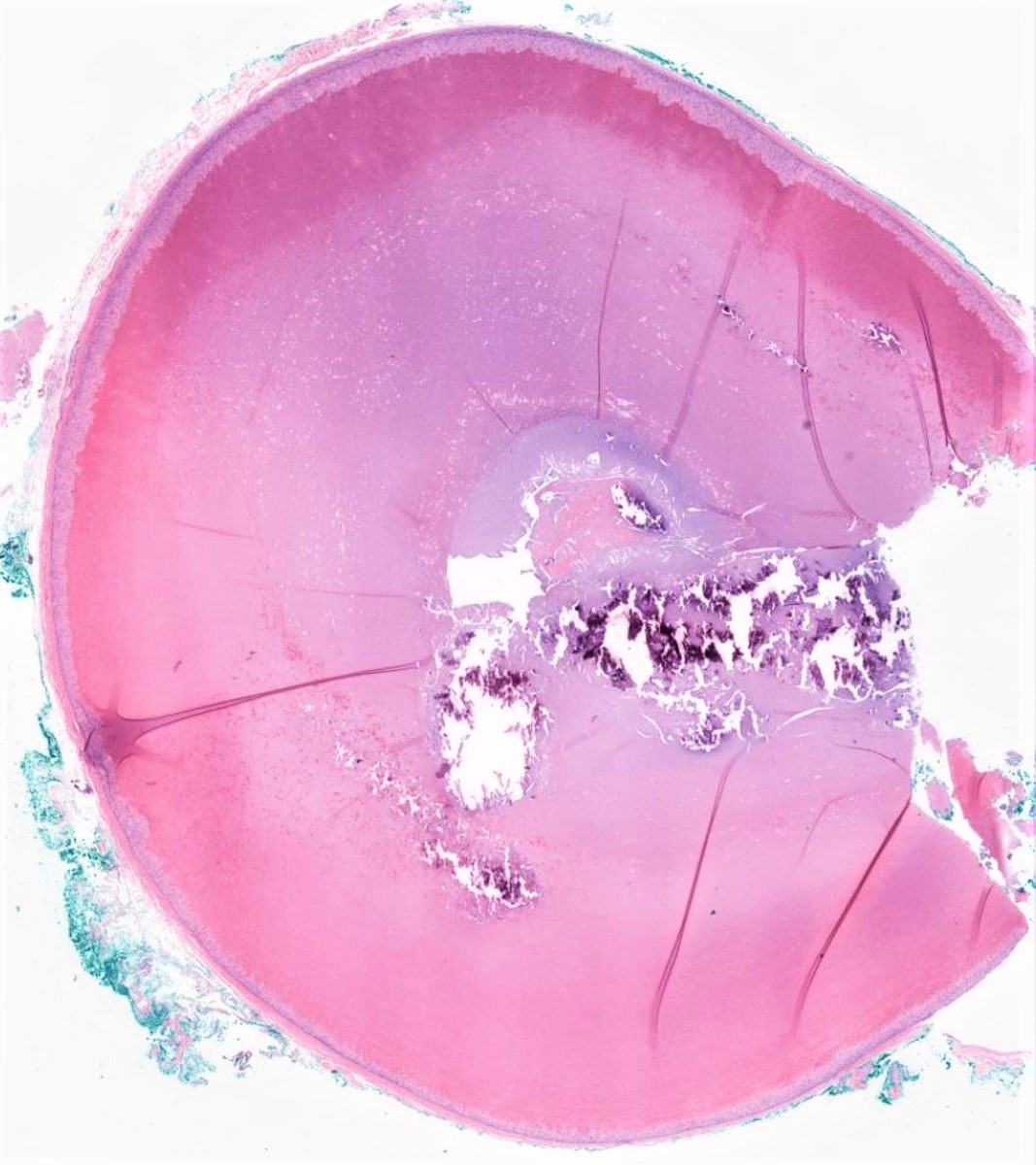
Isthmus catagen (pilar) cyst!
Top: opening of sebaceous gland
Bottom: insertion of arrector pili muscle

A patient presents with reticular hyperpigmented macules and papules, biopsy shows elongated rete, basal hyperpigmentation, and suprabasal acantholysis. Mutations in the associated gene can also be seen in what blistering disorder?
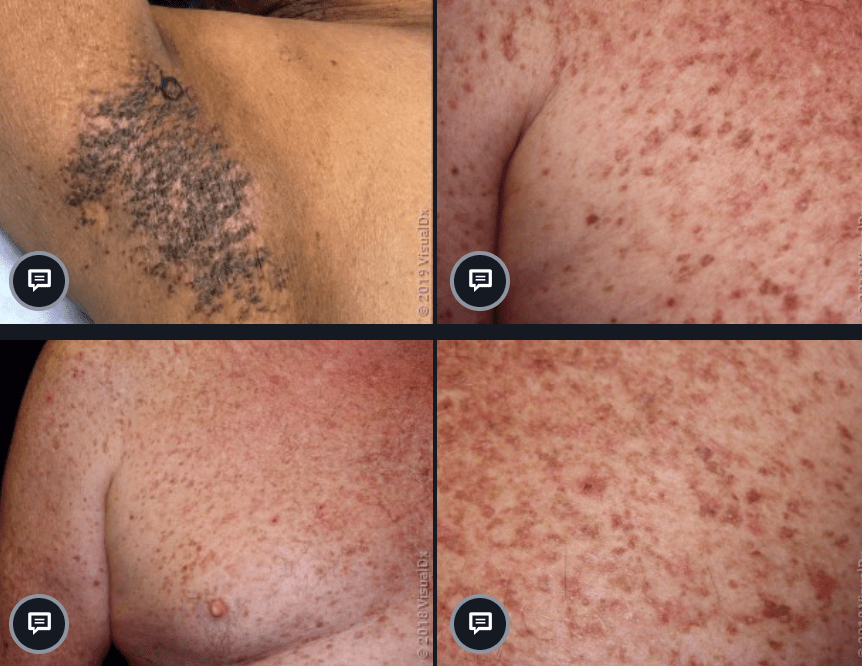
Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex! (KRT5/14)
Galli-Galli, AD KRT5 mutation (basal keratinocytes)
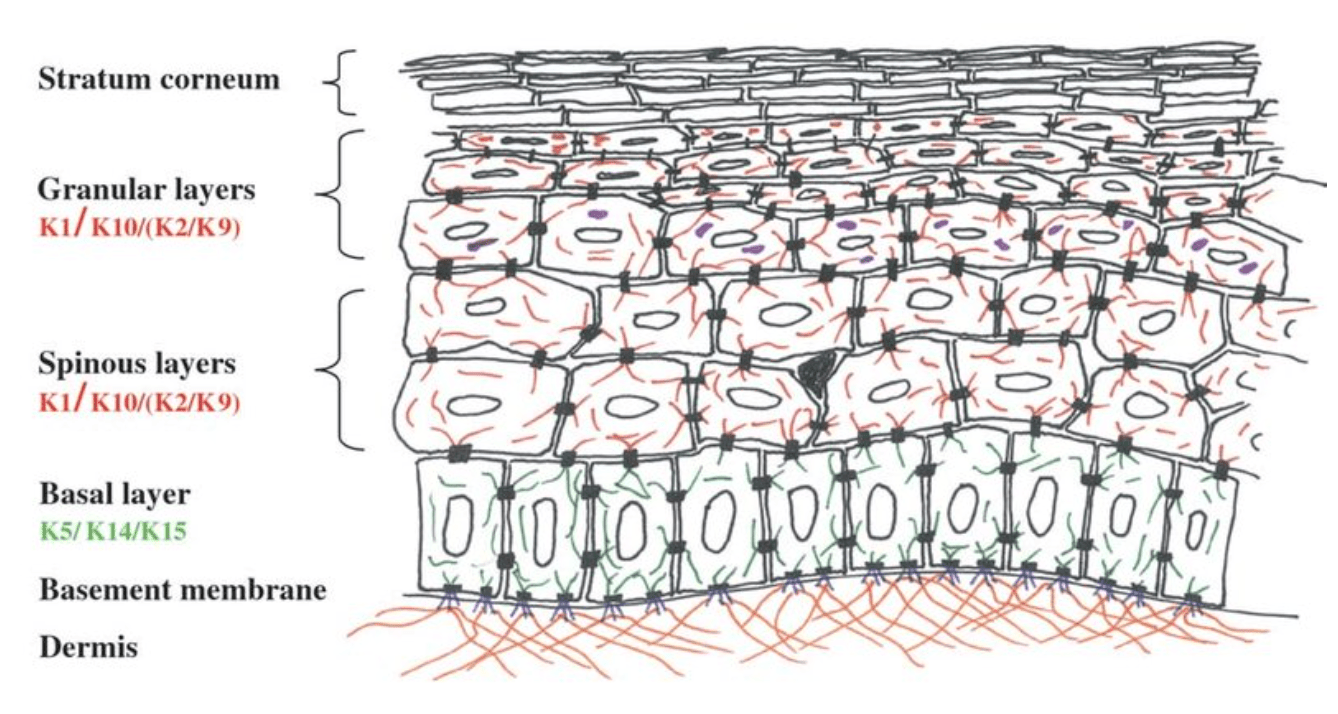
Other conditions with mutations in basal layer keratins:
-- Naegeli-Franscetti-Jodassohn, Dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis (Krt14)
What are the mutations in the AR and AD forms of this condition?
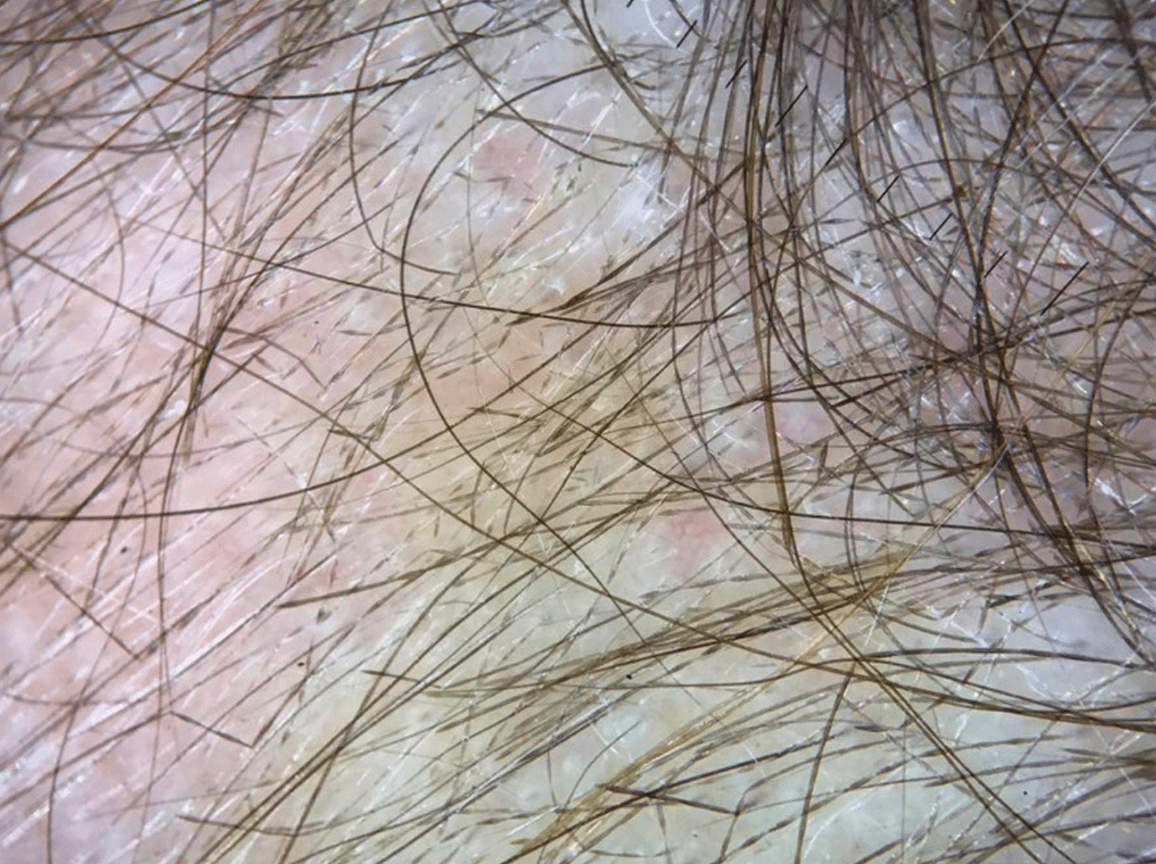
AR = desmoglein 4
AD = keratin 81, 83, 86 (expressed in cortex)

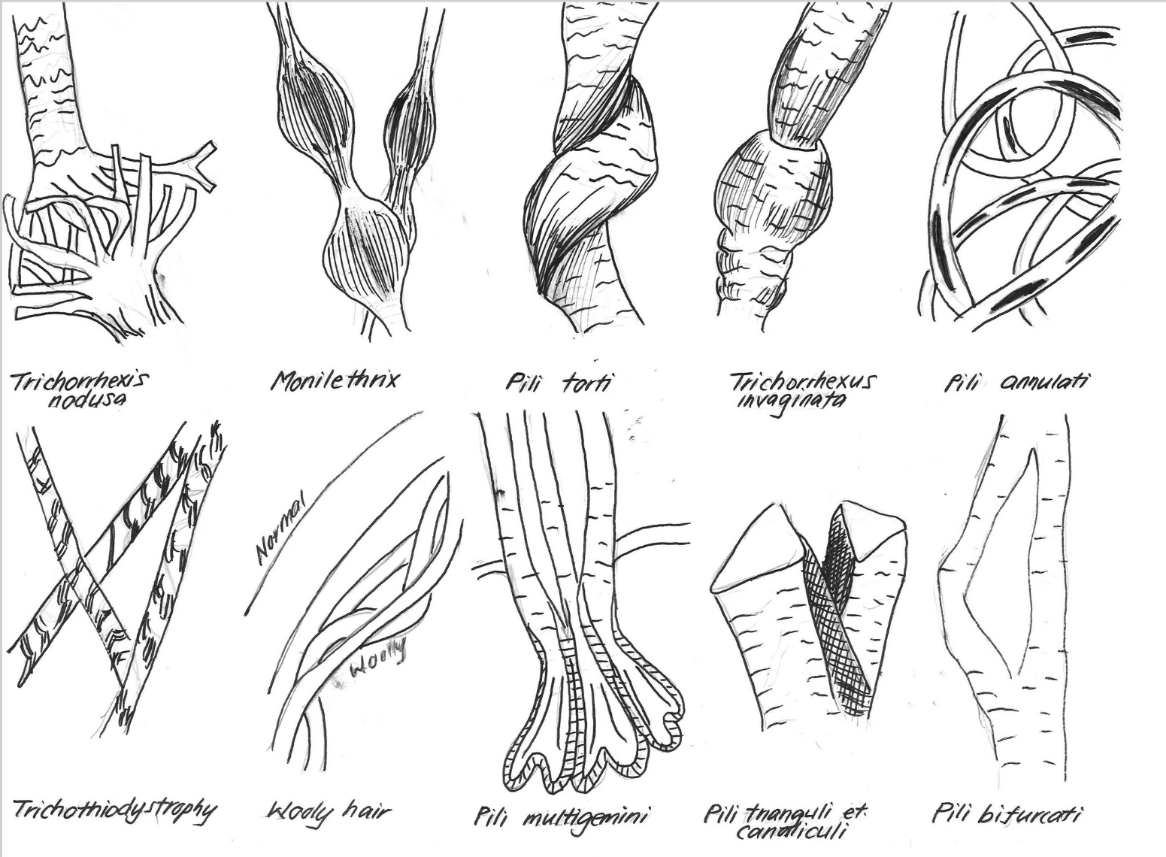
Identify the toll-like receptor based on ligand/function:
(a) Recognizes bacterial flagellin
(b) Activated by imiquimod
(c) Activated by P. acnes, inhibited by retinoids; regulates production of skin AMPs
(a) TLR5 (5lagellin)
(b) TLR7
(c) TLR2


Scar strength at 1 week, 3 weeks, 3 months, 1 year?
1 week = 5%
3 weeks = 20%
3 months = 50%
1 year = 80%
What are the wavelengths of the ultraviolet spectrum?
UVC -- 200-280 nm
UVB -- 280-320 nm
UVA -- 320-400 nm (AII 320-340, AI 340-400)
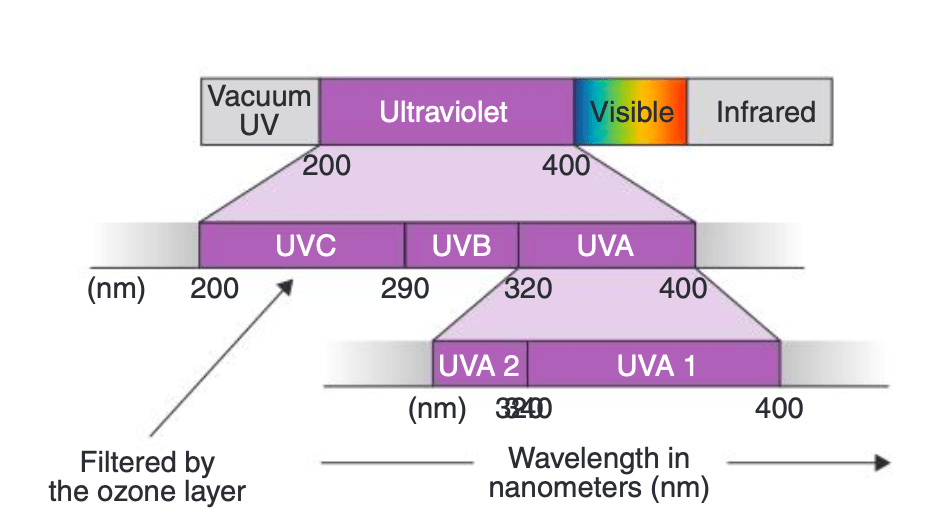
Longer wavelength penetrates deeper: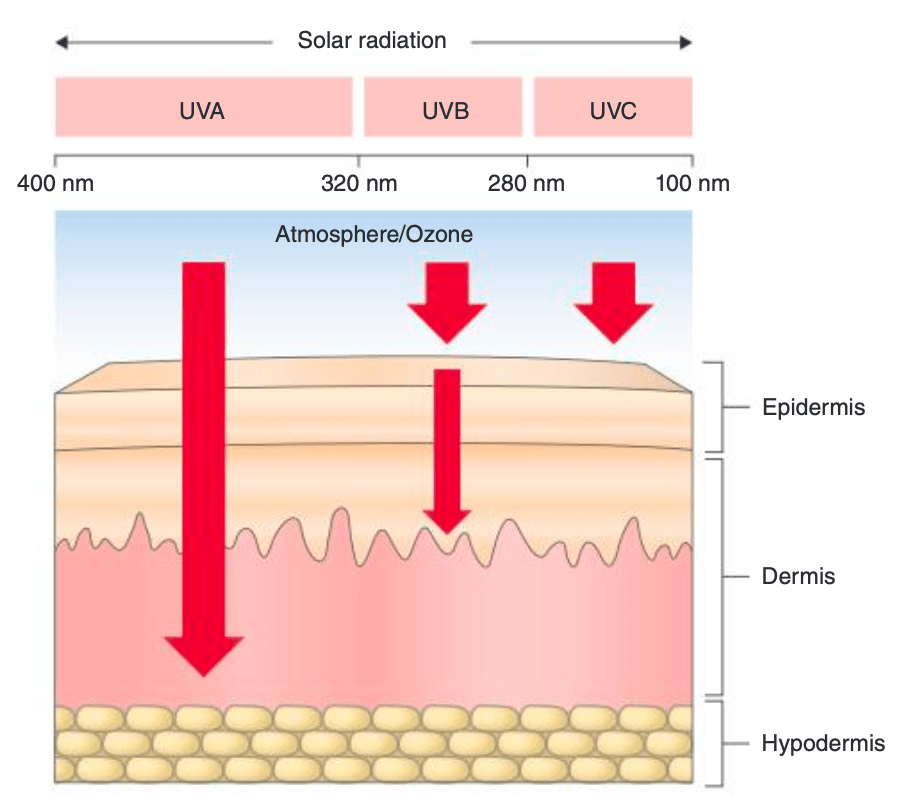

The gene mutated in this condition encodes an epidermal protein. What structure does it form and what is the function?
Gap Junctions (intercellular communication)!
KID Syndrome (keratosis, ichthyosis, deafness)
-- mutation in GJB2/connexin 26


You biopsy a blister of this 75yo male and H&E shows a subepidermal split with eosinophils + some neutrophils. Immunohistochemistry with collagen IV stains which part of the blister?
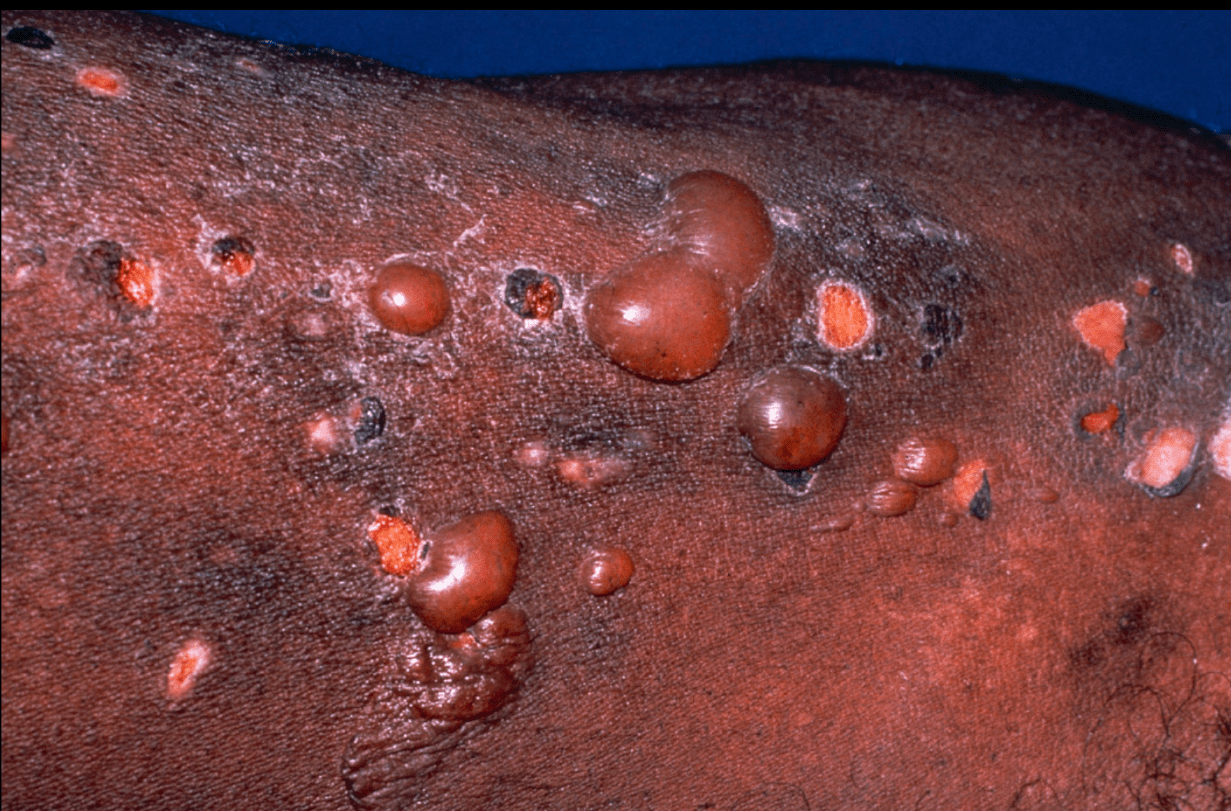
The floor!!!
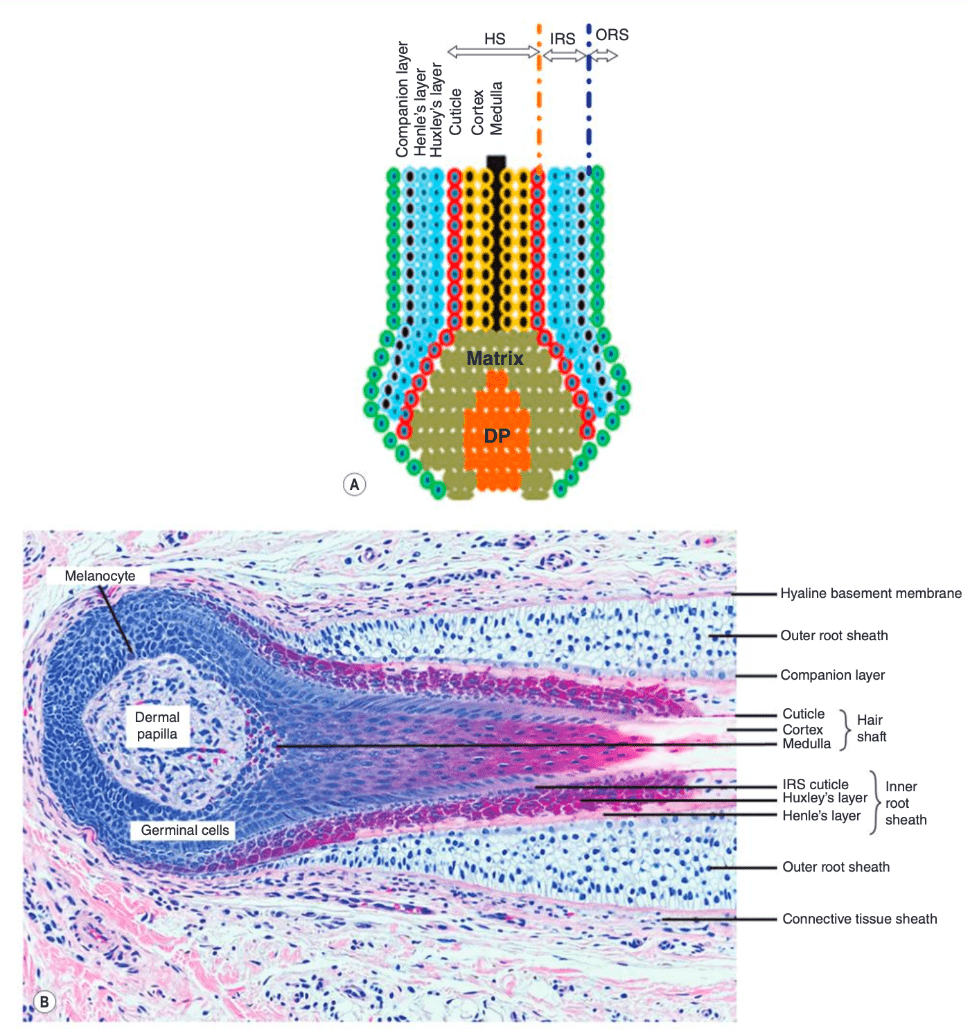
4 layers of the hair shaft (outer to inner)
(1) Glassy membrane (connective tissue sheath)
(2) Outer root sheath
(3) Inner root sheath (Henle, Huxley, cuticle)
(4) Hair shaft (cuticle, cortex [keratins here], medulla)

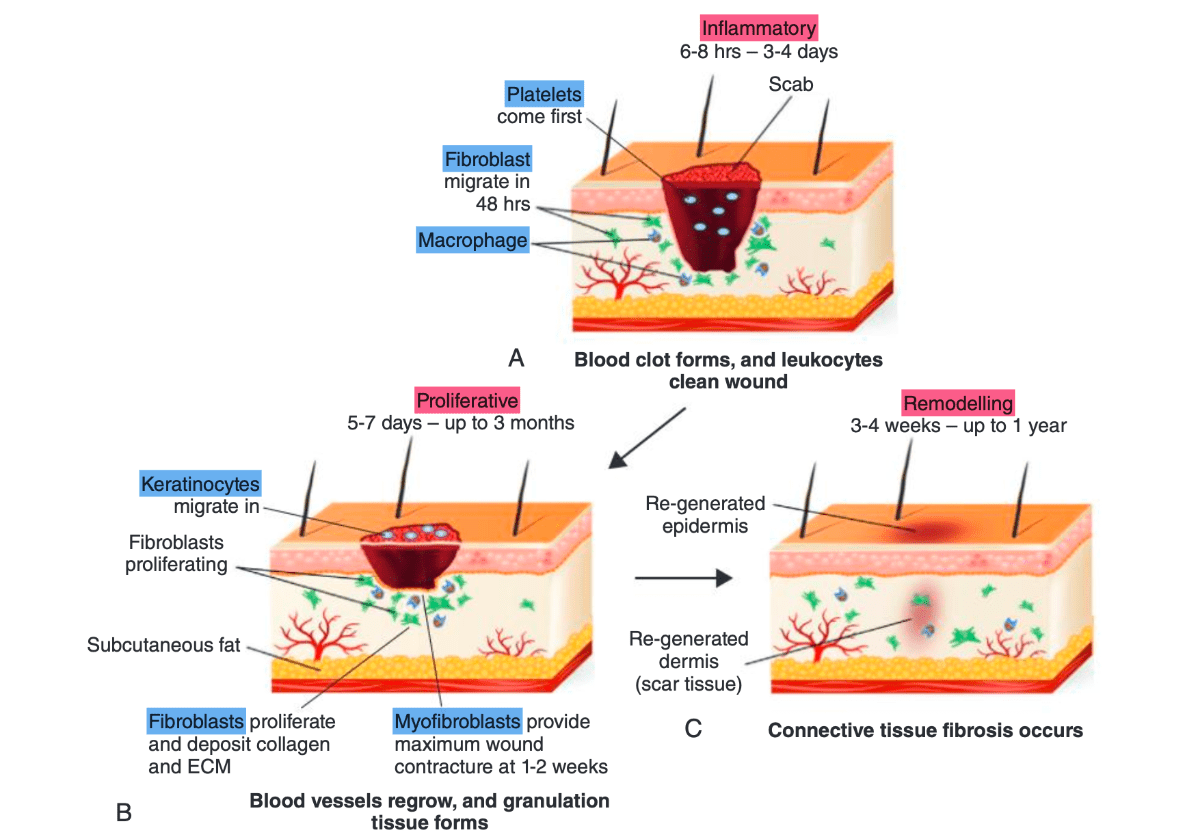
What are the three phases of wound healing (time period for each)?
1. Inflammatory phase: starts within the first 6 - 8 hours and can last 3 - 4 days
2. Proliferative phase: starts around day 5 - 7 and may last up to 1 month
3. Remodeling phase: starts at 3 - 4 weeks and can take 1 year
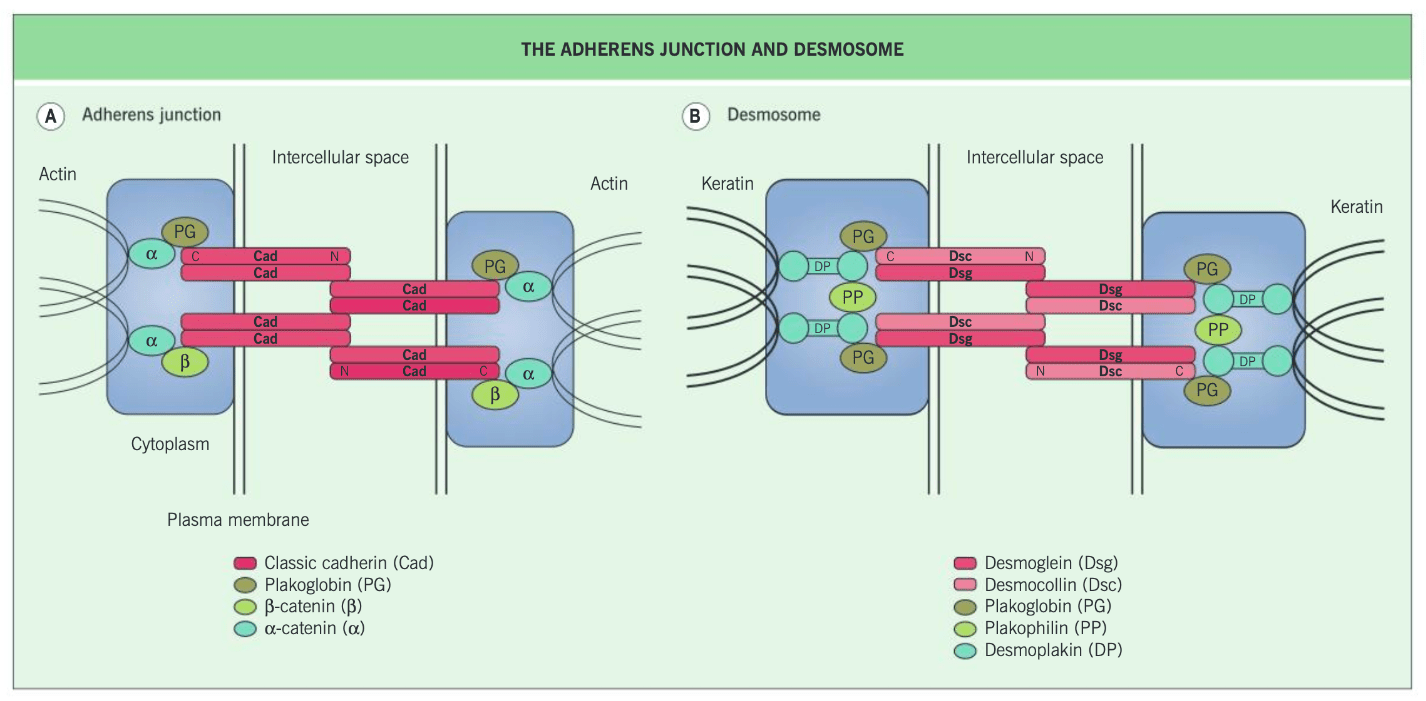
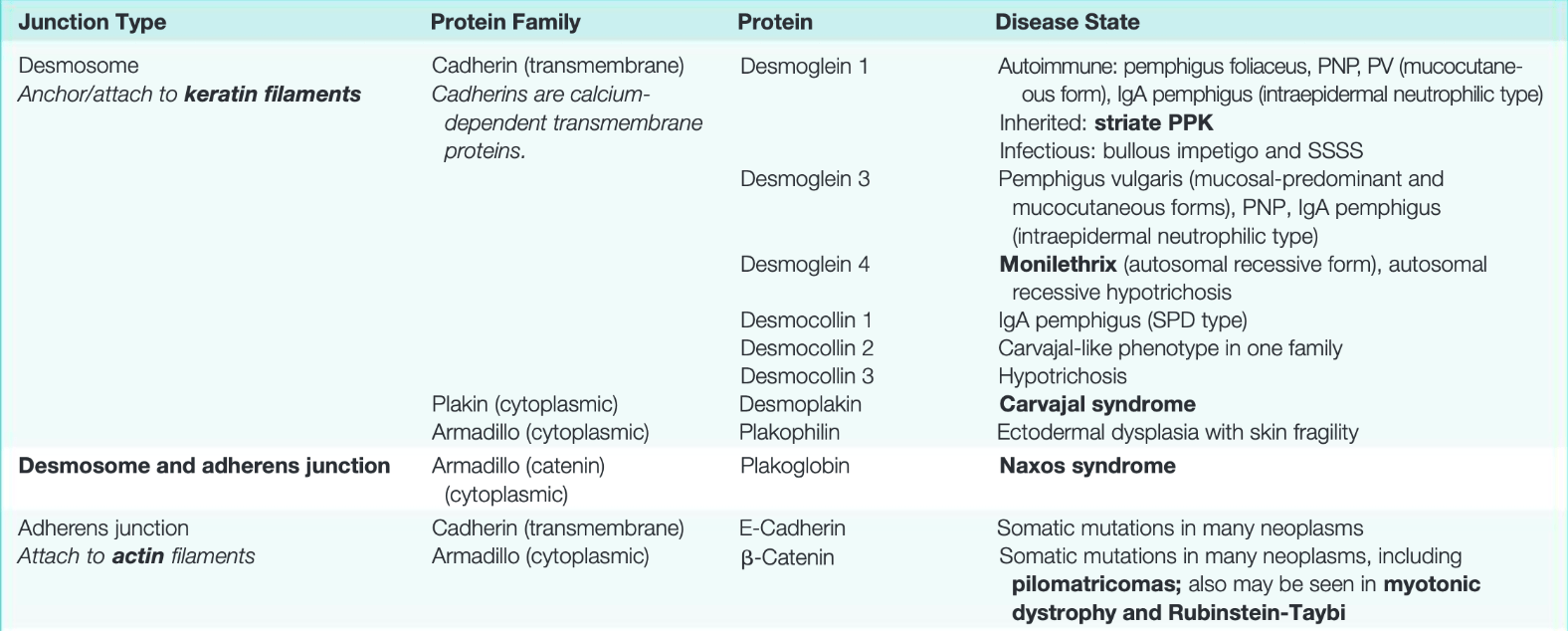
What is the shared component between adherens junctions and desmosomes?
What is the associated condition?
Plakoglobin!
(Naxos Syndrome - plaxoglobin)
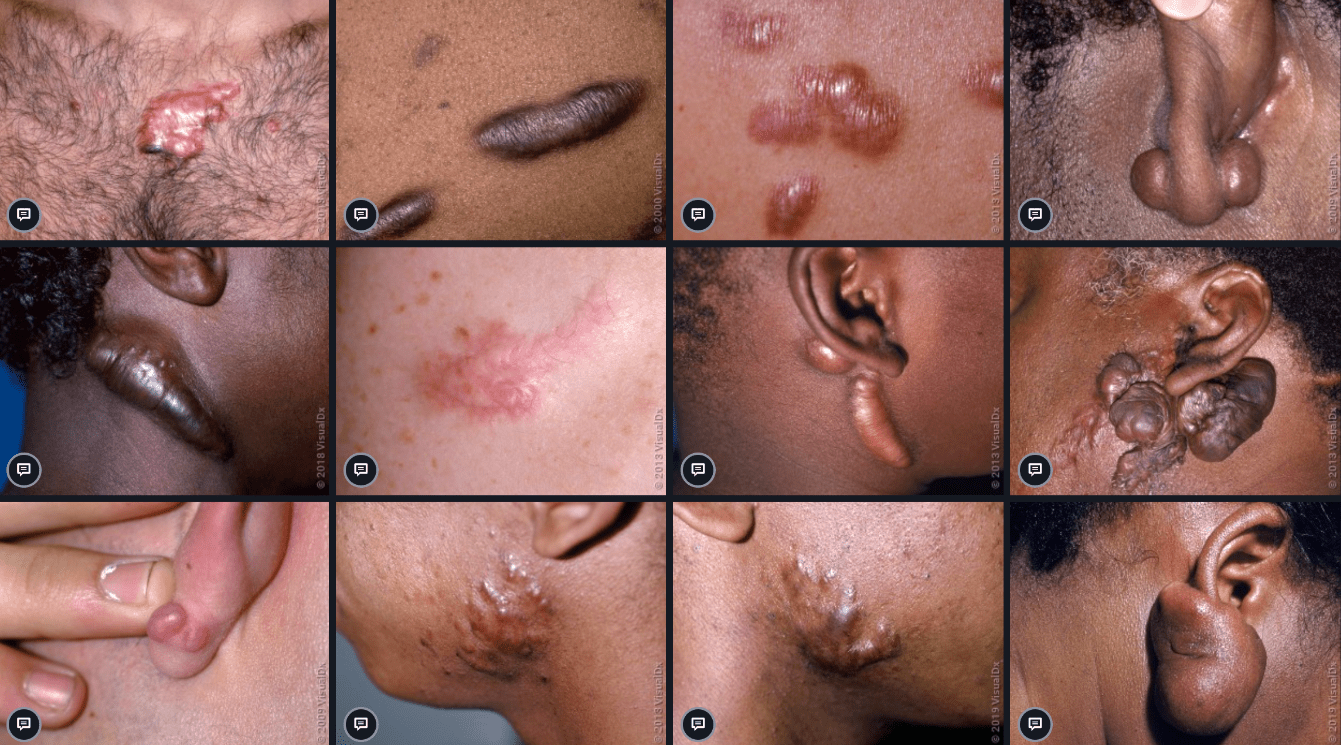
What are these called at the following locations:
(a) Areolae/nipples
(b) Eyelid tarsal plate
(c) Eyelash
(d) Labia minora/prepuce
(e) Vermilion lip
Ectopic sebaceous glands!
(a) Montgomery tubercles
(b) Meibomian glands (occlusion = hordeolum/stye)
(c) Zeis glands (not ectopic; occlusion = chalazion)
(d) Tyson glands
(e) Fordyce spots
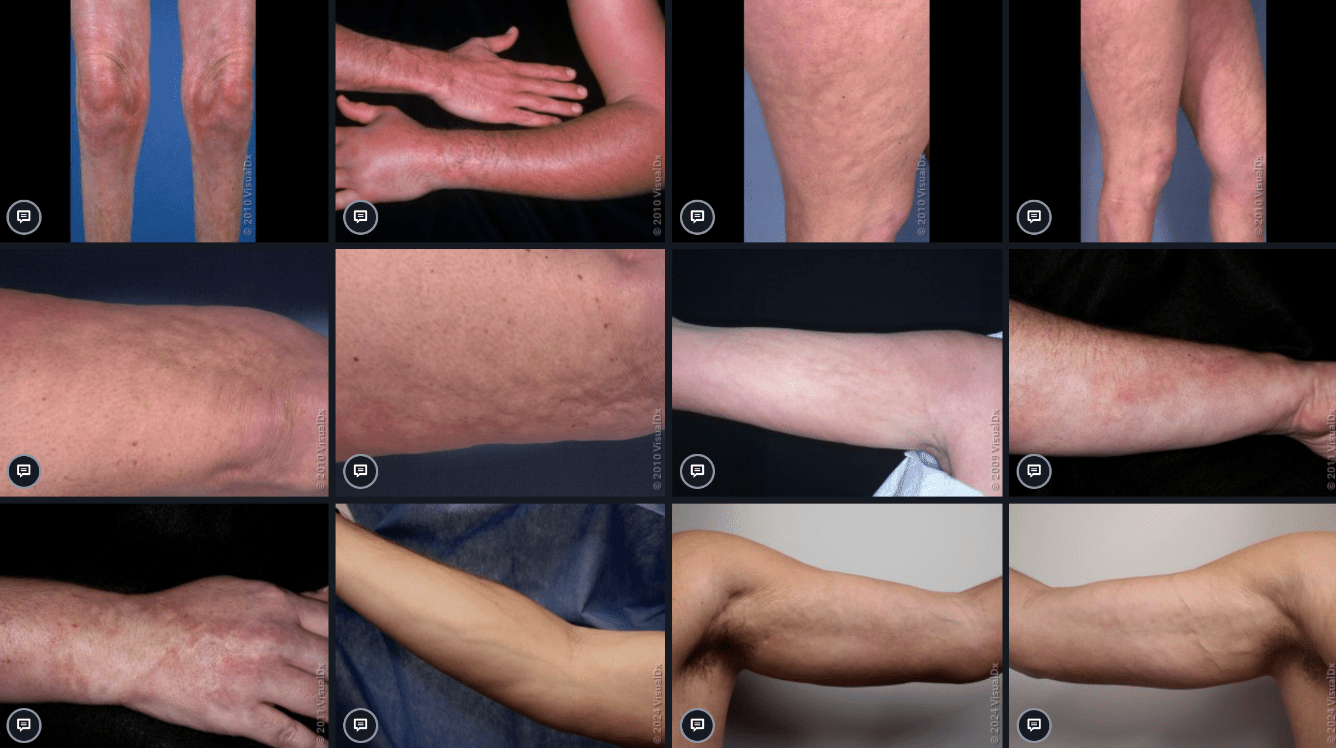
The signaling pathway upregulated in these lesions is also dysregulated in what steroid-responsive inflammatory condition?
Eosinophilic fasciitis!
(TGF-beta signaling, persistently active in keloids/hypertrophic scars)
Rearrange the conditions in ascending order of their disordered collagen:
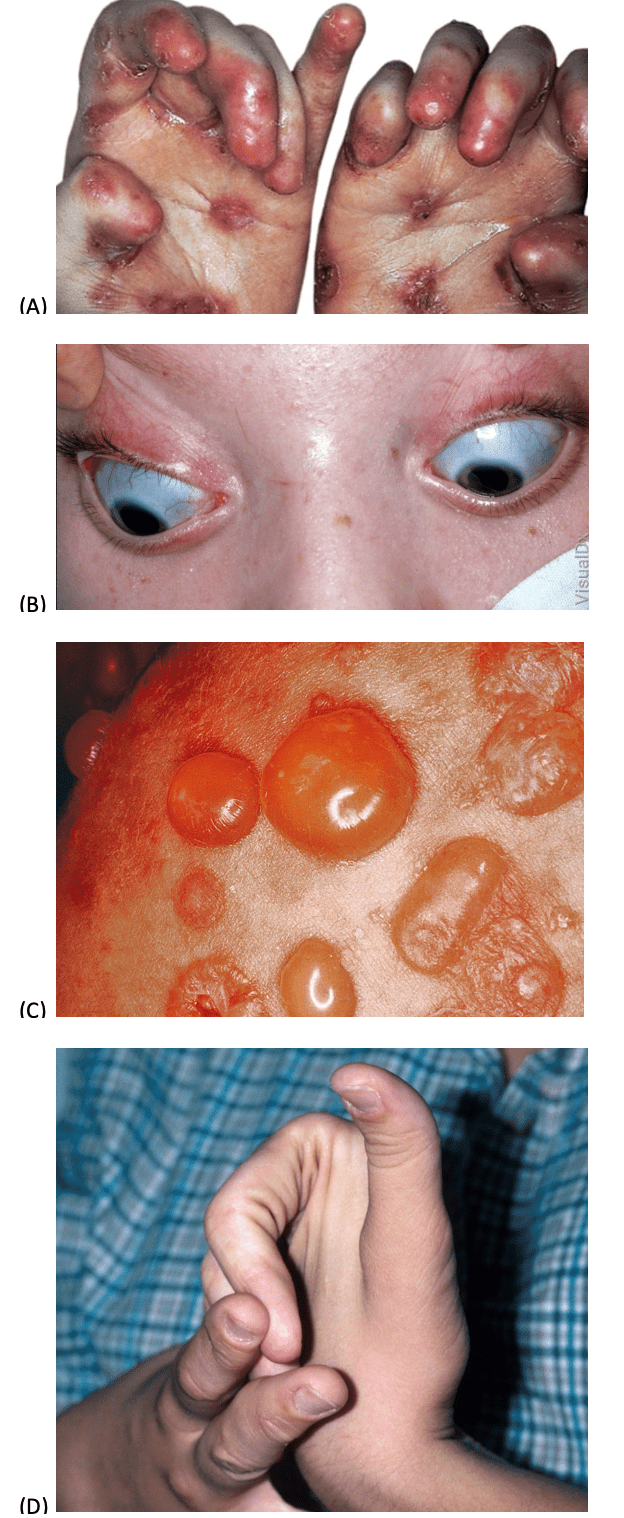
(B) Collagen 1 -- OI (slate-grey sclerae)
(D) Collagen 5 -- EDS (classic)
(A) Collagen 7 -- RDEB (mitten deformity)
(C) Collagen 17 -- BP (BPAG2!)
Match the specialized nerve fibers to function and adaptation:
Krauss end bulbs, Meissner's corpuscles, Ruffini corpuscles, Paccinian corpuscles, Merkel nerve endings


Superficial to deep: MMRP (almost alphabetic?)

Free nerve endings (itch and pain):
- A-delta (larger, myelinated)
- C-polymodal (smaller, unmyelinated)
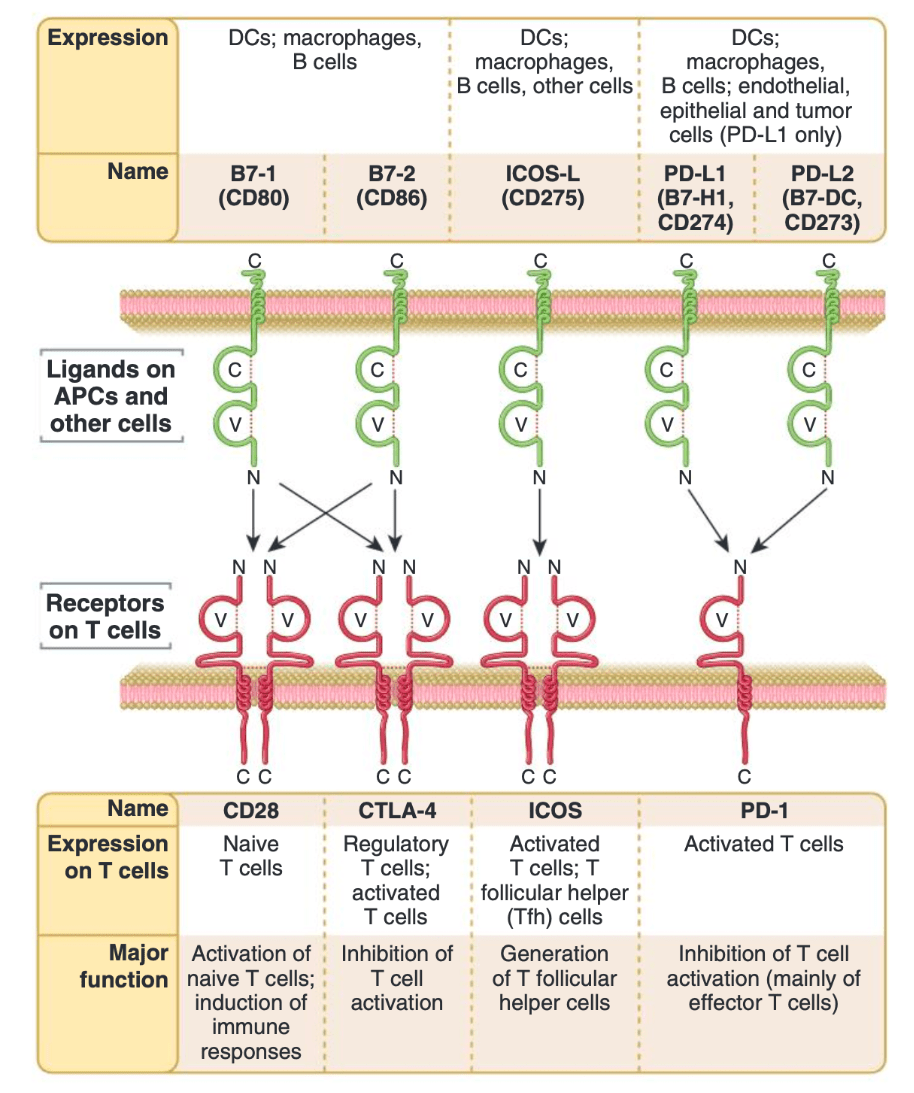
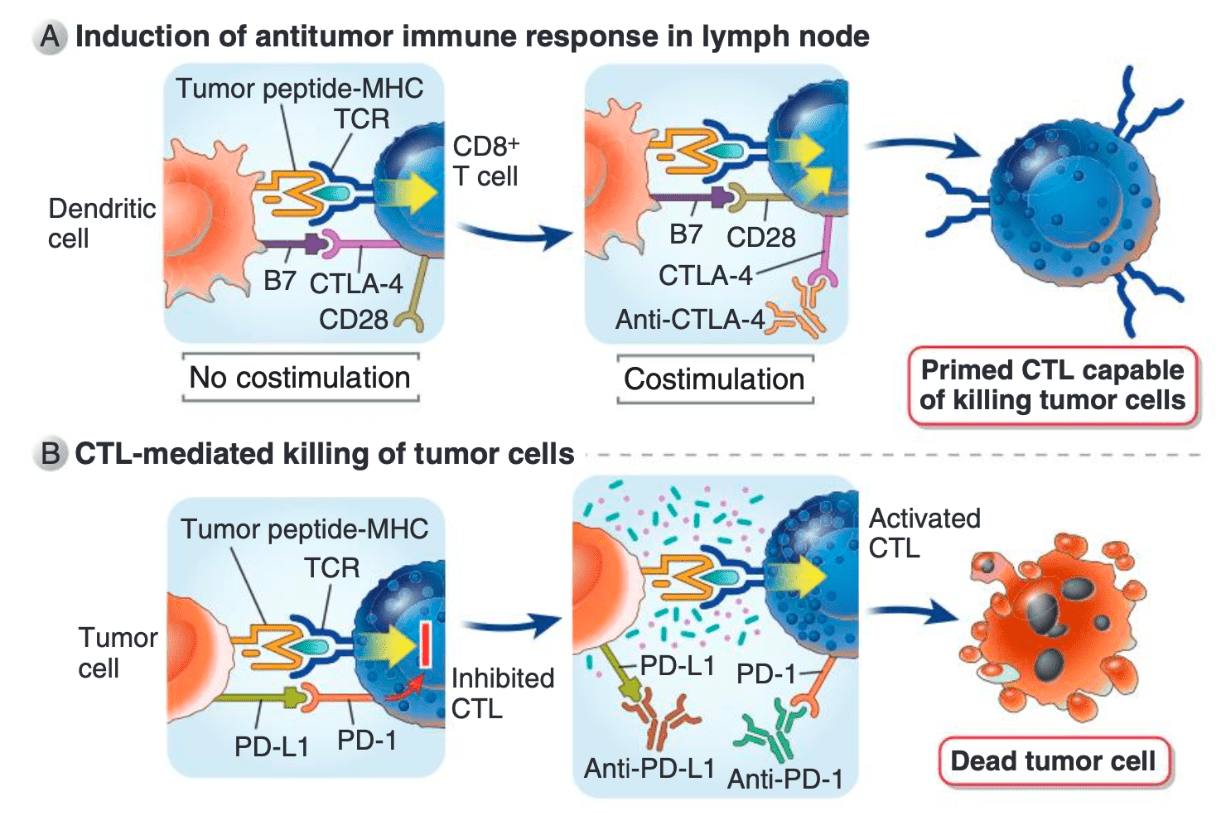
Match the APC - T-cell co-stimulatory signal combinations:
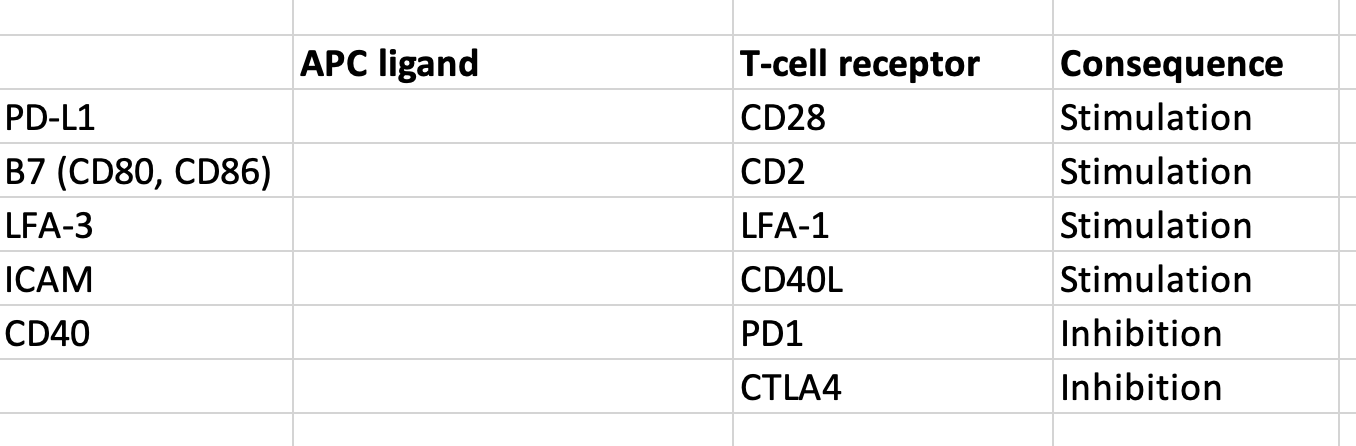
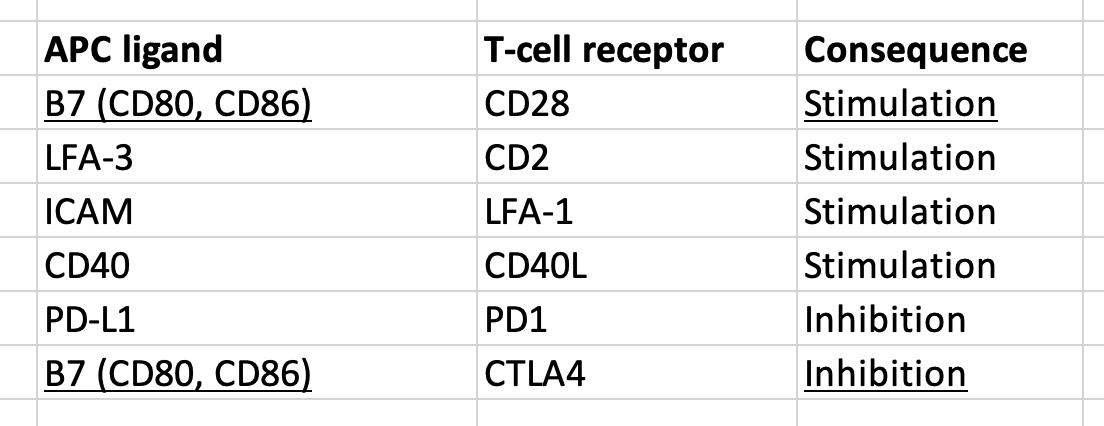 MHCI -- CD8, MHCII -- CD4 (1x8=2x4)
MHCI -- CD8, MHCII -- CD4 (1x8=2x4)
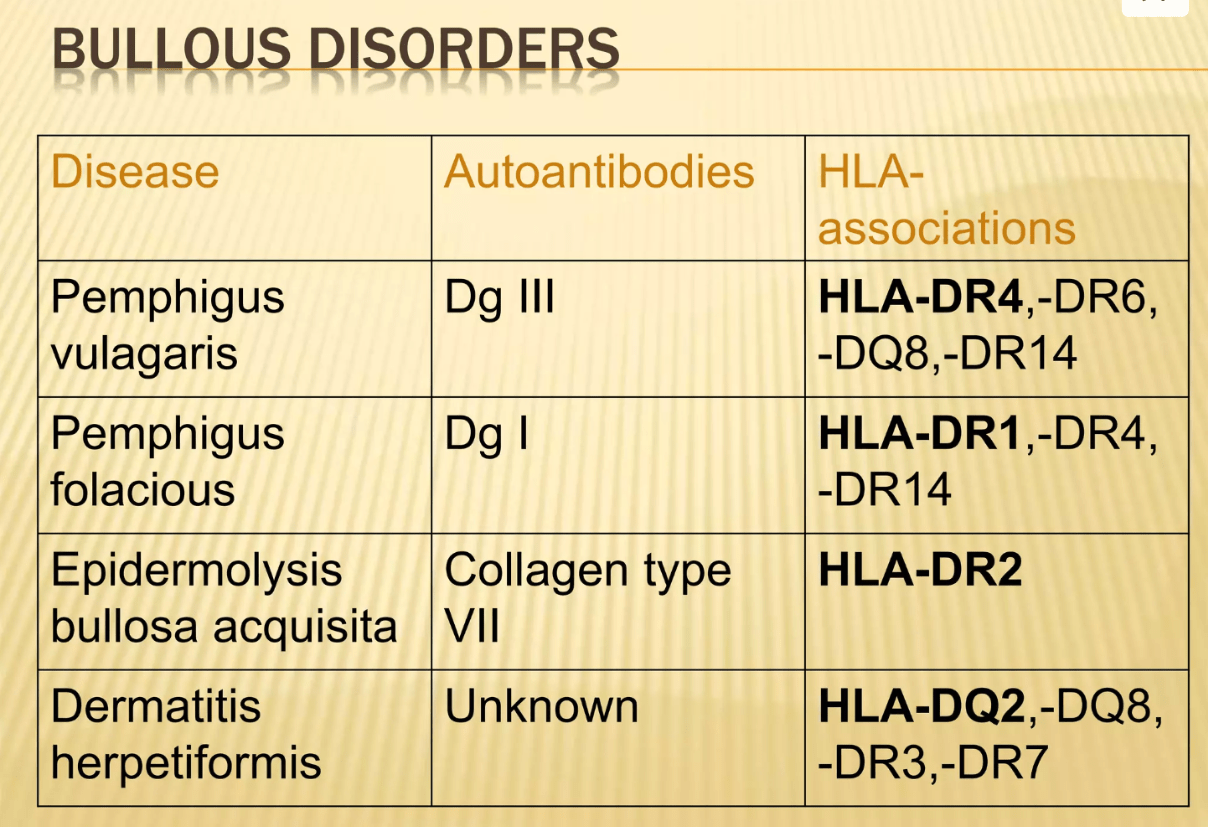
Match the columns for the conditions associated with the following functions and gene mutations



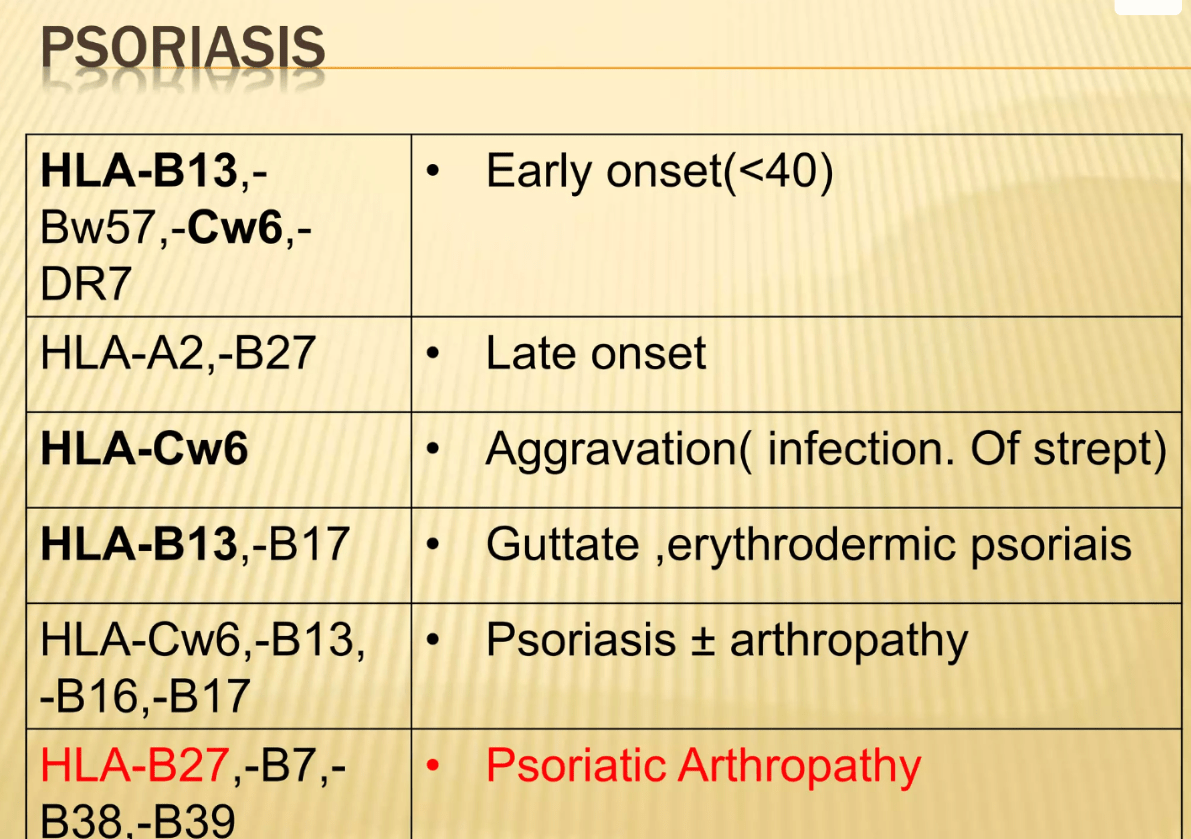
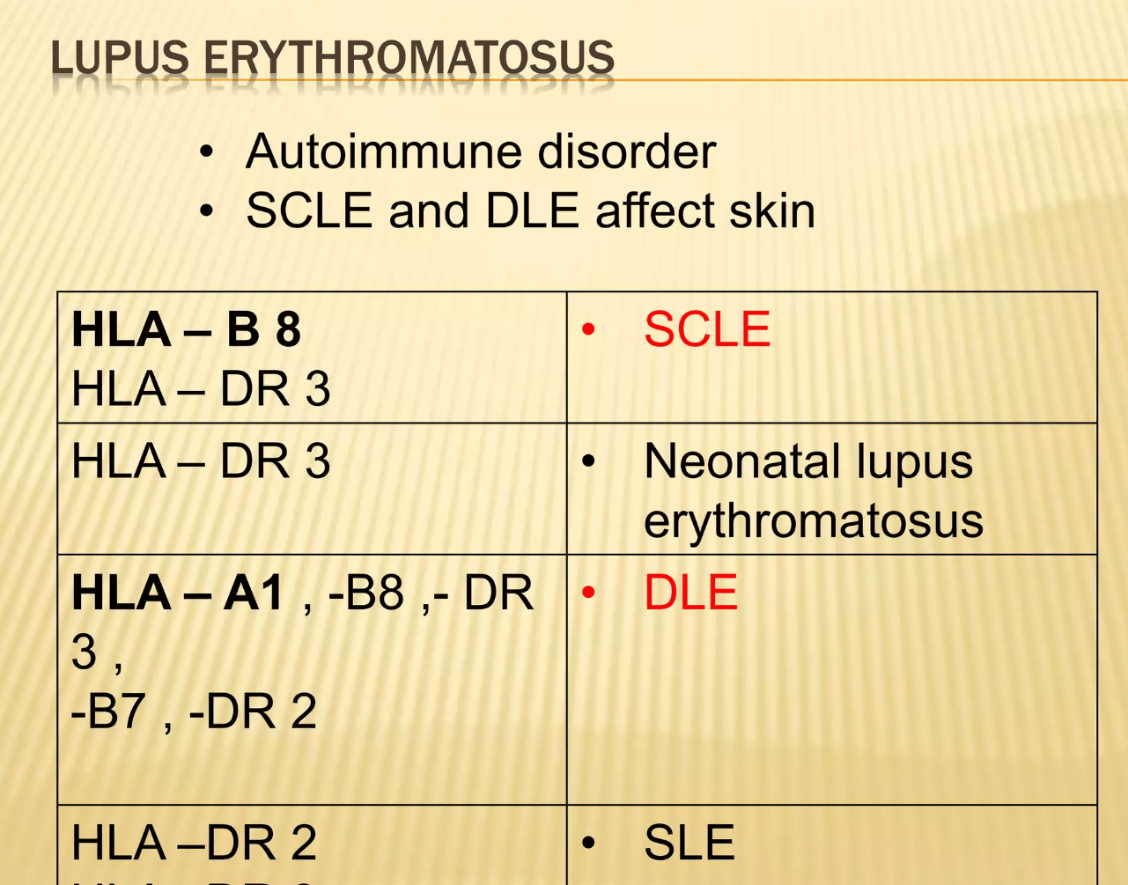
What are the most important MHC HLA subtypes associated with:
(a) Psoriasis (early onset)
(b) Psoriatic arthritis
(c) Behcet's Dz
(d) Dermatitis herpetiformes
(e) Pemphigoid gestationis
(f) SCLE and SLE
(a) HLA-Cw6
(b) HLA-B27
(C) HLA-B51
(D) HLA-DQ2
(E) HLA-DR3/4
(F) HLA-DR3
MHCI --> HLA-B,C,D
MHCII -> HLA-DP,DQ,DR
The lesion is derived from a type of specialized dermal cell. What structure is it derived from and what is the normal function?
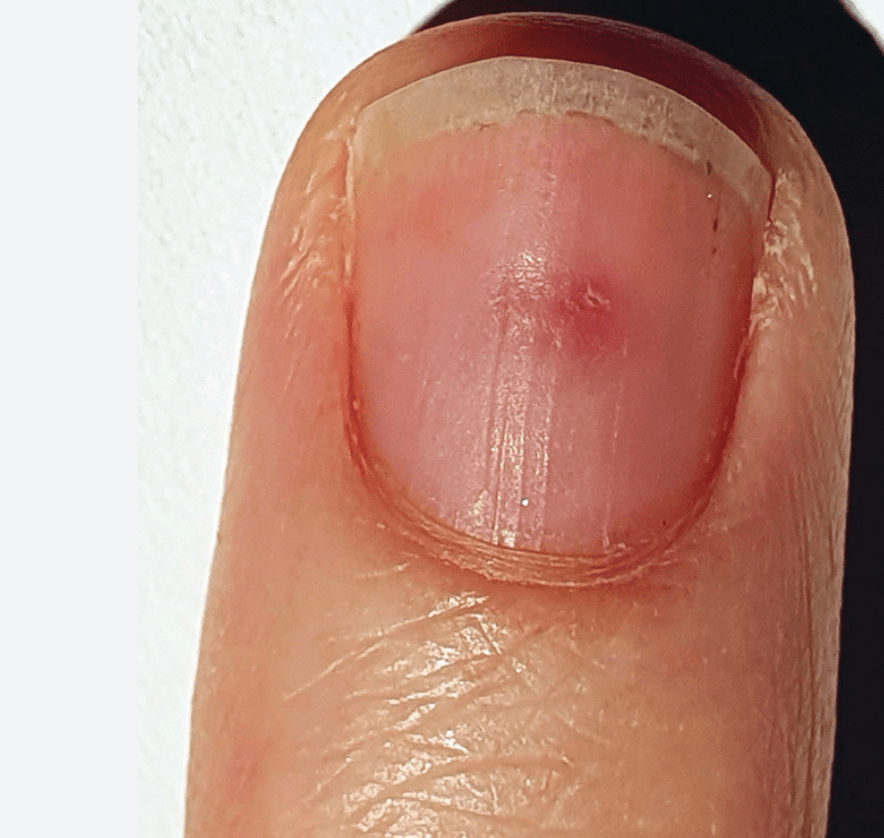
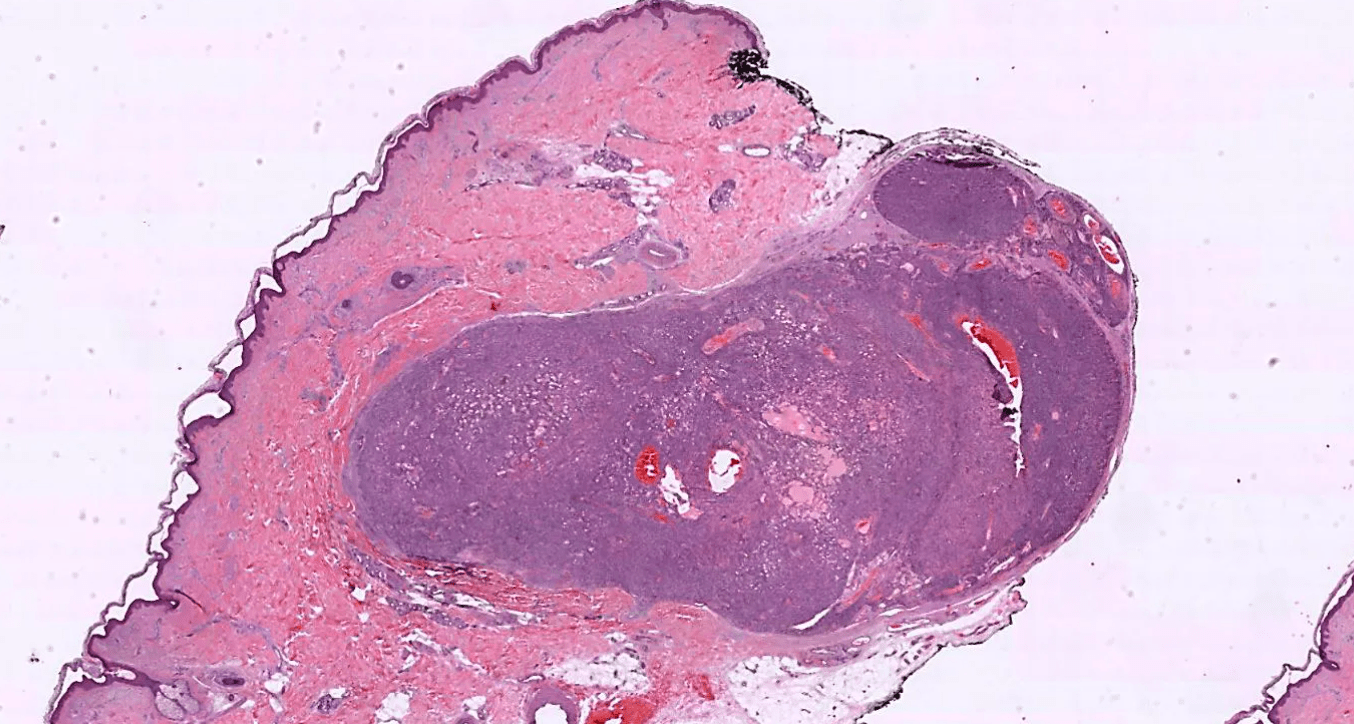
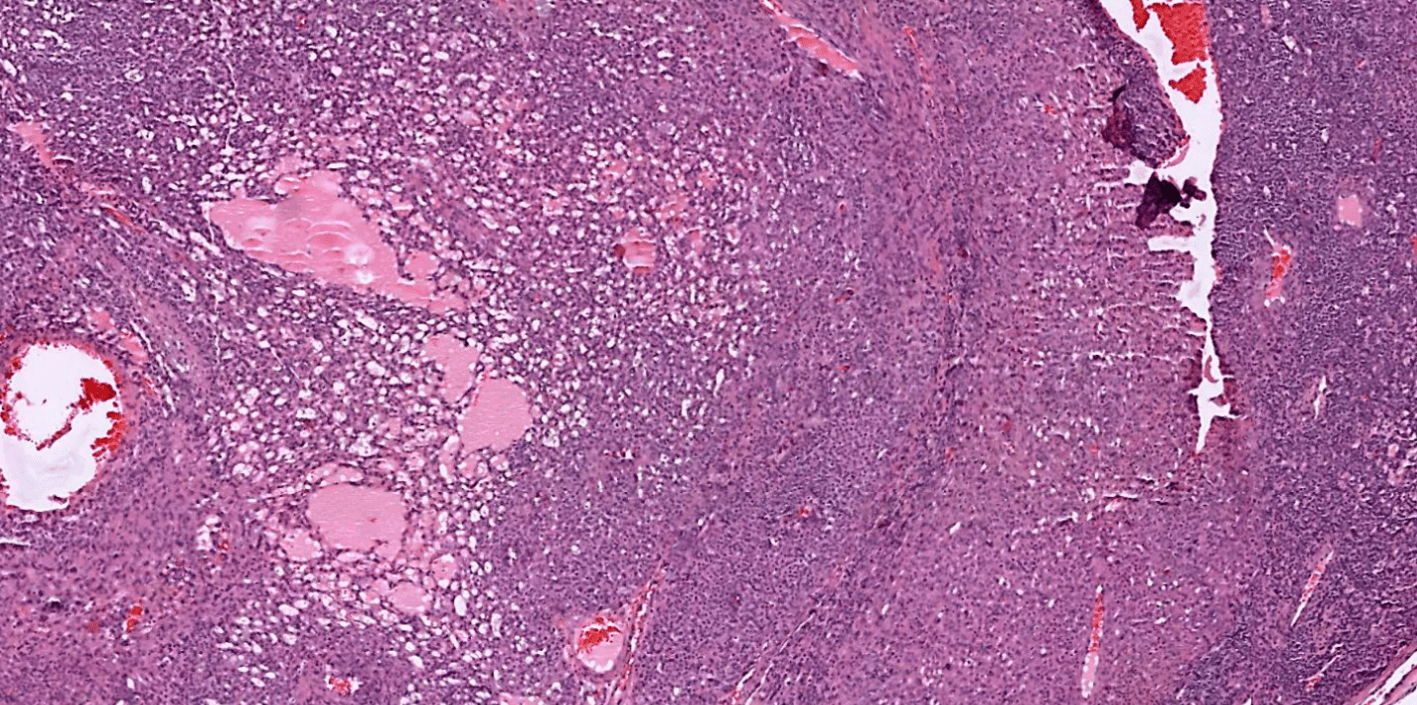
Special smooth muscle derived from Sucquet-Hoyer canals!
Normally around blood vessels, assist in thermoregulation via blood shunting from arterioles to venus (bypass capillaries)
Normally on palms/soles
The deficient factor in this condition is required for what enzymatic reaction in the dermis?
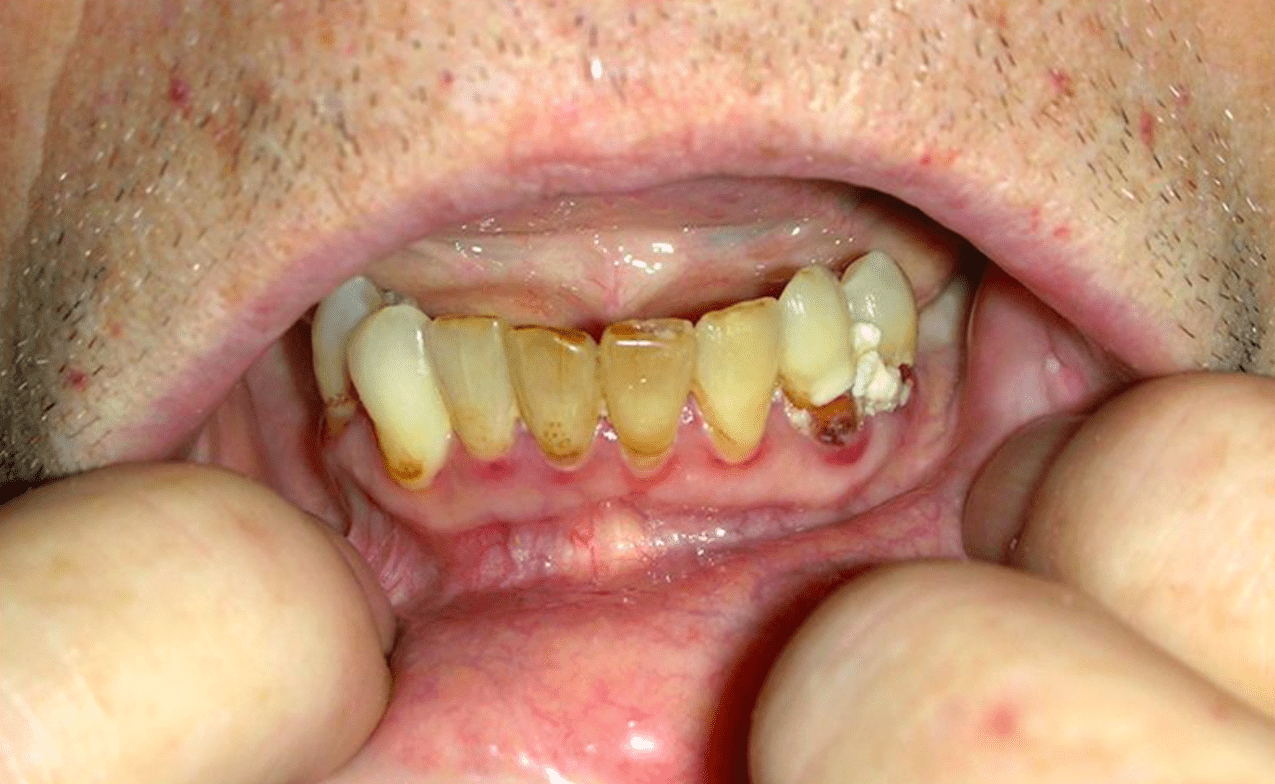
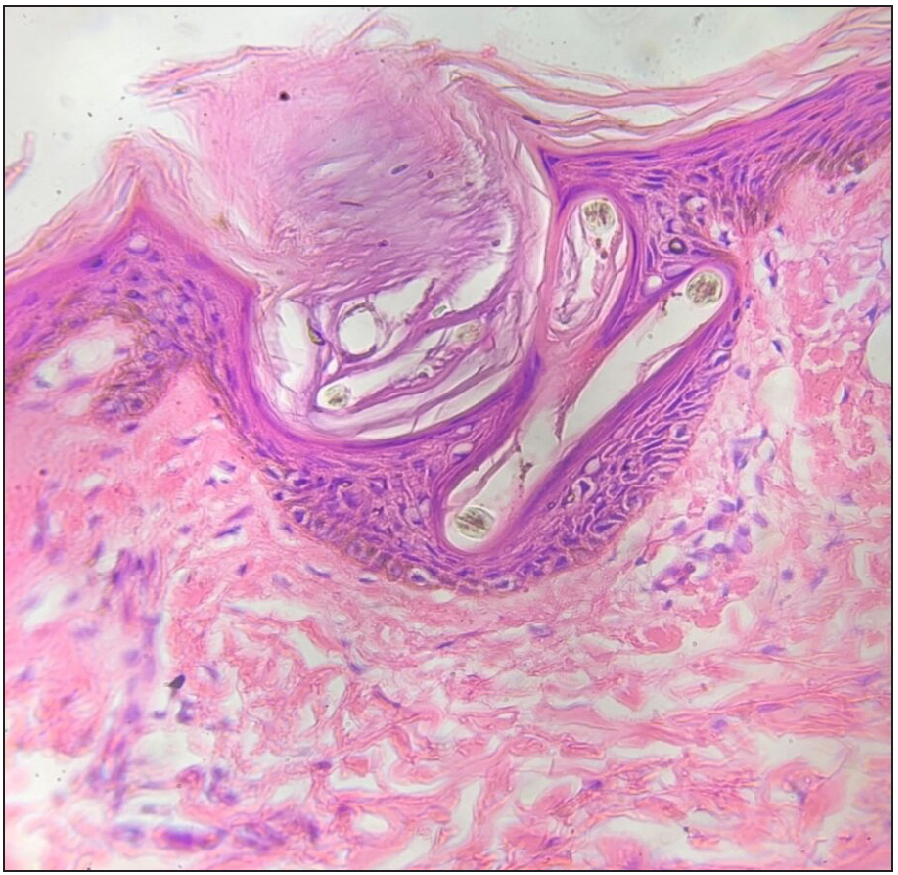
Cross-linking of collagen (lysyl and prolyl hydroxylases)
Scurvy: corkscrew hairs, perifollicular hemorrhage/ hyperkeratosis (first cutaneous sign), hemorrhagic gingivitis, splinter hemorrhage of nails