400
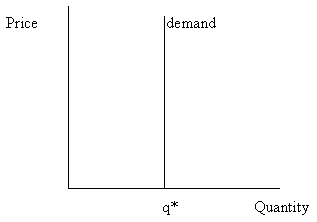
In elastic demand, the value of PED is greater than one and less than infinity. If a product has elastic demand, raising the price of the product will lead to a fall in the quantity demanded, so the total revenue gained by the firm will fall as well. Otherwise, to increase total revenue, the price of the product should not be raised.
What is the effect of a product that has elastic demand on the firm’s total revenue?