These are used to describe the locations of organs on your appendages.
What is distal and proximity?
Groups of cells
What is a tissue?
Kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, and urethra
What is urinary or excretory system?
Breaking down ingested foodstuffs to simple molecules that can be absorbed into the blood
What is digestive?
This carries blood away from the heart
What is arteries?
This keeps our body shapes
What is the skeletal system?
Organs Working together
What is an organ system?
Heart, blood vessels
What is cardiovascular?
Increase in size of the body part or the organism
What is growth?
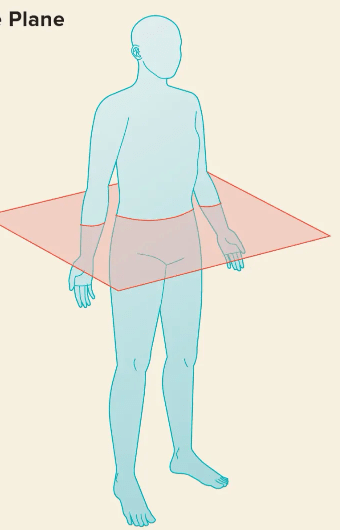
What is the transverse?
The study of the functions of the human body is called
What is Physiology?
Lowest level of organization
What is an atom?
Nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, lungs, trachea, bronchus
What is respiratory?
Protects the body from pathogens?
What is the immune/lymphatic system?
From smallest to largest, what are the living levels of organization within an organism?
What are atoms, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, & organisms?
How many bones do you have in your body
What is 206?
Discrete structure with at least two different tissue types
What is an organ?
Brain, sensory receptors, nerves, spinal cord
What is nervous?
Removing waste from the body
What is excretion?
Controls voluntary and involuntary actions
What is the nervous system?
The study of the structures of the human body is called
What is Anatomy?
Smallest unit of all living things
What is a cell?
Thyroid gland, pituitary gland, pineal gland, thymus, adrenal gland, pancreas, ovary, testis.
What is endocrine?
transports nutrients
What is the blood?
The bodies ability to maintain relatively stable internal conditions.
What is homeostasis?