A sequence of organisms that eat one another in an ecosystem.
What is a food chain?
These organisms consume producers
What is a primary consumer?
A brine fly consumes benthic algae, making it a member of this trophic level.
What is a primary consumer?
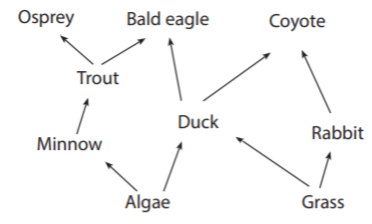
An increase in the duck population provides more food for the coyote population.
What is yes, this interaction could happen in this community?
A river is polluted with nutrients, causing algae populations to grow out of control. Name one reason why this negatively impacts the ecosystem.
What is big changes to one population could affect other populations in ways we can not predict?
All of the feeding relationships in an ecosystem.
What is a food web?
These organisms create their food using processes such as photosynthesis
What is a producer?
The coyote hunts multiple birds found at Mono Lake. After a California gull had consumed its fill of brine shrimp, the coyote strikes, making it a member of this trophic level.
What is a tertiary consumer?
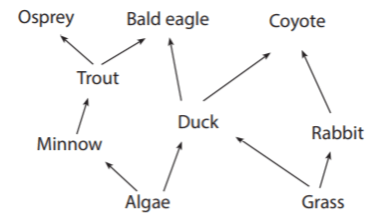 Ospreys and bald eagles compete for food.
Ospreys and bald eagles compete for food.
What is yes, this interaction could happen in this community?
Describe the feeding relationship between a spider and a fly.
Energy flows from the fly to the spider when the spider eats the fly, so an arrow should be pointing from the fly to the spider.
How energy and materials are transferred between trophic levels when consumers eat producers or other organisms; relationship between one organism that consumes another in an ecosystem.
What is a feeding relationship?
These organisms feed at the top of a trophic pyramid
What is a tertiary consumer?
Planktonic algae creates its food using photosynthesis, making it a member of this trophic group.
What is a producer?
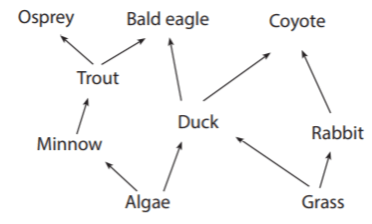
It is possible that an increase in the algae population would cause a decrease in the rabbit population.
What is no, this interaction could not happen in this community?
Aquatic snails were found only on the algae-covered rocks. Based on this statement, aquatic snails could be found at this trophic level.
What is primary consumer?
An organism that is able to produce its own food through photosynthesis.
What is a producer?
These organisms feed on primary consumers.
What is a secondary consumer?
A snowy plover consumes a meal of brine flies at Lake Mono. After eating the flies, it is eaten by a coyote, putting it at this trophic level.
What is a secondary consumer?
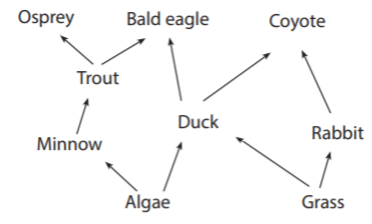
Removing the coyotes will help the osprey get more food.
What is no, this interaction could not happen?
Name at least two benefits of a food-web model for explaining the interactions between organisms in an ecosystem.
What is a food-web model shows what eats what and connections between organisms and shows how energy or food flows through the system?
An organism that consumes parts of dead organisms and converts all the biomass into simple chemicals.
What is a decomposer?
These organisms feed at all levels of a trophic pyramid.
What is a decomposer?
Halobacteria consumes dead matter from all levels and produces food via chemical synthesis, putting it at this trophic level
What is a decomposer?
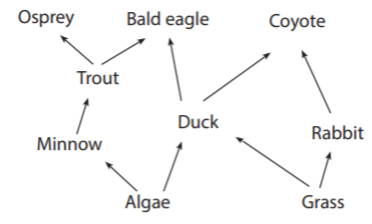 Coyotes depend on rabbits as their only food source.
Coyotes depend on rabbits as their only food source.
What is no,this interaction could not happen in this community?
Name at least two limitations of a food-web model for explaining the interactions between organisms in an ecosystem.
What is a food-web model only shows feeding interactions between organisms, doesn't show population size for each organism, and doesn't show how much food transfers between organisms or to the environment?