A 65-year-old female is admitted for encephalopathy. In the emergency room, a urinalysis was collected. She denies urinary frequency, urgency, and dysuria. E. coli grows on the reflex culture one day after admission.
Her mental status is now much improved, and her encephalopathy is thought to be secondary to drug accumulation with her AKI. What antibiotic therapy should she receive?
Trick question! We do not treat asymptomatic bacteriuria unless patient is pregnant or about to undergo a urologic procedure
Guidelines:
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). "Urinary Tract Infections in Adults | Quality Standards." 2023.
Gupta, K. et al. "International Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis and Pyelonephritis in Women: A 2010 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases." Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52(5);e103-20
How can you adjust your antibiotic plan with a negative nasal MRSA PCR in a patient with pneumonia?
Should discontinue MRSA coverage (vancomycin, linezolid, etc.)
Parente, Diane M et al. “The Clinical Utility of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Nasal Screening to Rule Out MRSA Pneumonia: A Diagnostic Meta-analysis With Antimicrobial Stewardship Implications.” Clinical infectious diseases : an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. 2018;67(1):1-7.
FO is a 52-year-old female who presents to the ED with complaints of abdominal distension and subjective fevers. Her HR is 120 bpm, BP is 105/60, and Tmax is 39.2oC. Blood cultures, CBC, and CMP are collected. Diagnostic paracentesis is performed in the ED and the cell count show PMN count of 349/mm2.
Are antibiotics indicated for FO? If yes, what antibiotic regimen?
Yes - Ceftriaxone 2 g IV Q24H
Biggins, Scott W. et al. "AASLD Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Management of Ascites, Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis and Hepatorenal Syndrome: 2021 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases." Hepatology. 2021;74(2):1014-48.
RW is a 47-year-old female found to have vertebral MRSA osteomyelitis. You are planning on treating her with vancomycin.
What is an appropriate duration of therapy for her osteomyelitis?
6 weeks
Berbari, E. F. et al. "2015 Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Native Vertebral Osteomyelitis in Adults." Clin Infect Dis. 2015;61(6):e26-46.
Li, Ho-Kwong et al. "Oral Versus Intravenous Antibiotics for Bone and Joint Infection." New England Journal of Medicine. 2019;380(5):425-36.
What are the three most common causative organisms for pediatric acute otitis media?
Streptococcus pneumoniae, nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis.
Lieberthal, Allan S, et al. “The Diagnosis and Management of Acute Otitis Media.” Pediatrics. 2013;131(3):e964–e999.
What antimicrobial is inactivated by lung surfactant and requires CK lab monitoring during treatment?
Daptomycin
Daptomycin. Package Insert. Merck & Co., Inc; 2017
AJ is a 29-year-old female with no past medical history admitted to the general medicine service for pyelonephritis. She was treated with cefuroxime as an outpatient, but her symptoms progressed, so she presented to the ED. Cultures taken as an outpatient are now growing >100,000 cfu Enterococcus faecalis. Susceptibilities are still pending.
Based on the University of Utah Hospital antibiogram, what would be an appropriate oral antimicrobial regimen for AJ?
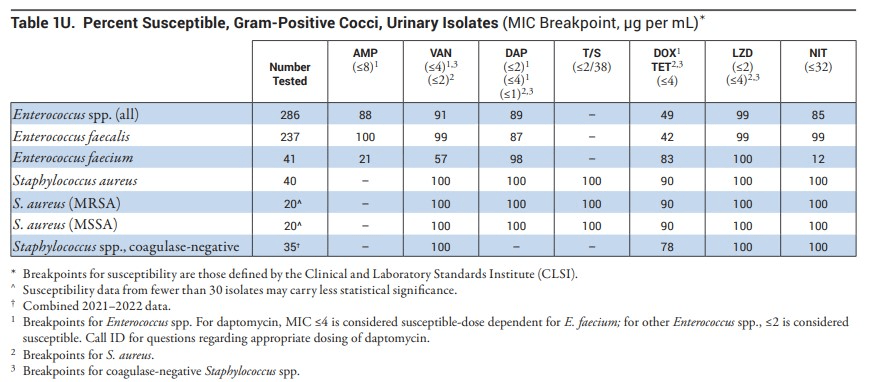
One appropriate option could be: Amoxicillin 1000 mg BID
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). "Urinary Tract Infections in Adults | Quality Standards." 2023.
Gupta, K. et al. "International Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis and Pyelonephritis in Women: A 2010 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases." Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52(5);e103-20
CB is a 68-year-old male admitted to the internal medicine service for management of a COPD exacerbation. He reports increased sputum volume, increased sputum purulence and increased shortness of breath in the week leading to his admission. He has not experienced an exacerbation in the last decade and has not experienced any bacterial infection, respiratory or otherwise in the last decade either.
You’d like to start antibiotics for CB. What regimen do you order?
Azithromycin 500 mg PO qDay x3 days
“2023 Gold Report - Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease.” GOLD. 2023.
SJ is a 42-year-old male presenting with acute on chronic pancreatitis. He reports a 7-day history of poor oral intake and significant pain. He is afebrile, WBC 15,000 cells/mL, CT imaging shows a without presence of gas or evidence of necrosis, and he is hemodynamically stable. There are no interventional plans currently.
What is an appropriate empiric antibiotic regimen for SJ
Antibiotics are not indicated because there is no evidence of necrosis and risk of infection is low during the first 2 weeks of onset
Lenhart DK, et al. "MDCT of Acute Mild (Nonnecrotizing) Pancreatitis: Abdominal Complications and Fate of Fluid Collections." AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008;190(3):643-9.
TL is a 50-year-old male with type 2 diabetes. He presents to the hospital and is admitted for management of sepsis. He is noted to have a purulent wound on his left foot. He has not received antimicrobial treatment in the last 6 months.
What empiric antimicrobial therapy would you order for TL and for what duration?
Amoxicillin/clavulanate X 1-2 weeks
Alternatives: Ampicillin/sulbactam OR 2nd/3rd generation cephalosporin (cefuroxime, ceftriaxone)
Senneville Éric, et al, “IWGDF/IDSA Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetes-related Foot Infections (IWGDF/IDSA 2023)” Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2023
A 4-year-old patient presenting to the emergency department is diagnosed with moderate-severe CAP and requires hospital admission. Upon further questioning, you discover that the patient is not fully immunized.
What is the appropriate empiric treatment regimen if M. pneumoniae and C. pneumoniae are significant considerations?
Ceftriaxone 50-100 mg/kg/day
OR
Cefotaxime 150-200 mg/kg/day in divided doses
AND
Azithromycin 10 mg/kg once daily
Meyer Sauteur, PM, et al. “Infection with and carriage of mycoplasma pneumoniae in children.” Frontiers in Microbiology. 2016;7:329.
Bradley JS, et al. “The management of community-acquired pneumonia in infants and children older than 3 months of age: Clinical practice guidelines by the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society and the infectious diseases society of america.” Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2011;53(7).
Vancomycin is recommended to be administered empirically in combination with ceftriaxone when there is concern for bacterial meningitis.
Which organism is empiric vancomycin added to cover in meningitis?
Penicillin-Resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae
Van de Beek D,t al. “Community-acquired bacterial meningitis.” Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2. 2016
A patient is being treated for acute bacterial prostatitis. They initially received piperacillin/tazobactam but as they near discharge, you are working to find them an acceptable oral regimen.
Of note, they take methadone for opioid use disorder and their last documented QTc is 515 ms. Their eCrCl is 80 mL/min and their potassium is 3.8 mEq/L.
What is an appropriate antibiotic choice for this patient?
Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole
Guidelines:
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. "Prostatitis (Acute): Antimicrobial Prescribing: Guidance." NICE. 2018.
IM is a 45-year-old female admitted for community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). She has a past medical history pertinent only for asthma. She is hemodynamically stable. She reports she had received ampicillin/sulbactam during a previous admission after which she developed anaphylaxis. Her eCrCl is 110 mL/min.
What antibiotic regimen could you initially order for treatment of her CAP?
Levofloxacin 750 mg PO qDay OR Ceftriaxone 1-2 gm q24h (if she is willing to challenge with cephalosporin)
+ Azithromycin 500 mg qDay OR Doxycycline 100 mg BID
Metlay Joshua P, et al. “Diagnosis and treatment of adults with community-acquired pneumonia. an official clinical practice guideline of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America.” American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2019;200(7).
LP is a 70-year-old female admitted following emergent surgical intervention for a large bowel perforation. According to the op note, there was gross contaminate in the abdomen, but complete source control and abdominal closure obtained. LP was started on ceftriaxone 1 gm q24h and metronidazole 500 mg q8h.
What is an appropriate antibiotic duration of therapy?
4 days of therapy post-op or after source control
Sawyer, Robert G. et al. "Trial of Short-Course Antimicrobial Therapy for Intraabdominal Infection." New England Journal of Medicine. 2015;372(21);1996-2005.
NH has MRSA septic arthritis and is being treated with vancomycin.
How will we monitor their vancomycin therapy for both safety and efficacy?
AUC:MIC (estimated using trough and random concentrations)
Goal: 400-600 mcg*hr/mL
No longer using trough-based goals
Rybak, M. J. et al. "Therapeutic Monitoring of Vancomycin for Serious Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Infections: A Revised Consensus Guideline and Review by the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, the Infectious Diseases Society of America, the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, and the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists." Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2020;77(11):835-64.
An immunocompromised 10-year-old patient is presenting to the emergency department with CMV.
What is an appropriate antimicrobial regimen, including duration of therapy?
Ganciclovir IV 5 mg/kg/dose q 12 hours x 2-3 weeks
Azevedo LS, et al. “Cytomegalovirus infection in transplant recipients.” Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2015;70(7):515-523
MS is a 30-year-old male with MSSA bacteremia and a 5 mm prosthetic mitral valve vegetation. CT Surgery elects to defer surgical intervention and to first manage with antibiotics alone.
What is an appropriate antimicrobial regimen for MS including duration of therapy?
Nafcillin 12 gm/day + Rifampin 300 mg TID x 6 weeks + Gentamicin 3 mg/kg/day x 2 weeks
Baddour LM, et al. “Infective endocarditis in adults: Diagnosis, antimicrobial therapy, and management of complications.” Circulation. 2015;132(15:1435–1486.
SJ is a 78-year-old female with an uncomplicated past medical history including hypothyroidism and hyperlipidemia with no recent hospitalizations or antibiotic use presents to the ED with altered mental status, dysuria, and back pain. Her HR is 110 bpm, BP is 105/60, PaCO2 is 29 mmHg, lactate is 2.4 mmol/L, and Tmax is 39.2oC. UA with culture reflex, blood cultures, CBC, and BMP are collected.
What other interventions should be done immediately (name, dose, route, rate, etc.)?
Administer crystalloid IV fluid at 30 ml/kg and ceftriaxone 1-2 gm IV x1
Guidelines:
Gupta, K. et al. "International Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Treatment of Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis and Pyelonephritis in Women: A 2010 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases." Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52(5);e103-20.
Guarino, M. et al. "2023 Update on Sepsis and Septic Shock in Adult Patients: Management in the Emergency Department." J Clin Med. 2023;(12)9.
MG is a 78-year-old male admitted to the Surgical ICU after a motor vehicle collision. MG was intubated in the ED three days ago. He now has new infiltrates on CXR, a rising white count, and increasing ventilator requirements. A sputum culture is obtained but you now need to start antibiotics.
What microbes should your antibiotic selection cover?
S. aureus (including MRSA), P. aeruginosa, and other GNRs
S. aureus (including MRSA), P. aeruginosa, and other GNRs
Kalil, Andre C. et al. "Management of Adults with Hospital-Acquired and Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: 2016 Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the American Thoracic Society." Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2016;63(5):e61-e111.
CT is a 52-year-old male with history of type II diabetes, gastroparesis with multiple obstructions and perforations admitted for a duodenal small bowel obstruction. On day 3 of hospitalization, CT imaging shows perforation. General surgery intervenes but is unable to obtain complete source control.
What is an appropriate antibiotic regimen if he has an anaphylactic allergy to amoxicillin, there is no abscess present, and he remains clinically stable?
Cefepime 2 gm q8h + Metronidazole 500 mg q8h + Fluconazole 800 mg followed by 400 mg qDay x 5-7days
Mazuski, J. E. et al. "The Surgical Infection Society Revised Guidelines on the Management of Intra-Abdominal Infection." Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2017;18;(1):1-76.
KT is a 55-year-old female who underwent a right total knee arthroplasty six months prior to presentation. She undergoes debridement but her prosthesis is retained. Cultures taken in the OR grow MSSA. Ortho requests she receive cefazolin therapy for 6 weeks.
What agent may be administered concurrently for to enhance antimicrobial penetration to the prosthesis?
Rifampin (300 mg BID)
Osmon, D. R. et al. "Executive Summary: Diagnosis and Management of Prosthetic Joint Infection: Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America." Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56(1):1-10.
What could you consider for RSV prophylaxis for a patient less than 12 months old, born before 29 weeks and without chronic lung disease of prematurity or congenital heart disease?
Palivizumab IM 15 mg/kg monthly throughout RSV season
Brady Michael T, et al. “Updated Guidance for Palivizumab Prophylaxis Among Infants and Young Children at Increased Risk of Hospitalization for Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection.” Pediatrics. 2014;134(2):415–420.
What are the respiratory fluoroquinolones and why are they considered respiratory FQs?
Levofloxacin, moxifloxacin, and gemifloxacin
Reliable coverage of S. pneumoniae
Zhanel, George G et al. “A Review of New Fluoroquinolones : Focus on their Use in Respiratory Tract Infections.” Treatments in respiratory medicine. 2006;5(6):437-65.
DJ is a a 60-year-old male with paraplegia, neurogenic bladder, and recurrent UTIs who presents to the ED with back pain, chills, and foul-smelling urine.
What is an appropriate empiric regimen for DJ if his historical urine cultures show this organism and its susceptibilities?
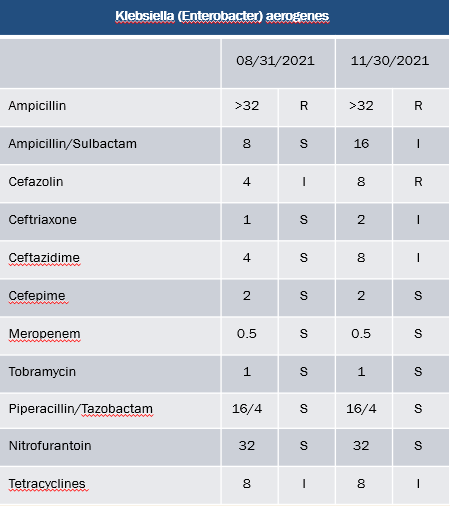
Cefepime 2 gm q8h
JS is a 29-year-old male with loculated left sided pleural effusion. Patient recently had community-acquired pneumonia, and felt like he never fully recovered. He was treated with azithromycin x 2 and prednisone. He eventually presented to the ED, and a CT scan showed a small basilar loculated effusion. He underwent attempted thoracentesis, but only a small amount of fluid could be drained. It was culture negative.
What empiric antibiotic therapy could you order for JS?
Ampicillin/sulbactam 3 g IV Q6H (or ceftriaxone 1 g IV Q24H + Metronidazole 500 mg IV Q8H)
Want to cover anaerobes, often culprit of empyema
Shen, K. R. et al. "The American Association for Thoracic Surgery Consensus Guidelines for the Management of Empyema." J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;153(6): e129-e46.
JT is a 72-year-old female with type 2 diabetes, chronic kidney disease (baseline SCr = 2.2 mg/dL), and cirrhosis complicated by ascites for which she receives intermittent therapeutic paracenteses (Child-Pugh Score 8, total bilirubin 2.8 mg/dL). JT’s reported medication allergies/intolerances include metformin (diarrhea), levofloxacin (arthralgia), and salicylates (rash).
What is the best regimen for chronic SBP prophylaxis for JT?
No chronic antimicrobial prophylaxis is indicated. JT’s ascitic fluid protein level does not yet meet criteria for chronic prophylaxis
Biggins, Scott W. et al. "AASLD Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Management of Ascites, Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis and Hepatorenal Syndrome: 2021 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases." Hepatology. 2021;74(2):1014-48.
Clindamycin is often added to antimicrobial regimens in patients with suspected necrotizing soft tissue infections for both empiric anaerobic coverage and its ability to decrease toxin production.
Which other antibiotic may have toxin inhibiting properties?
Linezolid
Ament PW, et al. “Linezolid: Its role in the treatment of gram-positive, drug-resistant bacterial infections.” American Family Physician. 2002;65(4):663-671
What treatment should be given to all pediatric patients admitted for measles?
Vitamin A
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “For healthcare professionals - diagnosing and treating measles.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2020
JR is a 76-year-old male with Crohn’s disease (on Humira), HTN, and HLD admitted for a right hip fracture. On hospital day 4, he develops pneumonia. He is administered vancomycin and piperacillin-tazobactam, respiratory cultures ordered, and rapid antigen tests collected. In the following days, he does not make significant improvement. You do not have any culture data yet, but you receive his rapid antigen results.
What adjustments should be made to JR’s pneumonia treatment regimen?
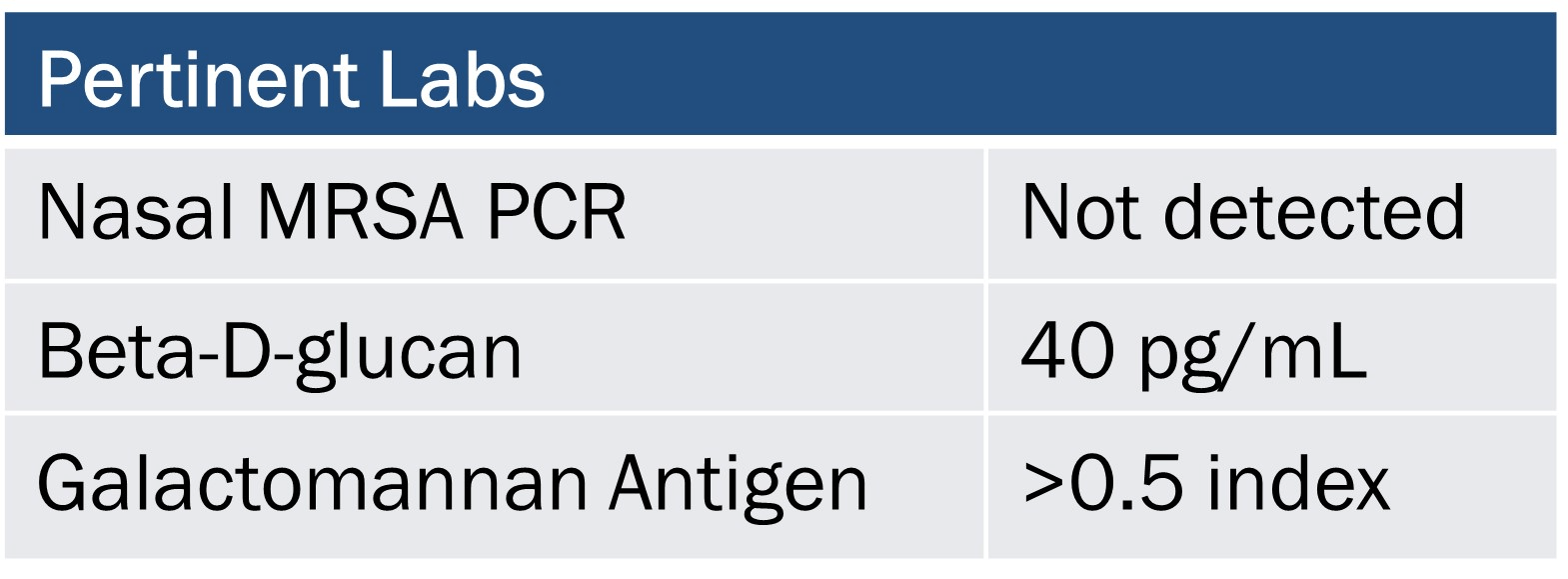
Discontinue Vancomycin and add Caspofungin 70 mg x 1 then 50 mg daily (or another aspergillus active antifungal)
Carr AL, Daley MJ, Givens Merkel K, et al. Clinical Utility of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Nasal Screening for Antimicrobial Stewardship: A Review of Current Literature. Pharmacotherapy. 2018;38:1216-1228..
Finkelman MA. Specificity Influences in (1→3)-β-d-Glucan-Supported Diagnosis of Invasive Fungal Disease. J Fungi (Basel). 2020 Dec 29;7:14.