Heating through direct contact
What is conduction
Water attaches to water
What is cohesion
pH of 7
What is neutral
This determines identity
What are protons
This determines reactivity
What is valence electrons
Heating through space. Heat goes in all directions
What is radiation
Water travels up a surface
What is adhesion
Sour and sticky
What is an acid
Number of neutrons in an atom of Francium.

What is a 136
Elements in this period have 4 energy levels
What is period 4
Heating through liquids and air. Heat rises.
What is convection
This allows insects to “walk” on water
What is surface tension
Slippery and bitter
What is a base
The area of an atom that is overall positively charged
What is the nucleus
These elements are nonreactive
What are noble gases
will also accept “group 18 or 8A”
Often called “Mass in Motion”, an increase in these two variables will increase momentum
What is mass or velocity
Water has a high surface tension because of this related property
What is cohesion
High pH
What is a base
Charge inside the nucleus of an element with 11 protons, 12 neutrons, and 11 electrons
What is +11
This element has a smaller atomic mass than lithium but the reactivity
What is hydrogen
Reason why a bowling ball has more momentum than a golf ball when they are moving at the same speed.
What is a bowling ball has more MASS
Adding these two things together until the solution has a pH of 7 produces water and salt is called neutralization
What is an acid and base
Products of mixing and acid and base
What is water and salt
Element shown below
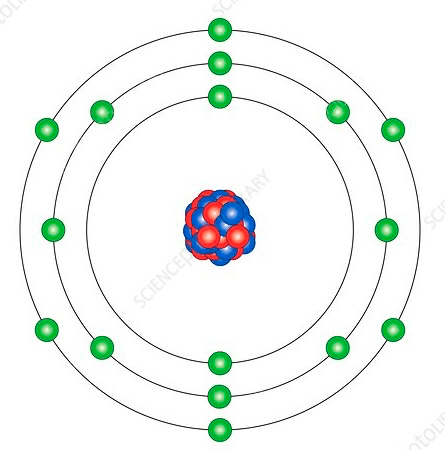
What is Sulfur
Element with 4 energy levels and 2 valence electrons
What is calcium
The coefficient ratio for the following equation
Fe2(SO4)3 + KOH → K2SO4 + Fe(OH)3
1-6-3-2
Fe2(SO4)3 + 6 KOH → 3 K2SO4 + 2 Fe(OH)3