This term describes the increase in coronary blood flow that occurs in response to increased heart muscle activity.
What is active (or functional) hyperemia?
This simple bedside test can reveal ST-segment changes that may indicate ongoing myocardial ischemia and is commonly performed to assess heart rhythm, rate, and infarction.
What is an EKG?
Atherosclerosis begins with damage to this layer of the arterial wall.
What is the endothelium?

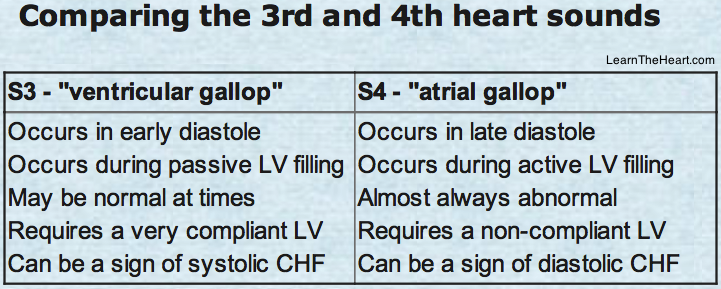
This heart sound occurs just after S2 and is associated with rapid ventricular filling.
What is S3?
This structure forms over the atherosclerotic core and helps stabilize the plaque.
What is the fibrous cap?
Coronary blood flow primarily occurs during this phase of the cardiac cycle.
What is diastole?
This type of imaging uses exercise or medication to stress the heart and assesses for areas of poor blood flow.
What is a nuclear stress test?
This class of drugs lowers LDL by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase.
What are statins?

S4 is best heard with this part of the stethoscope in the left lateral decubitus position.
What is the Bell?
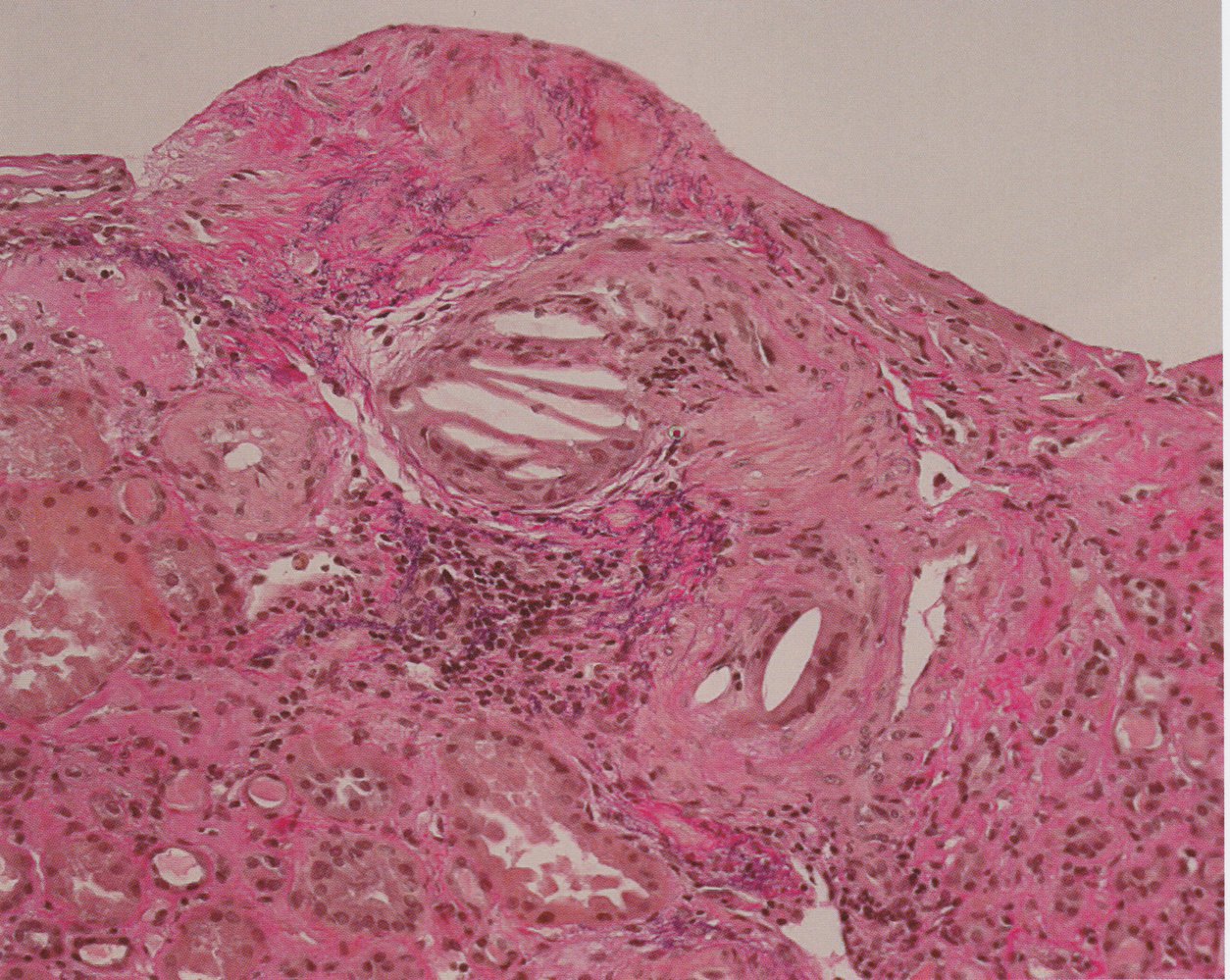
These needle-shaped spaces found in atherosclerotic plaques represent areas where this lipid was once present.
What are cholesterol clefts?
In severe coronary stenosis, this phenomenon occurs when vasodilatory reserve is lost. This phenomenon can be exacerbated by vasodilatory medications.
What is coronary steal?

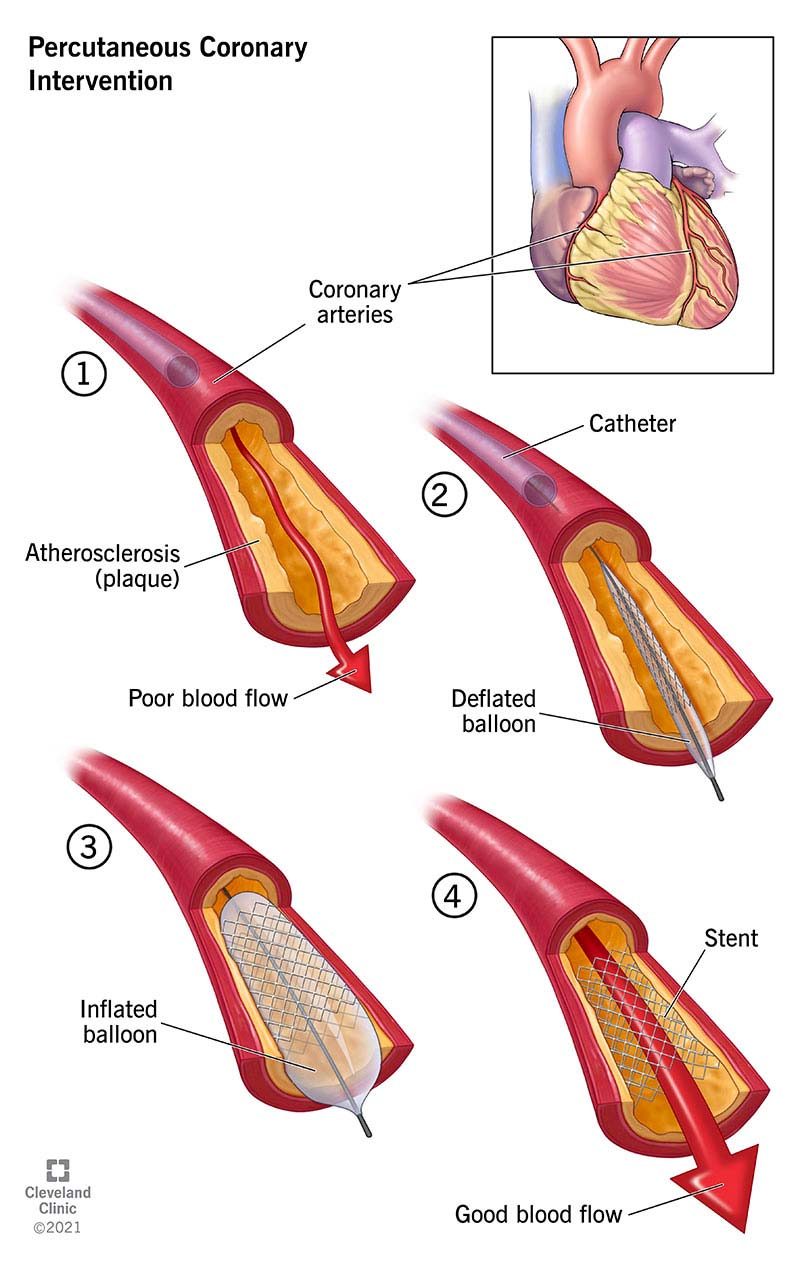
This term refers to the collective use of angioplasty and stenting to treat coronary artery disease.
What is percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)?
These two types of cholesterol are often called "bad" and "good," respectively.
What are LDL and HDL?
The S4 heart sound results from this mechanical event in the cardiac cycle.
What is atrial contraction into a stiff ventricle?
This change in myocardial tissue occurs within 12–24 hours after ischemia.
What is coagulative necrosis?

This layer of the heart is most vulnerable to ischemia due to high extravascular compression during systole.
What is the subendocardium?
This physiological measurement taken during angiography determines how much a coronary stenosis impairs blood flow.
What is fractional flow reserve (FFR)?
Per StatPearls:
Ischemia-producing stenosis (FFR less than 0.75)/Revascularization
Non–ischemia-producing stenosis (FFR greater than 0.80)/Medical Therapy
Gray zone (FFR 0.75 to 0.80)/Revascularization versus Medical therapy
These immune cells engulf oxidized LDL in the vessel wall and become foam cells.
What are macrophages?

This condition makes S4 impossible to hear, even if the ventricle is stiff.
What is atrial fibrillation?
This type of histological cell infiltrate predominates 1–3 days after myocardial infarction.
What are neutrophils?

This law explains the relationship between vessel radius and resistance, highlighting why small changes in vessel radius have significant affects on flow.
What is Pouiseuille's Law?

After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) patients are usually placed on this type of medication regimen to prevent stent thrombosis.
What is dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT)?
These two NON-modifiable risk factors significantly increase the risk of developing atherosclerosis.
What are age and family history?
The simultaneous presence of S3 and S4, often heard during tachycardia, is called this and suggests advanced heart disease.
What is a summation gallop?

This type of collagen is deposited by fibroblasts in the healing phase of a myocardial infarction.
What is type I collagen?