A molecule that is made up of at least one metal and at least one non-metal.
What are Ionic Molecules/Compounds?
The 'small' numbers in a chemical formula that represent the number of atoms of a particular element are in a molecule.
What are subscripts?
The powerhouse of the cell; where cellular respiration takes place in the cell.
What is the mitochondria?
The four letters of the Nitrogenous Bases.
What is A, T, C, G ?
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine
DNA Replication happens during this phase of the cell cycle
What is S (Synthesis) Phase?
What are alleles?
? = Displacement/time
What is velocity?
All living things are made up of these types of molecules.
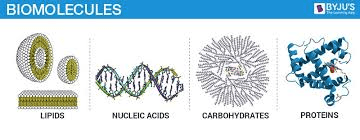 What are biomolecules (organic molecules)?
What are biomolecules (organic molecules)?
The energy-carrying molecule that is one of the products of cellular respiration.
What is ATP (adenosine triphosphate)?
The two broadest categories of cells
What are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Cells spend most of their life in this stage of the cell cycle
What is Interphase?
The enzyme in charge of attaching free nucleotides to the exposed strands of DNA during replication
What is DNA Polymerase?
The physical characteristics of an individual, or the result of the individuals genes
What is a phenotype?
The unit for acceleration
What is m/s2?
In these types of bonds, electrons are shared between atoms to fill their valence shells.
What are covalent bonds?
400-700 nm wavelengths within the electromagnetic spectrum.
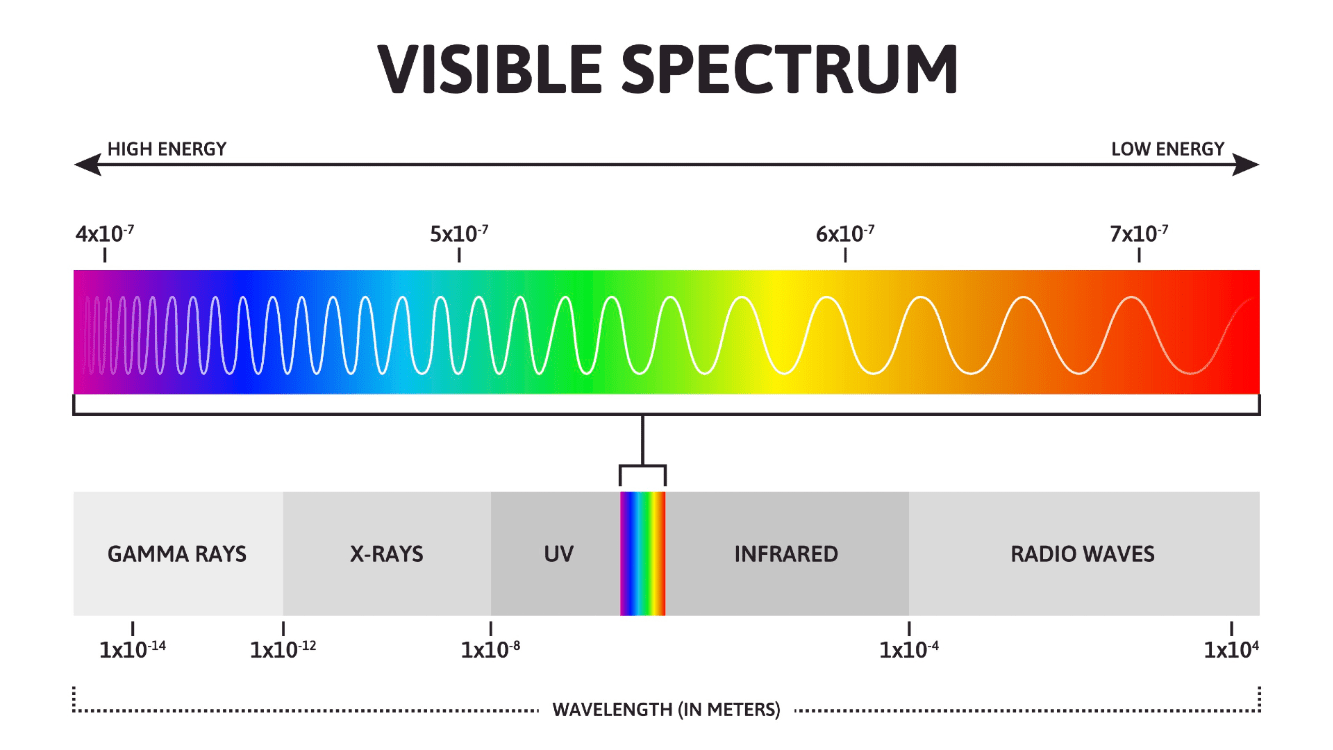 What is Visible Light? (ROYGBIV)
What is Visible Light? (ROYGBIV)
Two cell parts/organelles that differentiate plant and animal cells
What is 1) cell wall 2) chloroplasts 3) large, central vacuole?
Tumors can be caused by mutations to one of these types of genes
What are proto-oncogenes OR tumor suppressor genes?
Identify the phase of mitosis: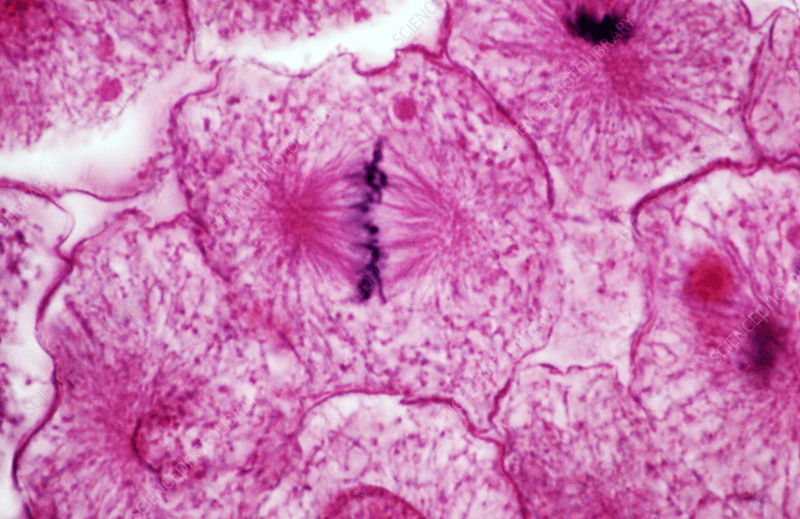
What is metaphase?
The allele that is expressed in a heterozygote
What is the dominant allele?
When velocity is constant, acceleration = ?
What is 0 m/s2?
These biomolecules are associated with energy.
What are carbohydrates? (sugars for short term, starches for long term)
Identify the reaction and fill in the blanks: CO2 + ____ ---> _____ + O2
What is Photosynthesis; H2O (water) and C6H12O6 (glucose)?
The cell part responsible for assembling proteins.
The 'keepers' of the cell cycle.
What are Stop and Go Proteins OR cell cycle regulators
This process takes place in the nucleus and converts DNA to mRNA
What is Transcription?
What type of disorder is shown in this pedigree?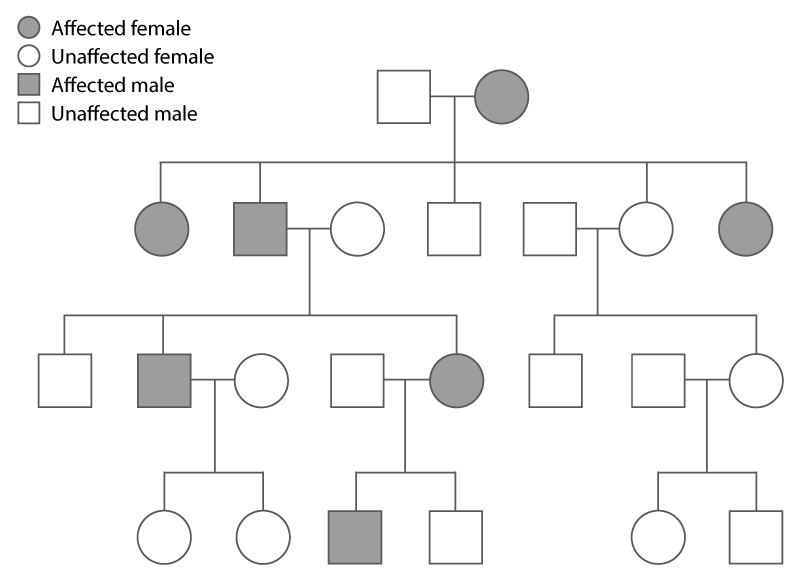
What is a dominant disorder?
A car is traveling 3 m/s North. It turns around and moves South at the same speed. What is its velocity?
What is -3 m/s?
Come up to the board and draw the Lewis Dot diagram for the following atoms: Oxygen, Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorous, and Sulfur
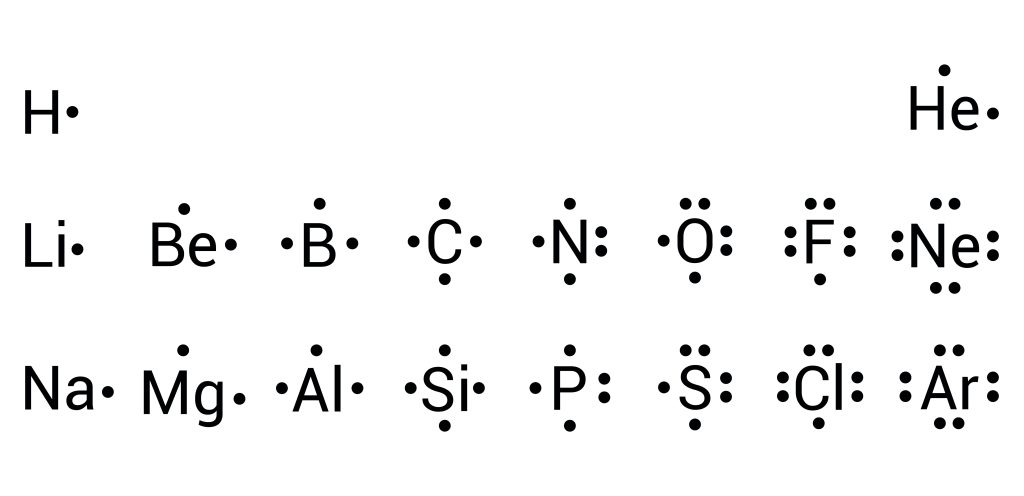
One way to measure the rate of cellular respiration.
What is O2 consumption OR CO2 production?
Would also accept: Heart Rate or Breathing Rate
Identify this cell: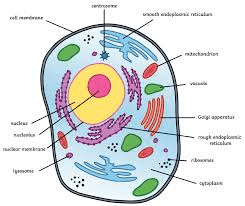
What is a eukaryotic, animal cell
TP53 codes for the TP53 protein which regulates cell division by keeping cells from growing or dividing uncontrollably, making it this type of gene
What is a tumor suppressor gene?
Transcribe and then use the Codon Chart to translate the following portion of DNA to the appropriate amino acid sequence: TAC GTA ATA ATT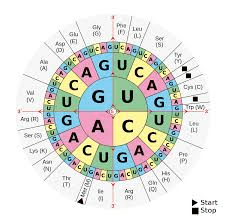
What is Met - His - Tyr - Stop?
AUG CAU UAU UAA
What is the genotypic and phenotypic ratio when you cross two heterozygous individuals?
Genotypic Ratio: 1:2:1
Phenotypic Ratio: 75% Dominant, 25% Recessive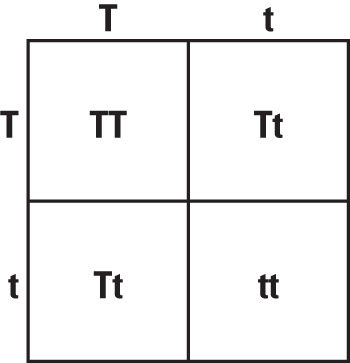
Describe the motion of this object: 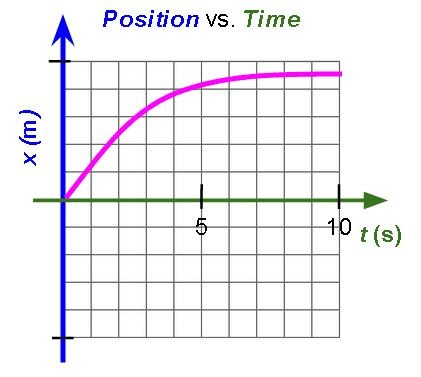
What is slowing down in the positive direction?