How do you detect MI in patients with paced rhythm or old LBBB
Modified Sgarbossa Criteria:
1. Concordant ST elevation ≥ 1 mm in ≥ 1 lead
2. Concordant ST depression ≥ 1 mm in ≥ 1 lead of V1-V3
3. Proportionally excessive discordant STE in ≥ 1 lead anywhere with ≥ 1 mm STE, as defined by ≥ 25% of the depth of the preceding S-wave
What is Reynold's pentad and what disease is it associated with
Cholangitis -
abdominal pain, fever, jaundice, altered mental status and shock
What vital sign changes would make you concerned for brain herniation?
Cushing's reflex (2/2 increased ICP): hypertension, bradycardia, irregular respirations
What is the usual source of infection and diagnostic criteria for PMN Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis (SBP)?
E. coli translocation from gut
Paracentesis positive if: total WBC > 500, PMN (neutrophils) > 250, pH < 7.34, low glucose, (+) gram stain/culture.
Hypotensive pediatric trauma, what should the initial bolus of blood and IVF be?
pRBC: 10cc/kg, crystalloid: 20cc/kg
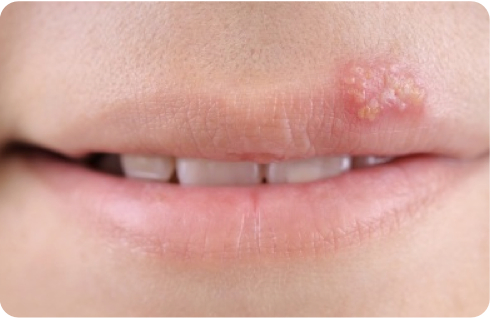
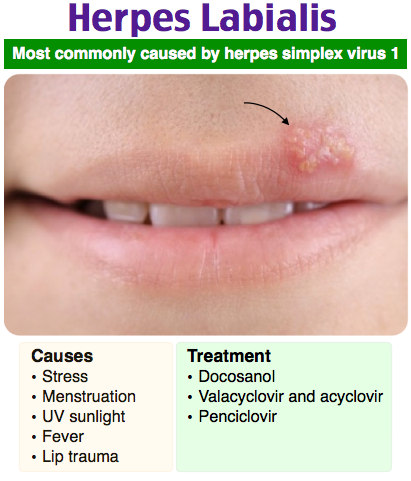
Diagnose this skin lesion
What medication can cause a bidirectional ventricular tachycardia?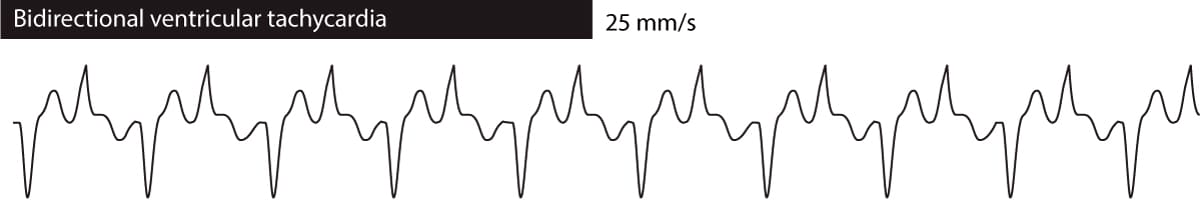
Digoxin
What pathogen causes neonatal conjunctivitis with purulent discharge
Neisseria gonorrhoeae conjunctivitis
Tx: systemic cefotaxmine. Topical tx is not enough
What are the CSF findings for bacterial meningitis
Opening pressure: ↑, WBCs: ↑↑ (>1000; neutrophil predominance), protein: ↑, glucose: ↓
What pathology would you suspect in a patient presenting with blood in their stool after a recent AAA repair. What part of the body does this typically involve?
Aortoenteric fistula
Triad: GI bleed ("herald bleed") + abdominal pain + palpable mass
Rare, but high mortality.
Duodenum is most commonly involved portion of the intestines.
What location of a dog bite is a candidate for primary closure?
Facial laceration (close approxiation is appropriate and does not lead to increased infection rates).
What is the most common cause of Small Bowel Obstruction?
Adhesions (very common with prior surgery) > tumor/mass > hernia
Name 4 causes of high output heart failure
Hyperthyroidism, Beriberi, AV Fistula, Severe anemia, Pregnancy
What two CNS mass lesions are associated with HIV/AIDS
1) Toxoplasmosis (multiple ring-enhancing lesions w/ edema)
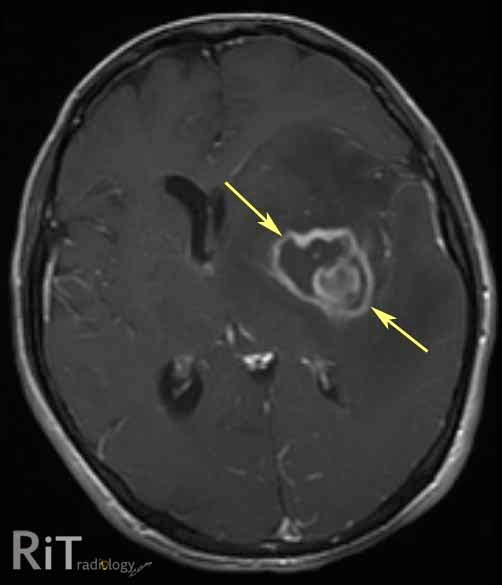
2) CNS lymphoma (hyperdense, round enhancing lesions)
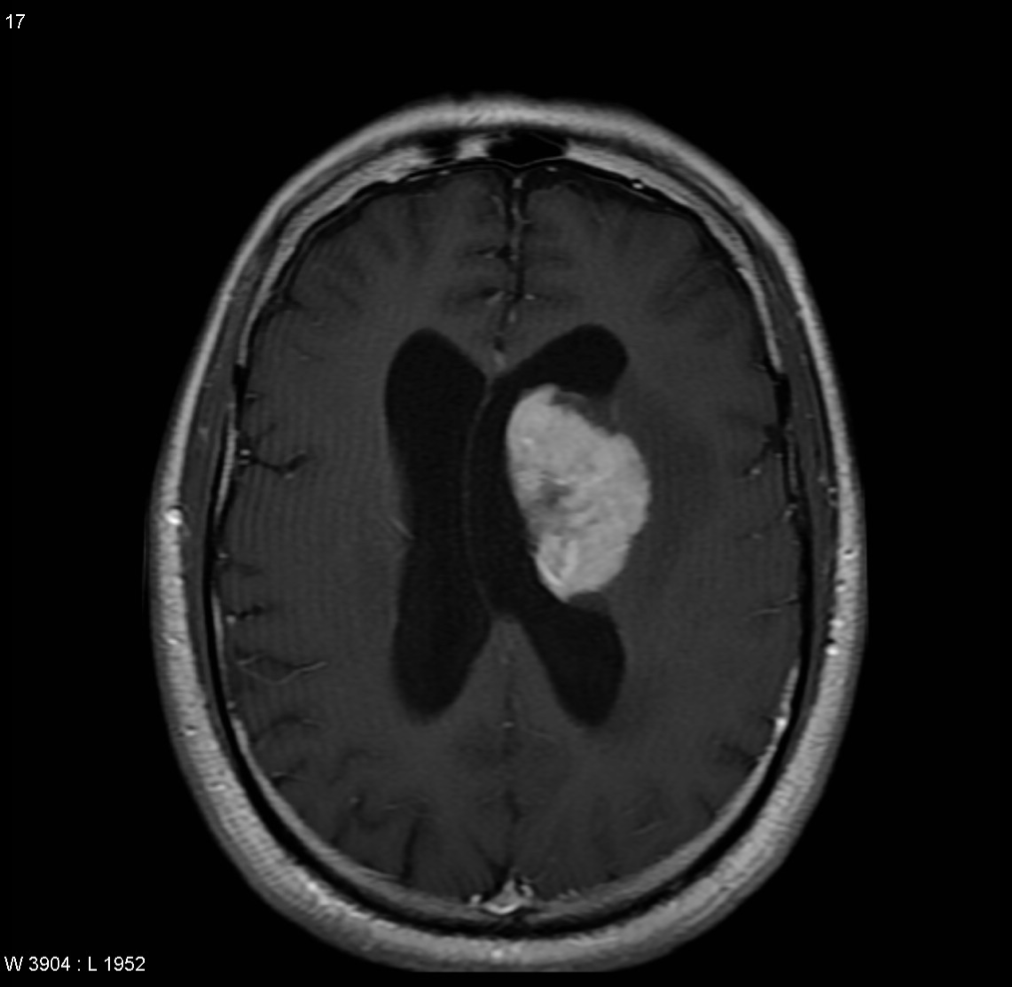
Best study to diagnose venous sinus thrombosis
MR venography = gold standard
Name 3 ways to treat bleeding from a trachea-innominate fistula
- Intubate to compress bleeding through trach site
- hyper-inflate cuff
- Compress vessel with finger.
What is the Parkland Formula
Resuscitation volume = 4 cc/kg x TBSA% x wt (kg)
50% in first 8hr since time of burn, 50% over next 16hr
You suspect your patient has bacterial vaginosis, what 3 exam findings confirm your diagnosis and how do you treat it?
Caused by Gardnerella vaginalis
Amsel criteria (3 out of 4 means positive test)
- vaginal pH greater than 4.5
- fishy odor (positive whiff test)
- milky discharge
- presence of clue cells on microscopic examination of vaginal fluid.
Tx: metronidazole
What meets STEMI criteria for leads V2-V3 versus all other leads?
V2-V3:
- ≥2mm in MEN ≥ 40yrs
- ≥2.5mm in MEN < 40yrs
- ≥ 1.5mm in WOMEN
All other leads: STE at the J-point of ≥ 1mm in two contiguous leads
Name 5 classic physical exam findings of Infective Endocarditis
- Osler Nodes (painful nodules on fingertips)
- Janeway Lesions (nontender hemorrhagic lesions on palms/soles)
- Roth Spots (retinal hemorrhages)
- Splinter hemorrhages (linear on nails)
- Petechiae
- New Murmur
What are the symptoms of anterior cord syndrome
Complete loss of motor function and sensation of pain and temperature below the injury.
Vibration, proprioception, and light touch are preserved.
What are 4 indications for emergent endosocopy for ingested foreign body?
- High-grade obstruction,
- object in esophagus >24hr, object >6cm
- sharp objects
- multiple objects swallowed
- button battery in esophagus
- button battery in stomach >48hr or if symptomatic (earlier)
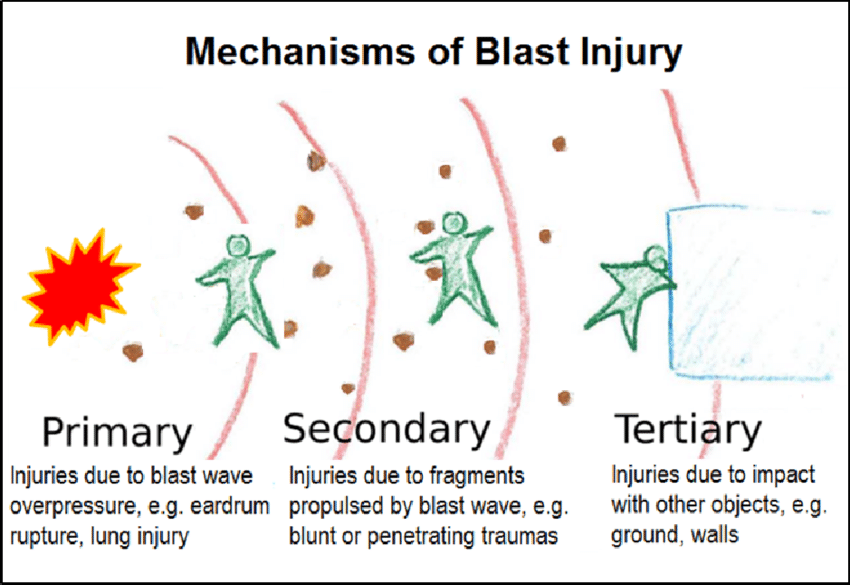
What is the definition of a secondary blast injury?
Injury due to projectiles from explosion (penetrating trauma, amputations, lacs)
Most common cause of painless vaginal bleeding during pregnancy?
Placenta previa: placenta partially or completely covering cervical os, which causes bleeding when the os starts to dilate
With cardiac arrest, what drugs can be given to adult and pediatric patients via ET tube?
NAVEL (adults): Narcan, Atropine, Vasopressin, Epinephrine, Lidocaine
LANE (peds): all except vasopressin
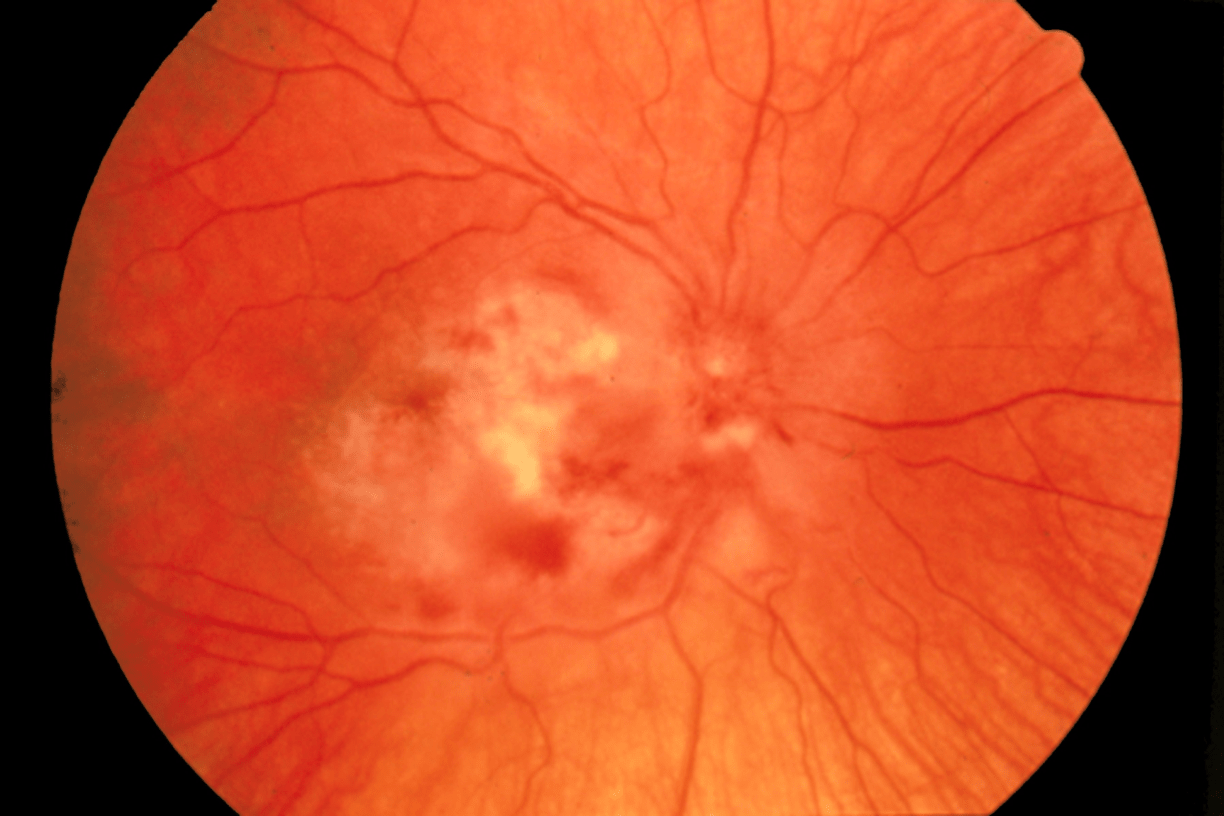
Under what CD4 count are HIV/AIDS patient at increased risk for CMV retinitis and what is the treatment?
CD4 <50
CMV retinitis is an AIDS defining illness
SSx: ↓ visual acuity, floaters/visual field cuts, photophobia.
Dx: Exam: white fluffy perivascular lesions with hemorrhage.
Tx: IV gancyclovir
Name 2 ways to distinguish Simple from Complex Febrile Seizures
Complex febrile seizure:
- Focal seziure
- Lasts >15 min
- Two or more seizures in a 24-hr period
Name 5 indications for emergent HD
"AEIOU"
Acidosis
Electrolytes (hyperK refractory to medical management)
Intoxication (toxins e.g. ethylene glycol, methanol, Li, etc.)
Overload (volume, any pulmonary edema)
Uremia with symptoms (e.g.pericarditis, AMS, BUN 100 or Cr 10)
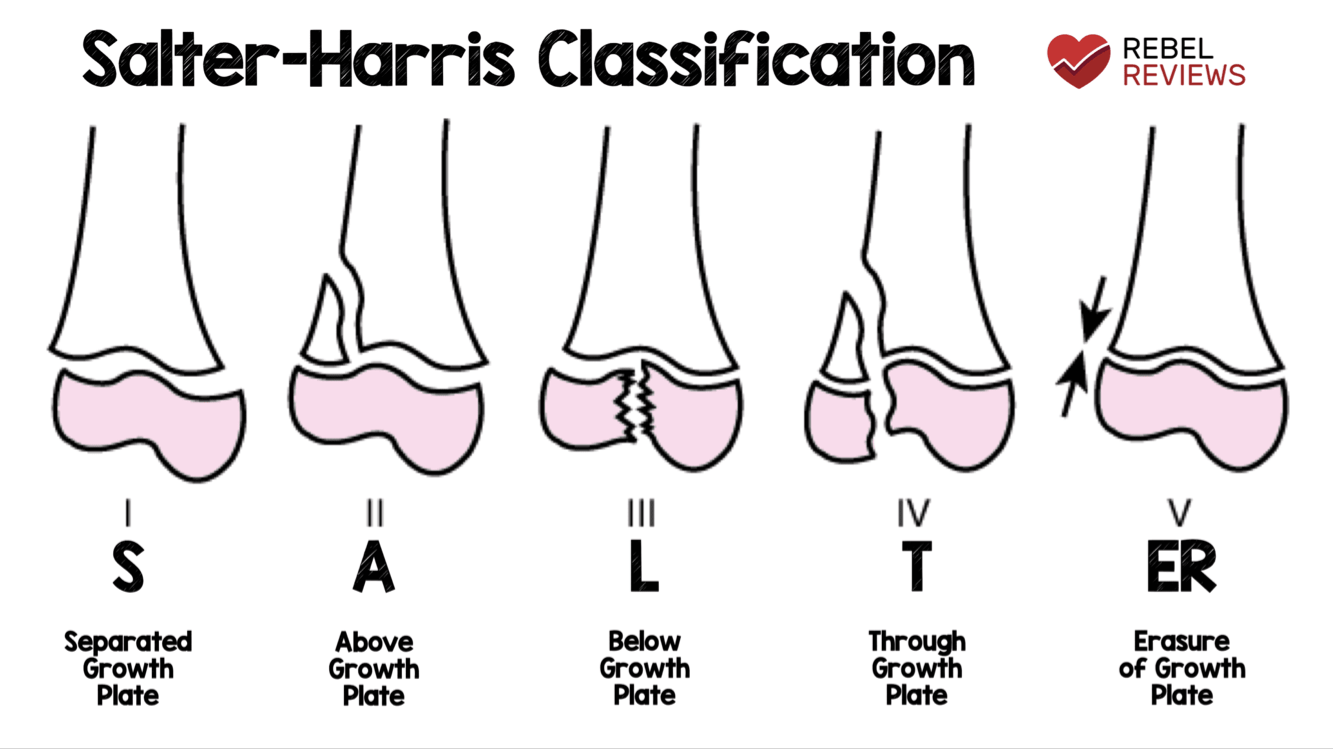
What are the Salter Harris classifications for pediatric fractures (1-5)?
What is the definition of an in inevitable abortion?
Inevitable: vaginal bleeding + IUP + open os
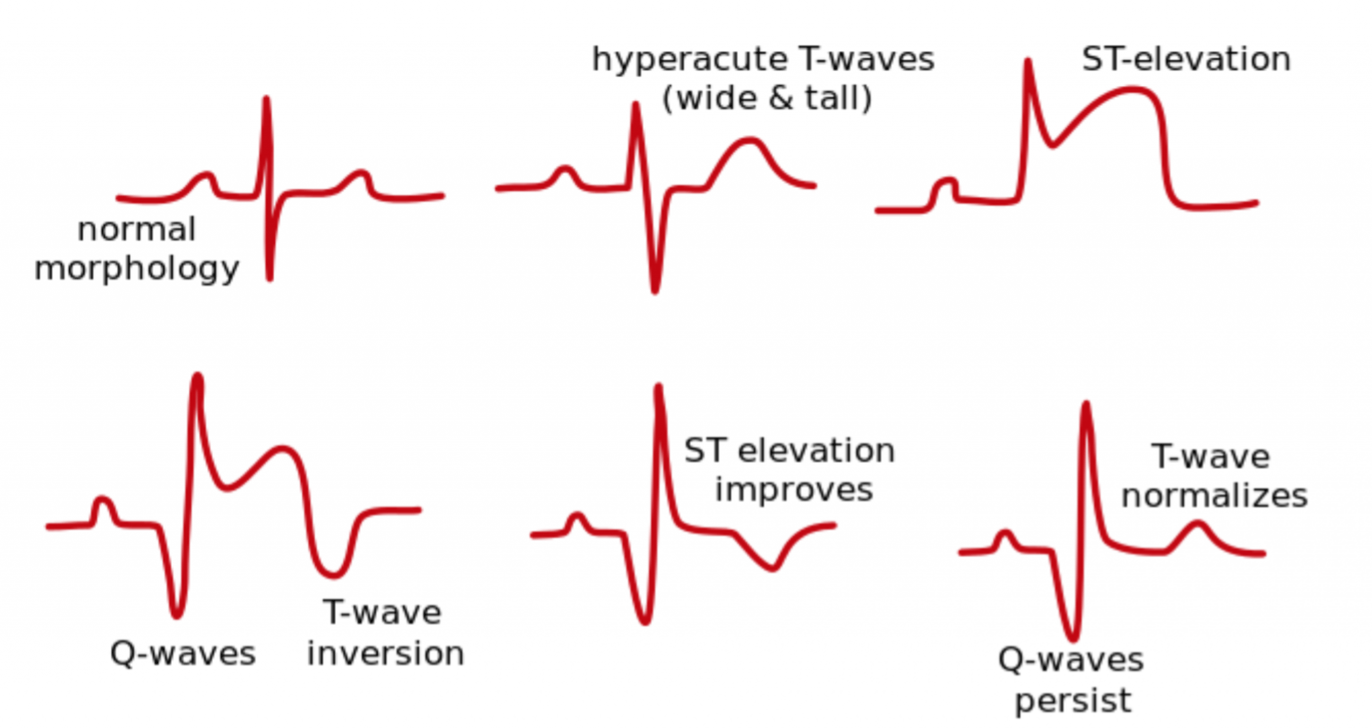
What is the progression of EKG changes in a patient with ACS?
Hyperacute T (very early and transient)
ST Elevations
ST Depression (ischemia or reciprocal)
Q waves
T wave inversions
What CXR findings can you expect to see in primary, reactivation and military TB?
Primary: lower lobes, looks like pneumonia
Reactivation: upper lobe granuloma ± cavitation.
Miliary: scattered nodules (millet seeds) throughout lung fields
Name 5 absolute contraindications for tPA for CVA
- Neurosurgery, head trauma, or stroke in past 3 months
- ANY ICH (current or previously)
- Clinical suspicion for SAH
- Known intracranial arteriovenous malformation, neoplasm, or aneurysm
- Uncontrolled hypertension (>185 mmHg SBP or >110 mmHg DBP) after reduction attempted
- possible reversible cause
- active bleeding or coagulopathy (Plt <100k, INR >1.7, PT>15s)
- Glucose <50
- Suspected/confirmed endocarditis
What volume of blood defines massive hemotpysis?
≥ 50 mL single expectorant or ≥ 500 mL / 24-hr
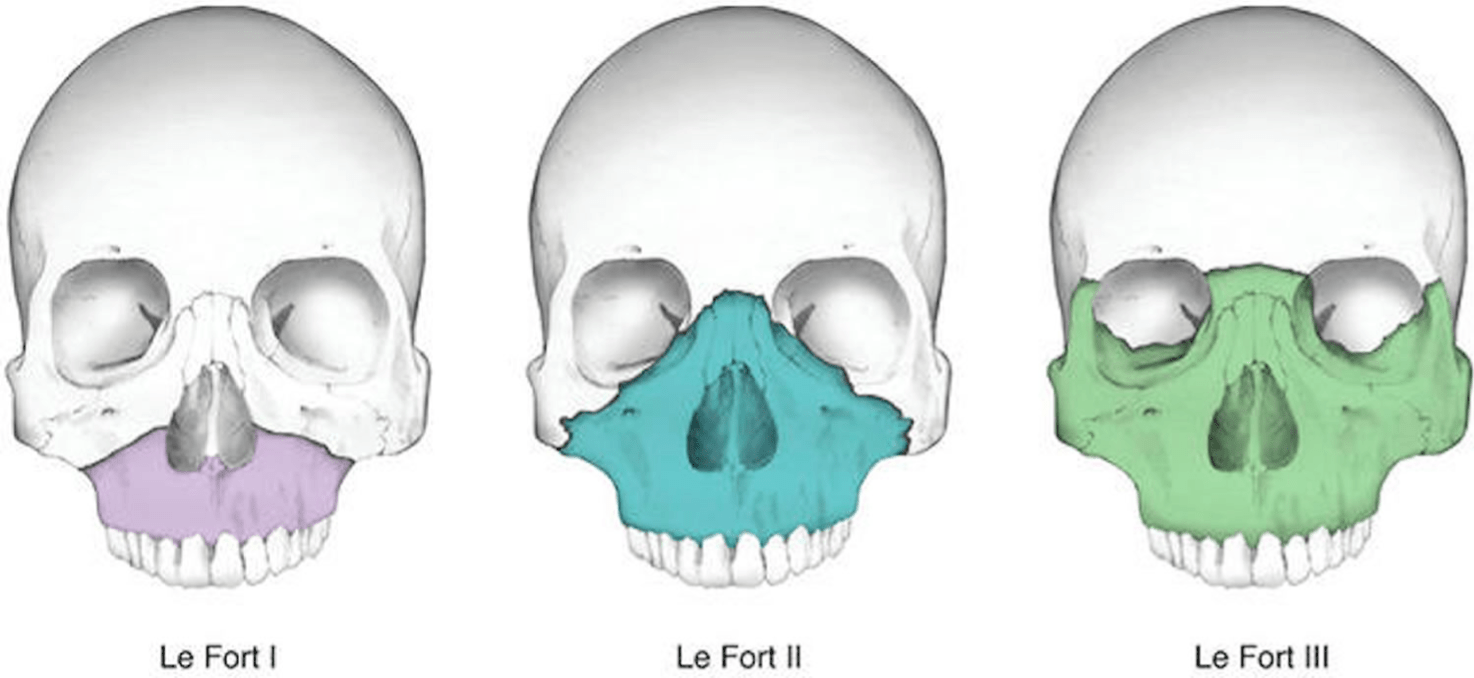
What are the classifications of LeFort fractures
LeFort I: palate mobile (fx below nose)
LeFort II: palate + nose mobile (inferior orbits)
LeFort III: entire face is mobile (zygoma bone)
Name 5 ductal dependent congenital heart lesions and 1 side effect of the medication used to treat them
Lesions: coarctation of aorta, critical aortic stenosis, hypoplastic left heart, tricuspid atresia, tetralogy of fallot, transposition of the great vessels
Tx: PGE1 (alprostadil) to reopen duct (side effects: hypotension, apnea, cardiac arrest)