This patient factor contributes to the largest reduction in functional residual capacity (FRC)
What is Obesity
The effects of propofol are typically terminated by this
What is redistribution?
This anesthetic induction agent lowers ICP the most
What is Propofol?
This is the pressure in the hospital pipelines delivering gas to the Anesthesia Workstation.
What is 55 mm Hg?
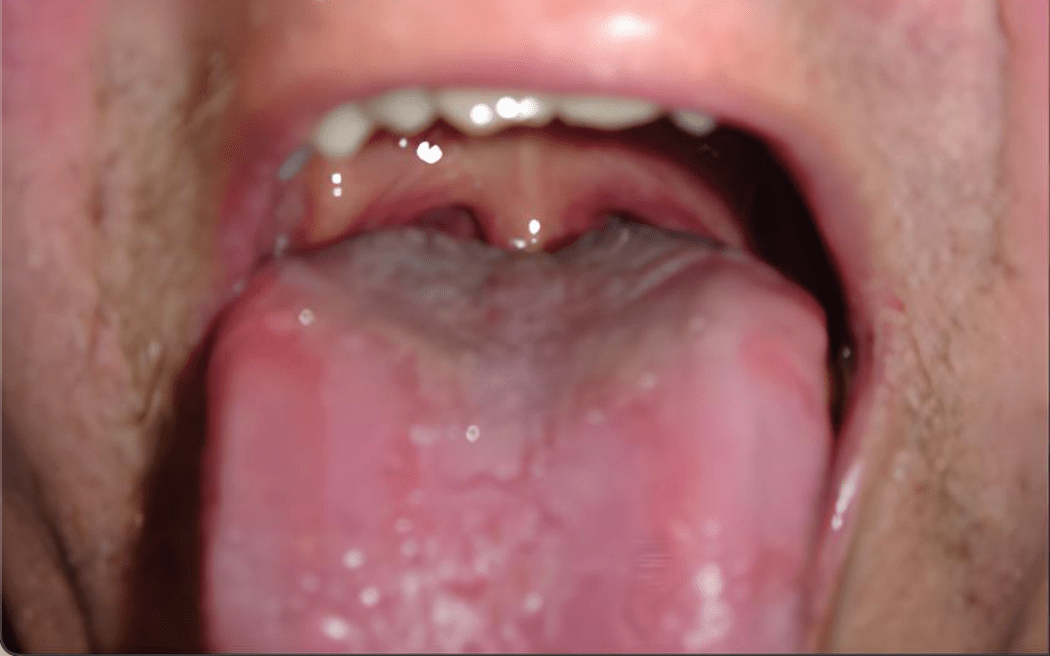
This is this patient's Mallampati Score
What is Mallampati 2?
According to Barash, this is the first sign of endobronchial intubation under general anesthesia.
Increased peak airway pressure with asymmetric breath sounds.
This volatile anesthetic increases heart rate by stimulating sympathetic activity, especially at higher MAC
What is Desflurane
Because this neuromonitoring modality assesses the dorsal column–medial lemniscal pathway, it is particularly sensitive to volatile anesthetics and hypothermia, which can lower its amplitude.
What are SSEPs?
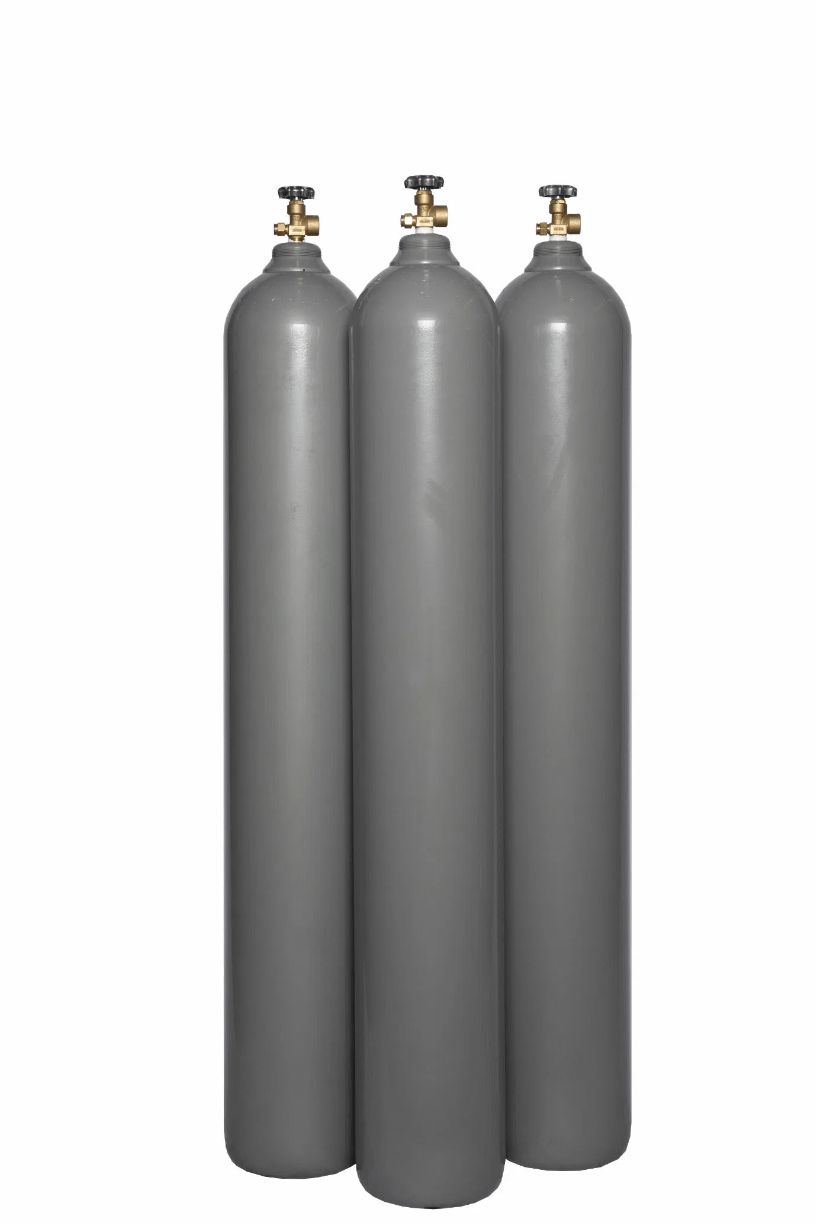

This gas is stored in this E-cylinder
What is CO2?
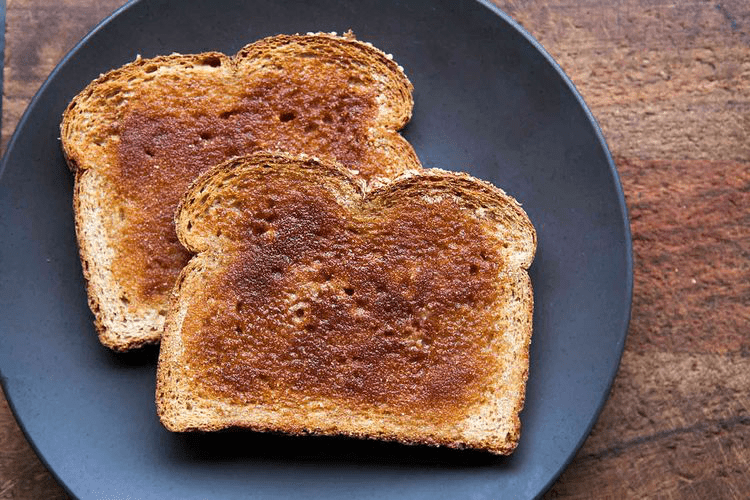

Looks like your patient didn't read his instruction packet and ate this for breakfast. This is the optimal time to wait prior to undergoing general anesthesia
What is 6 hours?
This is the best predictor of a difficult laryngoscopy out of the bedside tests.
Upper lip bite test (Barash Ch 19).
Class I: Lower incisors can bite upper lip above vermilion → easy
Class II: Lower incisors can bite upper lip below vermilion → usually easy
Class III: No contact between lower incisors and upper lip → high risk difficult laryngoscopy
At 1 MAC, this commonly used volatile anesthetic produces the greatest increase in cerebral blood flow (CBF)
Isoflurane produces the greatest increase in CBF among the commonly used agents at 1 MAC.
During a posterior fossa surgery, sudden bradycardia and hypotension indicate stimulation of this reflex
Trigeminocardiac Reflex
Afferent trigeminal fiber manipulation induces a powerful vagal response:
Bradycardia, Hypotension
This Mapleson circuit is best for spontaneous breathing.
What is a Mapleson Type A circuit?
In an insulin-dependent diabetic, this adjustment to their short-acting insulin regimen should be made on the day of surgery
What is holding their short-acting insulin dose?
TOPIC
Cardiac Physiology
Define "closing capacity" and explain when CC > FRC becomes clinically important.
CC = RV + closing volume; when CC exceeds FRC (elderly, smokers), airway closure occurs during tidal ventilation → hypoxemia.
These two neuromuscular blockers are degraded by exhaustive methylation.
What are Cisatracurium and Atracurium?
Dexmedetomidine effects on neurophysiologic monitoring (MEPs/SSEPs)
What are negligible effects on SSEPs; mild depression of MEPs but usually clinically acceptable
Of the inhalation anesthetic agents, this gas is measured by infrared absorption spectroscopy.
What is N2O?
This is the minimum wait time to undergo elective non cardiac surgery after a patient received a balloon angioplasty.
What is 14 days?
FYI....
BMS: >30 days
DES: > 3 months for time-sensitive, >6 months for other elective cases
In a patient with ARDS, Barash recommends this lung-protective strategy including tidal volume target and PEEP approach.
TV 4–6 mL/kg predicted body weight; moderate–high PEEP; permissive hypercapnia if needed.
Chronic carbamazepine use reduces the duration of action of many non-depolarizing neuromuscular blockers through these mechanisms
What are Hepatic enzyme induction + upregulation of acetylcholine receptors.
During aneurysm clipping, these are the physiological goals during temporary vessel occlusion. (List at least 2)
What are:
1)Reduce CMRO2 (Deepen anesthesia or induce burst suppression with propofol)
2) Maintain or increase MAP to support collateral flow and maintain CPP
3) Induce mild hypocapnia to reduce CBV while avoiding ischemia
These are two component of the Anesthesia circle system differentiates if from a Mapleson circuit.
What are one-way valves and CO2 absorber?
A patient presents to pre-op clinic and you decide to perform a RCRI as they are undergoing a hemicolectomy. He has a history of HTN, IDDM Type 2, CAD s/p DES 1 year ago and you determine that this is his RCRI score.
What is a RCRI score of 2?
Explain why patients with hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM) become hypotensive with tachycardia or decreased preload, and outline three essential intraoperative hemodynamic goals.
Tachycardia and reduced preload decrease left ventricular cavity size and increase contractility, which worsens dynamic LVOT obstruction and leads to hypotension.
Intraoperative goals are to:
(1) maintain preload (avoid hypovolemia),
(2) maintain or slightly increase afterload (e.g., with phenylephrine), and
(3) avoid tachycardia and inotropes, often using beta‑blockade to control heart rate and contractility.