IV anesthetic producing the most pronounced decrease in systemic BP compared to other induction meds
Propofol
- mostly through venodilation (decreased preload). Some through arterial dilation (decreased afterload), decreased sympathetic outflow (& reflex inhibition), & direct myocardial depression
Respiratory effects of opioids (think: CO2 response curve)
- directly affect the respiratory centers in the medulla, producing a dose-dependent depression of the ventilatory response to CO2 (decreased slope & rightward shift)
- apnea threshold (highest PaCO2 without ventilatory effort) is increased
- blunt increase in ventilation in response to hypoxemia
- decreases MV by decreasing RR (as opposed to decreasing TV)
- morphine & meperidine can cause histamine-induced bronchospasm
Difference between addiction and dependence
Addiction: compulsive drug seeking & use, despite harmful consequences
Dependence: presence of withdrawal symptoms if drug is withheld (physical or psychological)
Tolerance: need to increase the dose of medication to maintain effect
MOA of propofol
- mediated through GABA-A (potentiates chloride current, causing hyperpolarization); hypnotic; NO analgesia; decrease in CMR & CBF
- induction dose 1-2.5 mg/kg
- rapid onset & redistribution (DOA 3-8 min), short elimination half-life
- consider age (children need higher doses due to larger Vd & higher clearance; elderly need lower doses), neurologic state, comorbidities, other meds given
- hepatic metabolism (& lungs); renal excretion
Your patient in preop is very anxious. What benzodiazepine do you give them?
midazolam
IV anesthetic that is commonly associated with myoclonic movements. Can also cause hiccups and coughing after induciton
ETOMIDATE
- works by GABA-A receptor complex (potentiates chloride current)
- decreases CBF & CMR. maintains CPP
- increases epileptogenic foci
- has a much more stable CV profile than propofol
Name some side effects of opioids
sedation, respiratory depression, chest wall rigidity, bradycardia, hypotension, itching, nausea, ileus, urinary retention, miosis
** NOTE: opioids are hemodynamically stable when given alone, but cause decrease in CO, SV, & BP in combination with other anesthetics. They reduce MAC of volatile anesthetics
What is elimination half-life?
the time required for the drug concentration to fall by 50%
MOA of ketamine
NMDA (N-methyl-D0aspartate) noncompetitive antagonist
- NMDA receptors are glutamate, glycine, & D-serine activated excitatory ion channels
- also interacts with opioid receptors (mu, delta, & kappa), muscarinic receptors (partial antagonist effect -> bronchodilation, sympathomimetic, delirium), & sodium channel (mild LA like properties)
Your patient has a history of PONV. What IV anesthetic can be used as an infusion to help prevent post-op nausea & vomiting?
propofol
- has antiemetic properties
IV anesthetic that increases CMRO2, CBF, & ICP?
ketamine
All other ones decrease CMRO2, CBF, & ICP
Only opioid that is metabolized by plasma estarases
remifentanil
- rapid metabolism. Lasts 5-10 min regardless of infusion duration
- use when significant intraoperative stimulation but minimal post-op pain is expected (or when you need to assess neuro status post-op)
Definition of context-sensitive half-time
the time for the plasma level of the drug to decrease by 50% after cessation of an infusion

How does ketamine preserve HR, CO, and MAP?
via sympathetic stimulation
- if catecholamines are depleted (ex, trauma or sepsis), then it can unmask ketamine's intrinsic myocardial depressant effects and cause hemodynamic instability
Benzo overdose! What antagonist would you use?
Flumazenil
- works for 45-90 minutes. Might need to redose!
- is a GABA receptor antagonist
a short-acting IV barbiturate that was very popular but has been replaced by propofol, largely due to its involvement in euthanasia in capital punishment. It has also been used as "truth serum"
Thiopental
- developed in 1930s. Rapid onset of sedation, short duration of action & hypnosis. Propofol became available in 1990s. Main manufacturer of thiopental stopped its production in 2011, but it remains widely available in many low- and middle-income countries.
Which excitatory neurotransmitters are inhibited by opioid receptor activation? (presynaptic & postsynaptic)
glutamate, acetylcholine, & substance P
Define PRIS
Propofol infusion syndrome
- severe metabolic acidosis, rhabdomyolysis, cardiac failure, renal failure, & hypertriglyceridemia
- high mortality; supportive treatment
- highest risk in critically ill pts receiving high dose propofol infusions (>4mg/kg/hr) for prolonged periods of time
Enzyme inhibited by etomidate. By this mechanism, etomidate can cause adrenal suppression
- this is a dose-dependent, reversible inhibition
- leads to decreased production of cortisol & aldosterone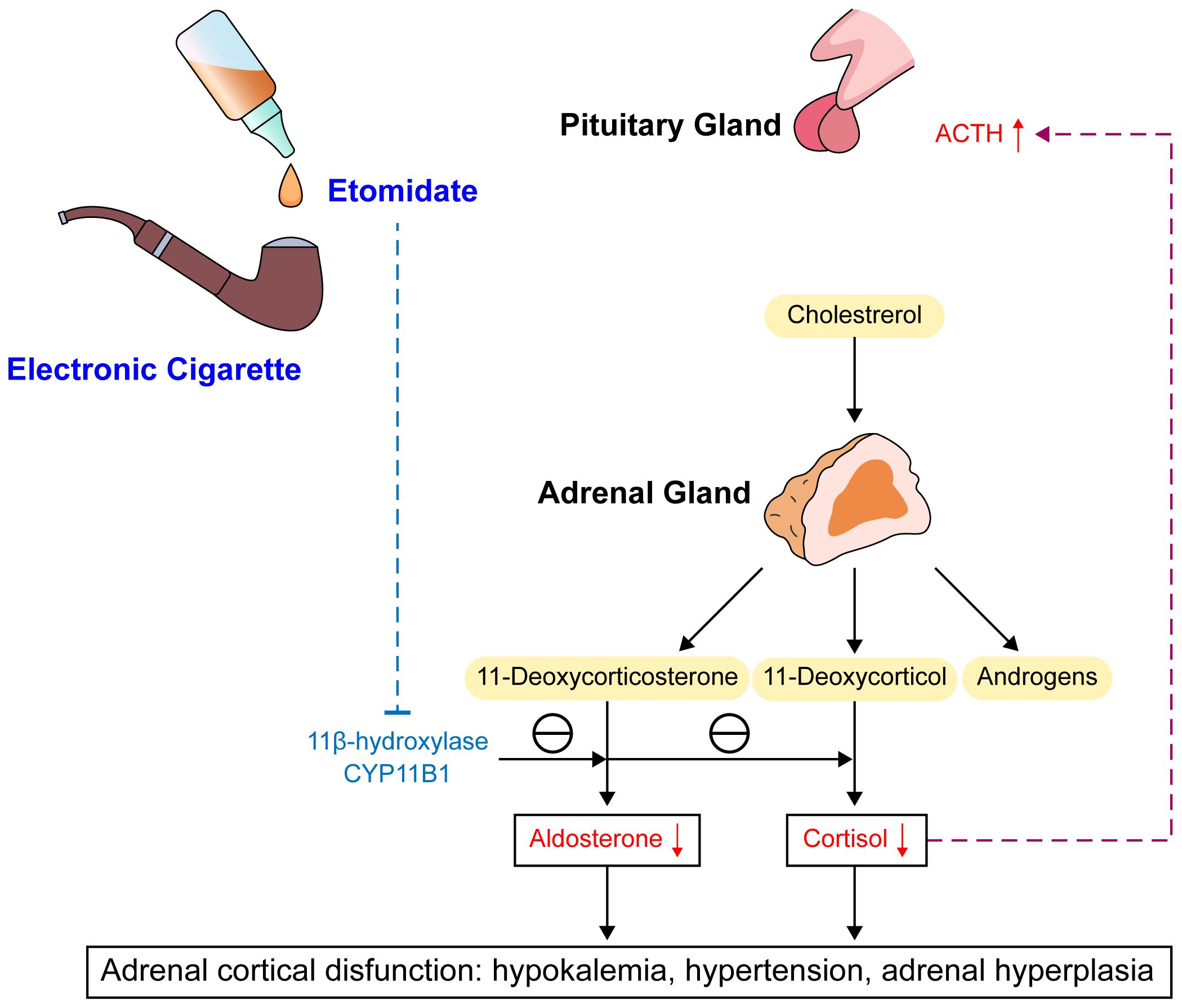
You decide to use an IV anesthetic that produces "dissociative anesthesia" so that your patient appears awake and maintains certain reflexes but has profound analgesia. What IV anesthetic would you use?
ketamine
IV anesthetics that have to be used with caution in patients with acute intermittent porphyria
BARBITURATES
- can increase aminolevulinic acid synthetase activity -> increases porphyrin synthesis -> abdominal pain, neurotoxicity, autonomic dysfunction, nerve damage (peripheral, intercostal, & phrenic)
A metabolite of what opioid can cause neuroexcitatory effects and cause seizures?
Meperidine
- the metabolite is normeperidine
- NOTE: meperidine can also cause histamine release & bronchospasm (just like morphine)
Difference between pharmacokinetics & pharmacodynamics
pharmacokinetics: how the body interact with the drug (absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion)
pharmacodynamics: the effect that the drug has on the body (ex, mechanism of action, drug-receptor interaction, dose-response relationship, biochemical & physiological effects)
The difference between the effect of propofol & barbiturates vs. benzodiazepines on GABA receptor
- Propofol & barbiturates decrease the rate of dissociation of GABA so they increase the duration of chloride channel opening
- Benzodiazepines facilitate the attachment to the GABA receptor so they increase the frequency of chloride channel opening
Most commonly used barbiturate in electroconvulsive therapy
Methohexital
- short duration of action
- does not affect seizure duration (etomidate increases seizure duration; propofol & benzos decrease seizure duration)